Multi-CBV Vaccine for Preventing or Treating Type I Diabetes
a type i diabetes and multi-cbv technology, applied in the field of antiviral compositions, can solve the problems of inability to discriminate between enteroviruses and t1d, inability to know which enterovirus serotypes are involved in the disease, and inability to prevent or treat type i diabetes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Seroneutralization Analyses
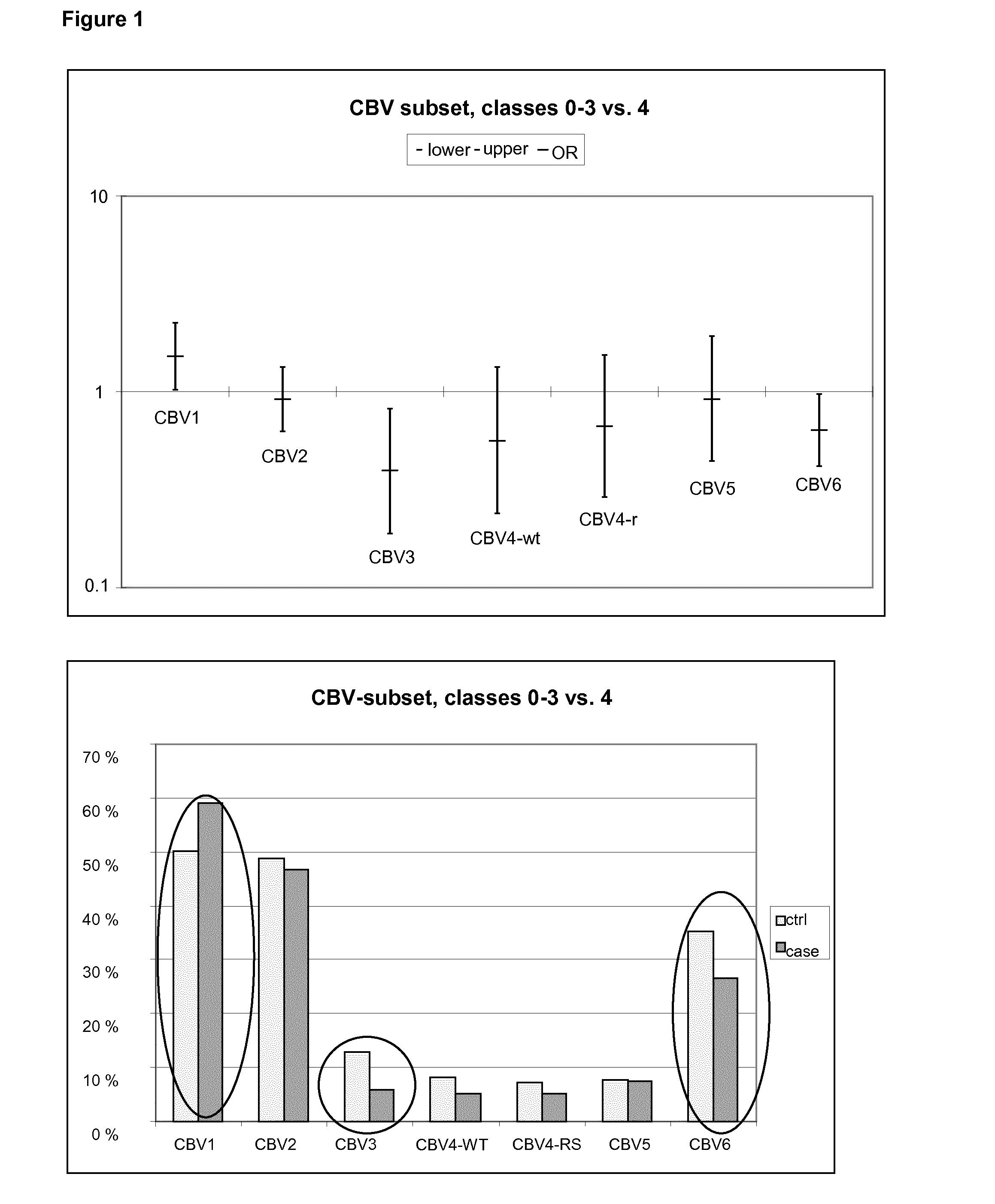
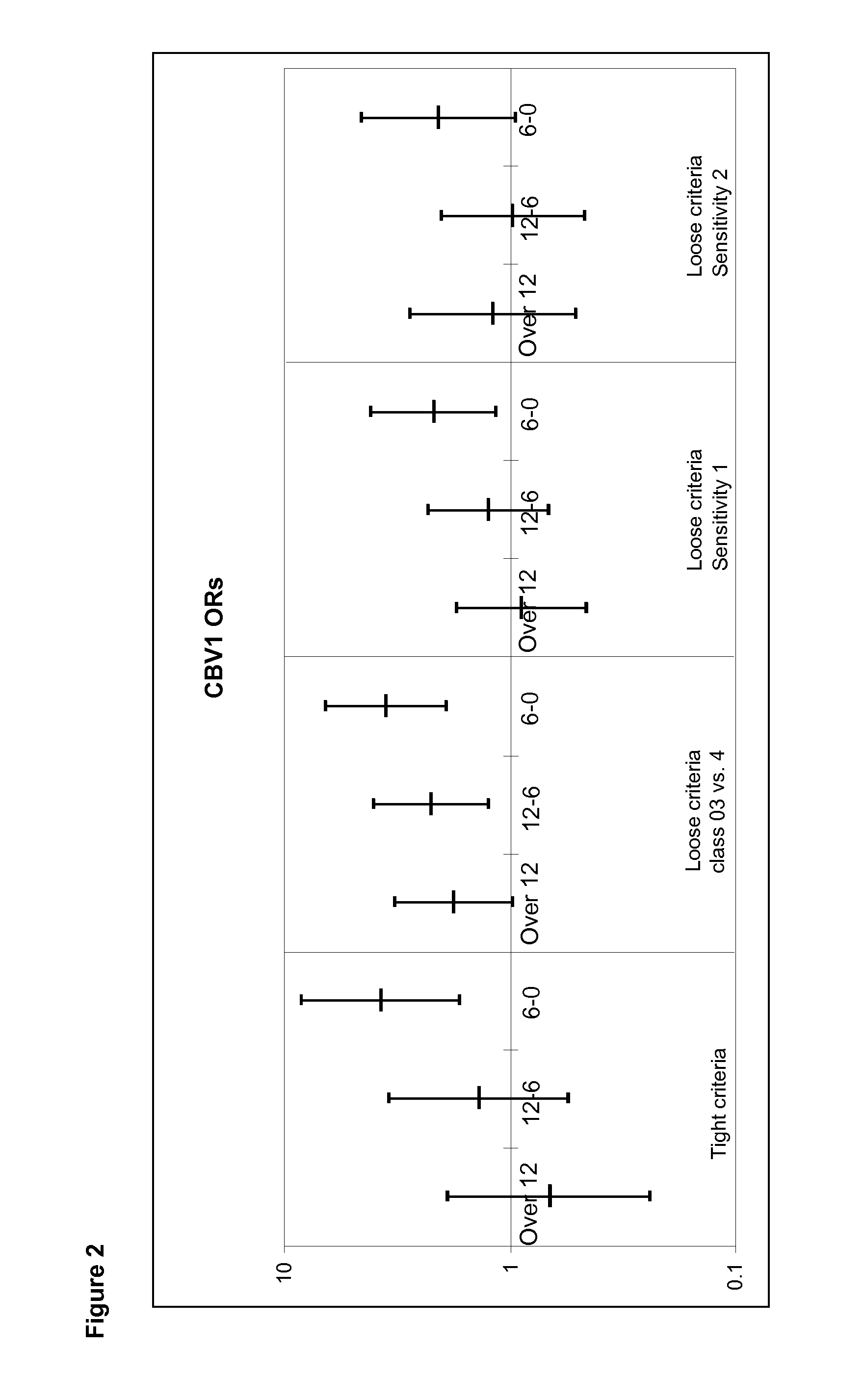
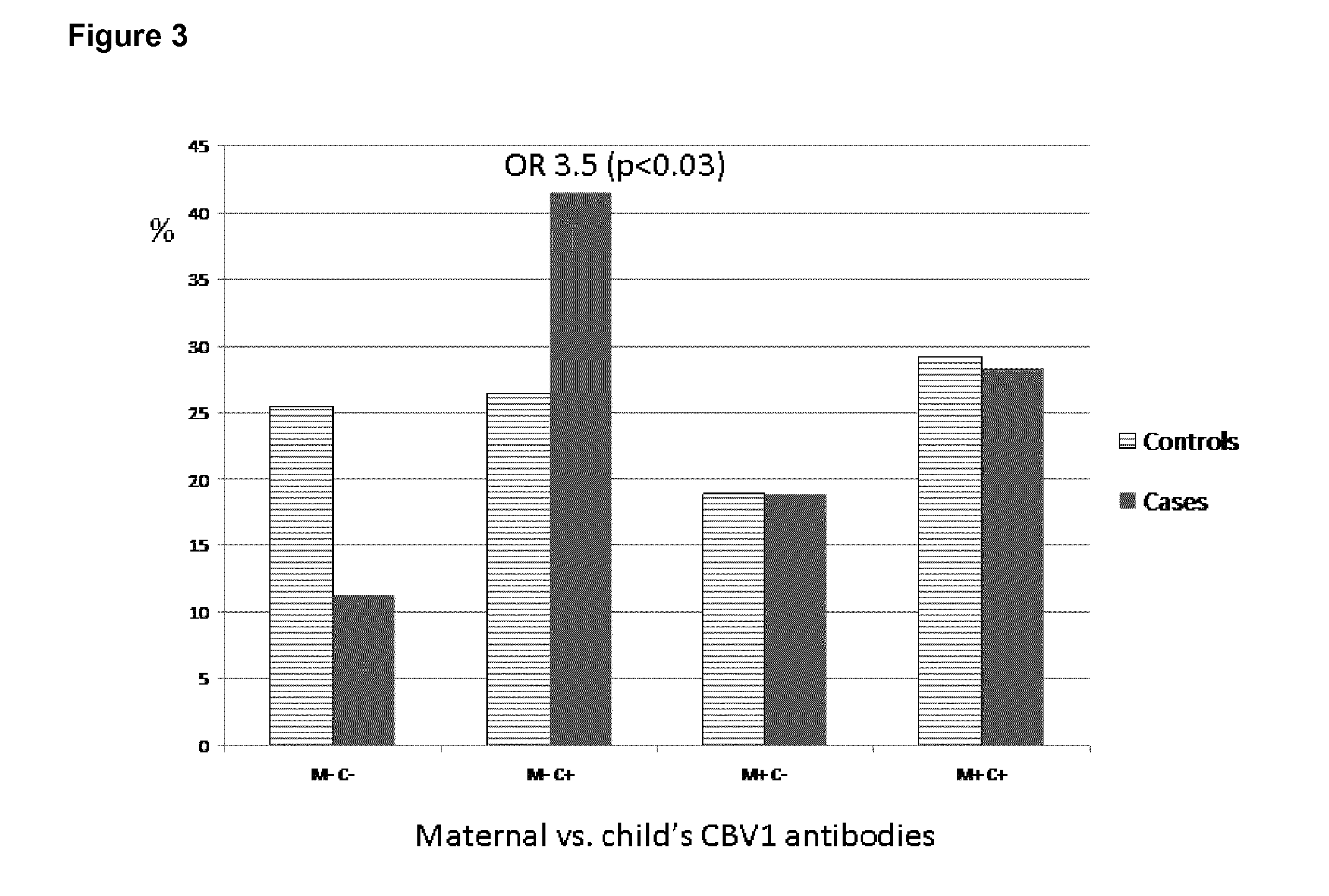
[0052]Neutralizing antibodies were analyzed against a wide panel of different enterovirus serotypes in the same serum sample which was the first autoantibody positive sample taken during the prospective follow-up. Thus, this time point represents the initiation of the beta-cell damaging process. In addition, antibodies against those serotypes which were found to be interesting in this initial screening were measured at additional time-points to study the timing of infections and their relationship with the initiation of the beta-cell damaging process.
