Screening device for analysis of bodily fluids
a technology of bodily fluids and screening devices, which is applied in the field of analysis of the presence of constituents in bodily fluids for drug test screening, can solve the problems of affecting the screening effect of drug test results, prone to operator error, and prone to tilting the proximal face of the screening device backwards, so as to prevent unintended saliva upward movement and capillary action. the effect o
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
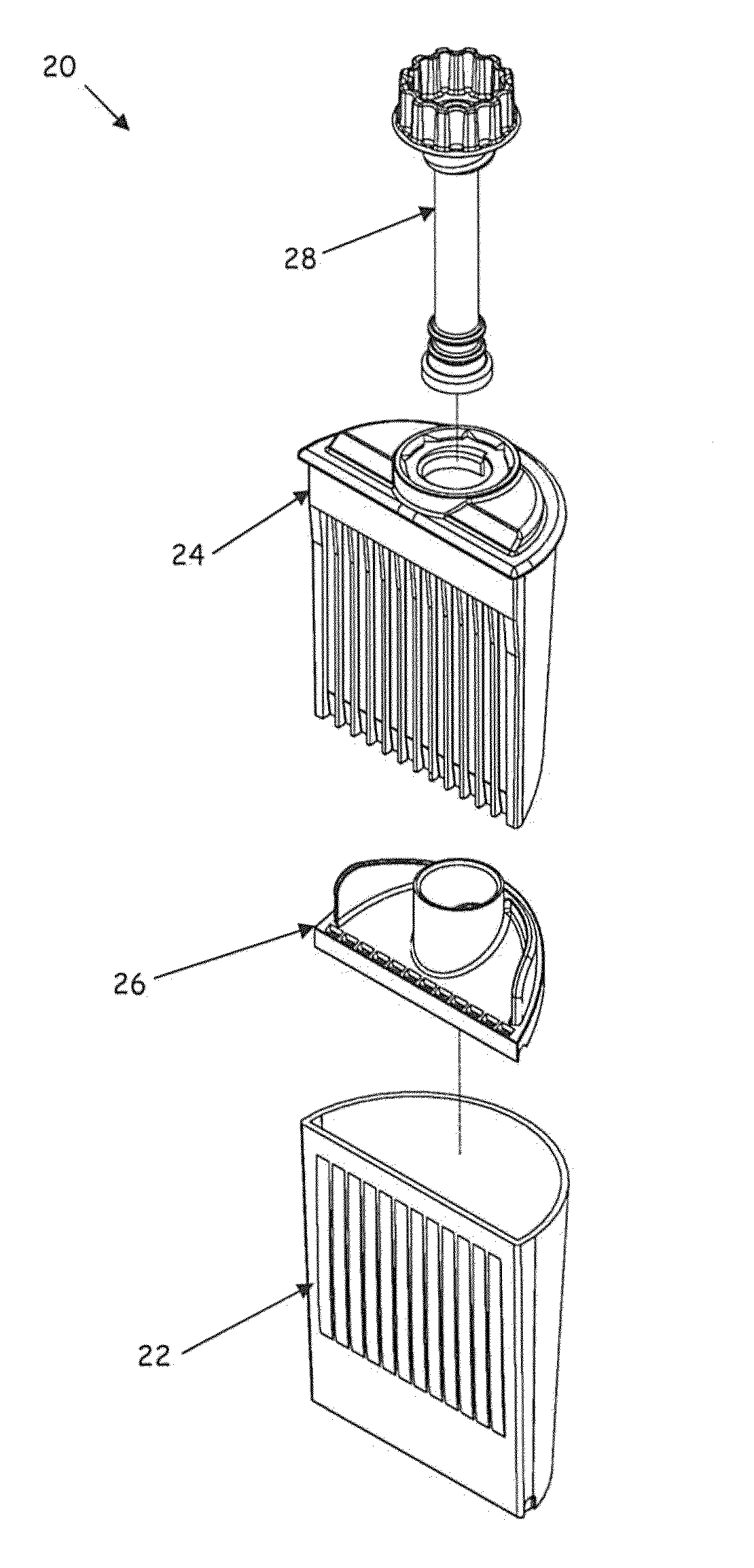
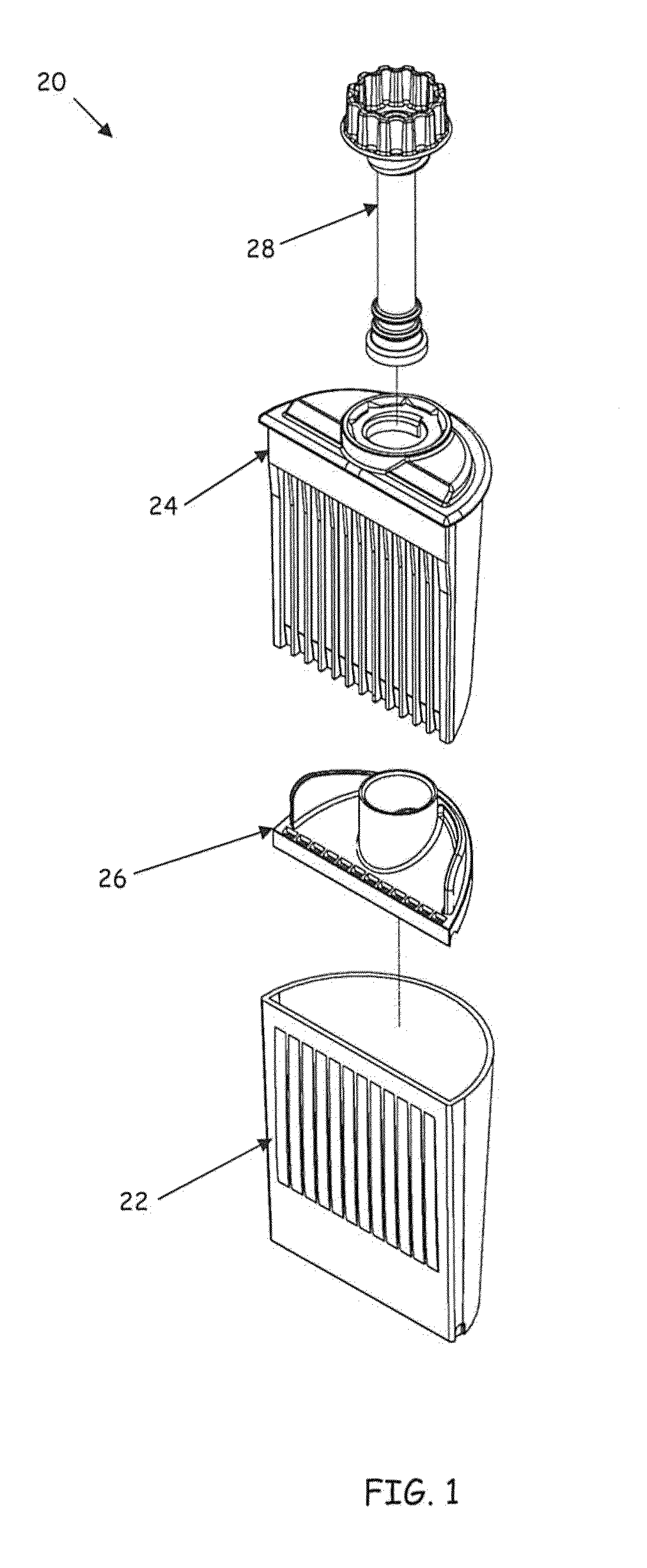
[0026]Referring to FIG. 1, a testing assembly 20 for screening bodily fluids for the presence of certain constituents is depicted in an embodiment of the invention. The screening device includes a container or cup 22, a test strip and sampling stem holder 24 (hereinafter “holder 24”), a three-dimensional gasket 26 and a sampling stem 28.
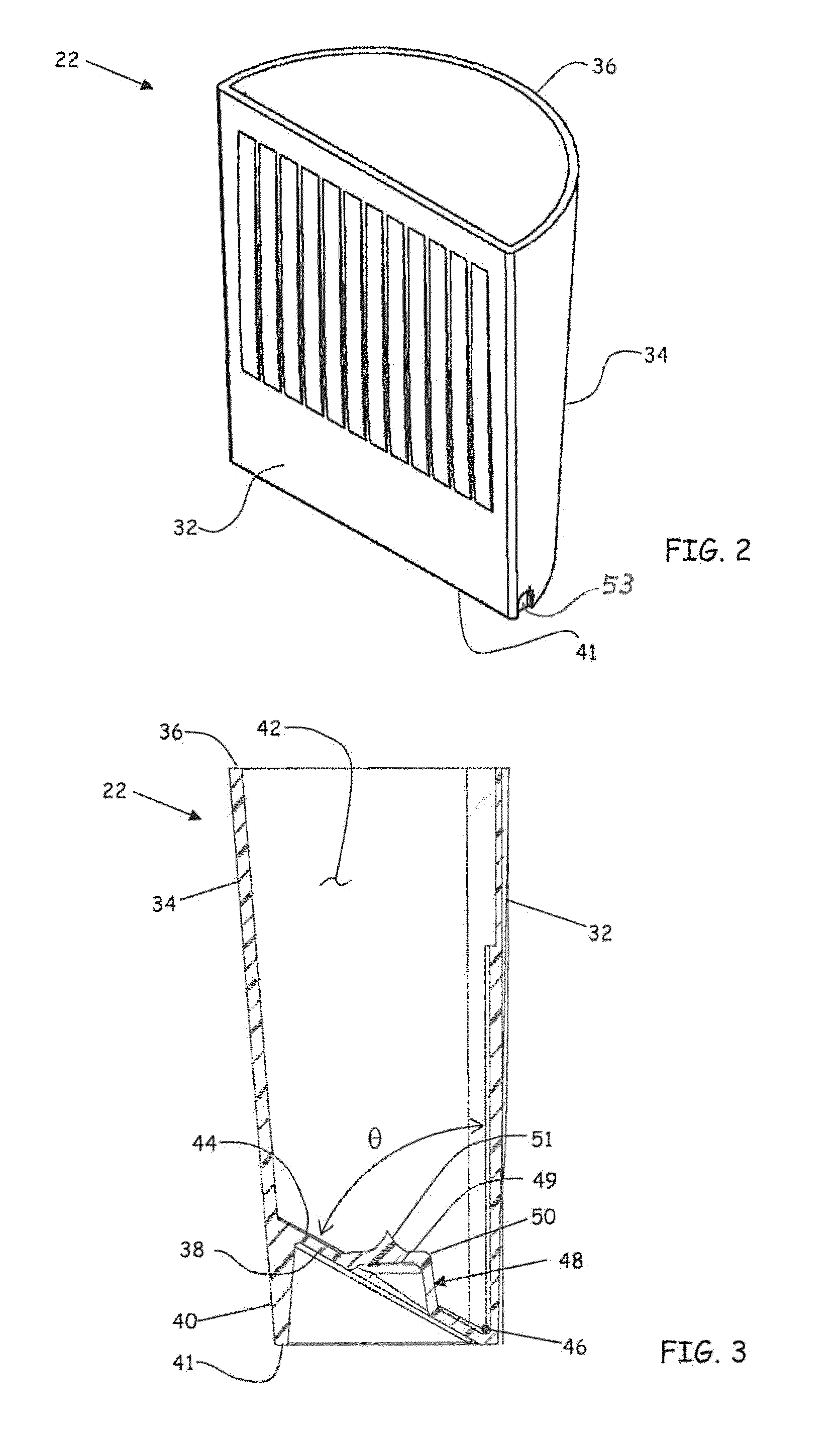
[0027]Referring to FIGS. 2 and 3, the cup 22 is depicted in isolation in an embodiment of the invention. The cup 22 includes a plurality of sides 32′ and 34 that extend upward from a containment bottom 38 to form a continuous upper edge 36, the sides 32, 34 and containment bottom 38 defining a cavity 42. The sides 32 and 34 can also extend below the containment bottom 38 to establish a base portion 40 with a lower edge 41 registers the testing assembly 20 in an upright position. A first of the sides (side 32 in FIGS. 2 and 3) can be substantially planar. In one embodiment, the containment bottom 38 defines an inclined surface 44 that intersects the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| perimeter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| extension structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| passage structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com