[0053]Altogether, seroneutralization analyses have been performed using 42 viruses and 522 serum / plasma samples (174 triplets, two control children for each case child). The completeness of the analyses in this virus set varies from 100% to 84% (Echo30) being for a majority of the viruses (35 / 40) more than 97.7%. In order to study the effect of the strain variation, two serotypes (CBV4 and Echo3) have been ana...
example 2
A CBV1 Inactivated Vaccine Protects Mice Against Viremia and Infection of the Pancreas
Method
[0111]An inactivated vaccine was produced by amplification of CBV1 in Vero cells, followed by sucrose purification and formol-inactivation. The dose of the vaccine is expressed as the initial content in infectious virus (equivalent CCID50).
[0112]BALB / c male and female mice, previously shown to be susceptible to CBV1 infection, were immunized by the i.m. route with three injections of formol-inactived CBV1 at D0, D21 and D35. Two doses of the vaccine (4×104 and 2×105 eq CCID50) were assessed for mice immunization. One week after the last immunization, mice were challenged with live CBV1 via the i.p. route. Viremia and infection of the pancreas were monitored in immunized and control mice by CBV1 genomic titration of blood samples and pancreas tissue homogenates.
Results
[0113]Immunogenicity of the vaccine was first evaluated by analyzing the induction of neutralizing antibodies in individual mou...
example 3
Virus Infection and Diabetes in SOCS-1 Transgenic NOD Mice
[0118]A recently developed model for enterovirus-induced type 1 diabetes was used with mice expressing the suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1) in pancreatic beta cells. By expressing SOCS-1 the pancreatic beta cells lose their ability to respond to interferons and by that also their ability to protect themselves against the virus. An analysis of the pancreata from infected SOCS-1 transgenic animals (here denoted SOCS-1-Tg NOD mice) demonstrate that diabetes is the result of beta cell destruction (Flodstrom, M. et al., 2002. Nat Immunol 3(4), 373-82; Flodstrom, M. et al., 2003. Diabetes 52(8), 2025-34).
[0119]Mice and Animal Husbandry:
[0120]All mice were breed and housed under specific pathogen free conditions. The SOCS-1-Tg NOD mice were bred as heterozygotes and screened for the presence of the SOCS-1-transgene by PCR.
Virus Infections
[0121]Mice aged 8 to 10 weeks were infected with one intra-peritoneal (i.p.) injectio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time window analyses | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com