Rotating cutting elements for pdc bits
a technology of rotary drill bits and cutting elements, which is applied in the field of cutting elements, can solve the problems of drill bit failure, cutter failure, and bit and pdc cutter being subjected to substantial abrasion forces during drilling operations,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
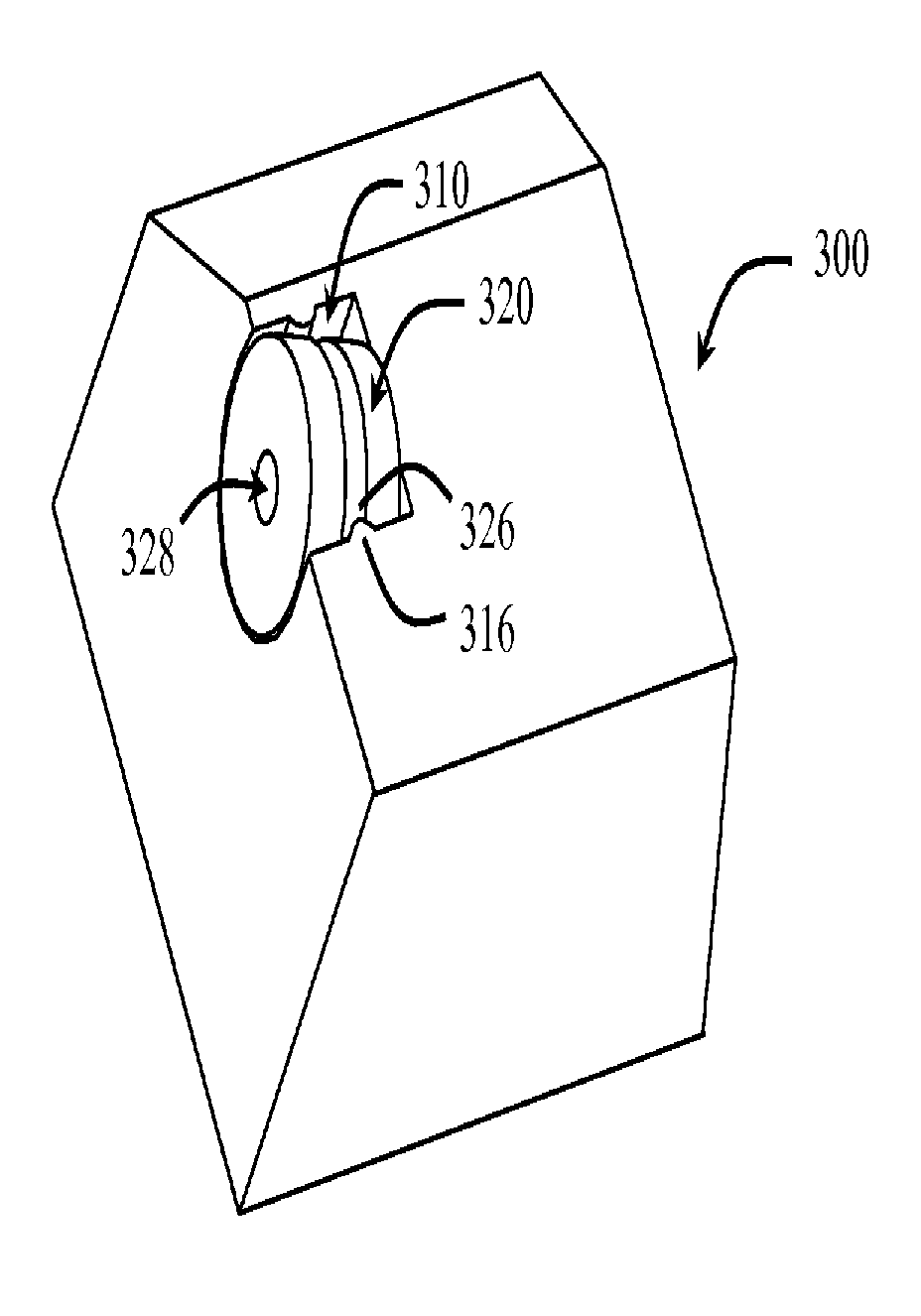
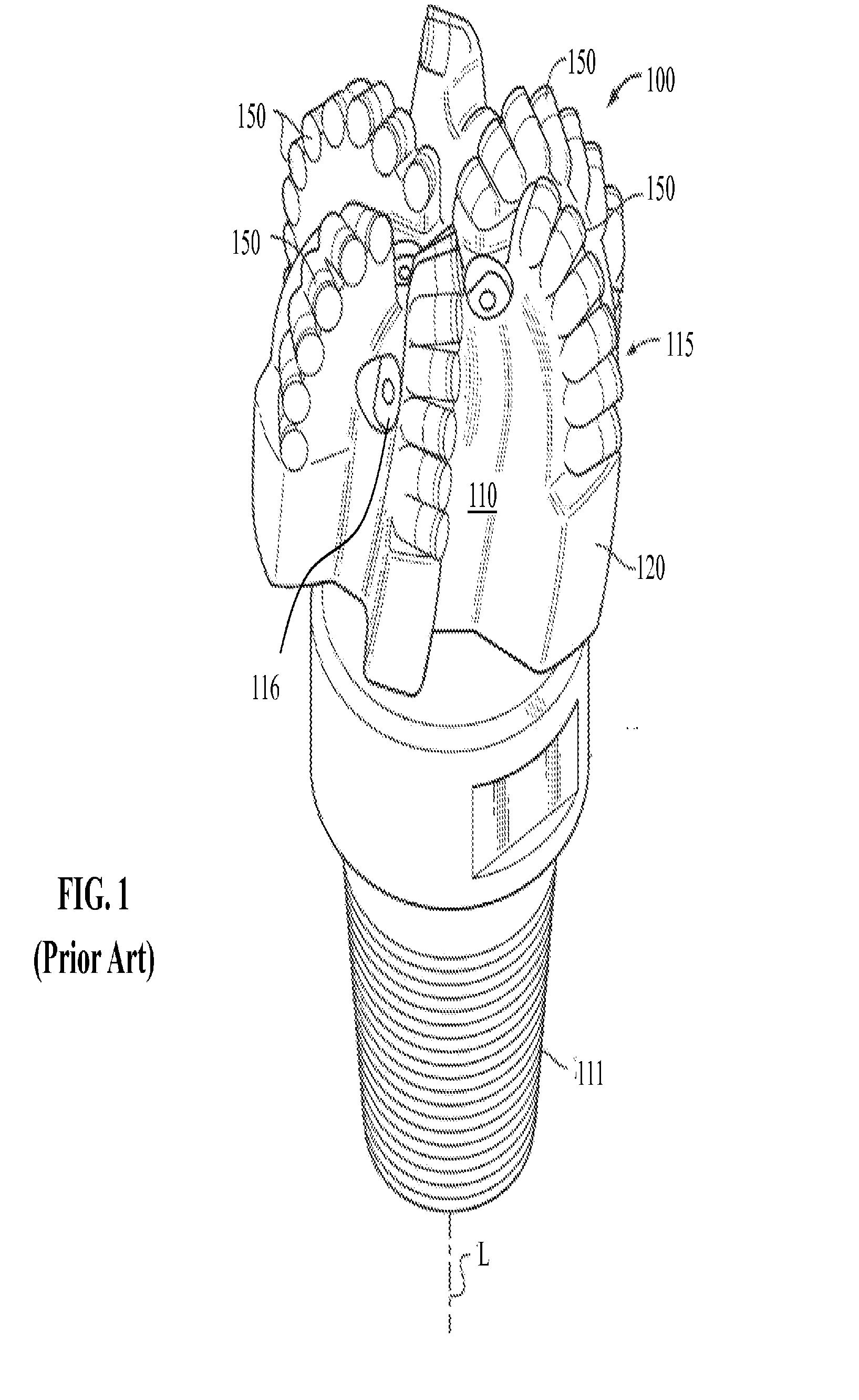
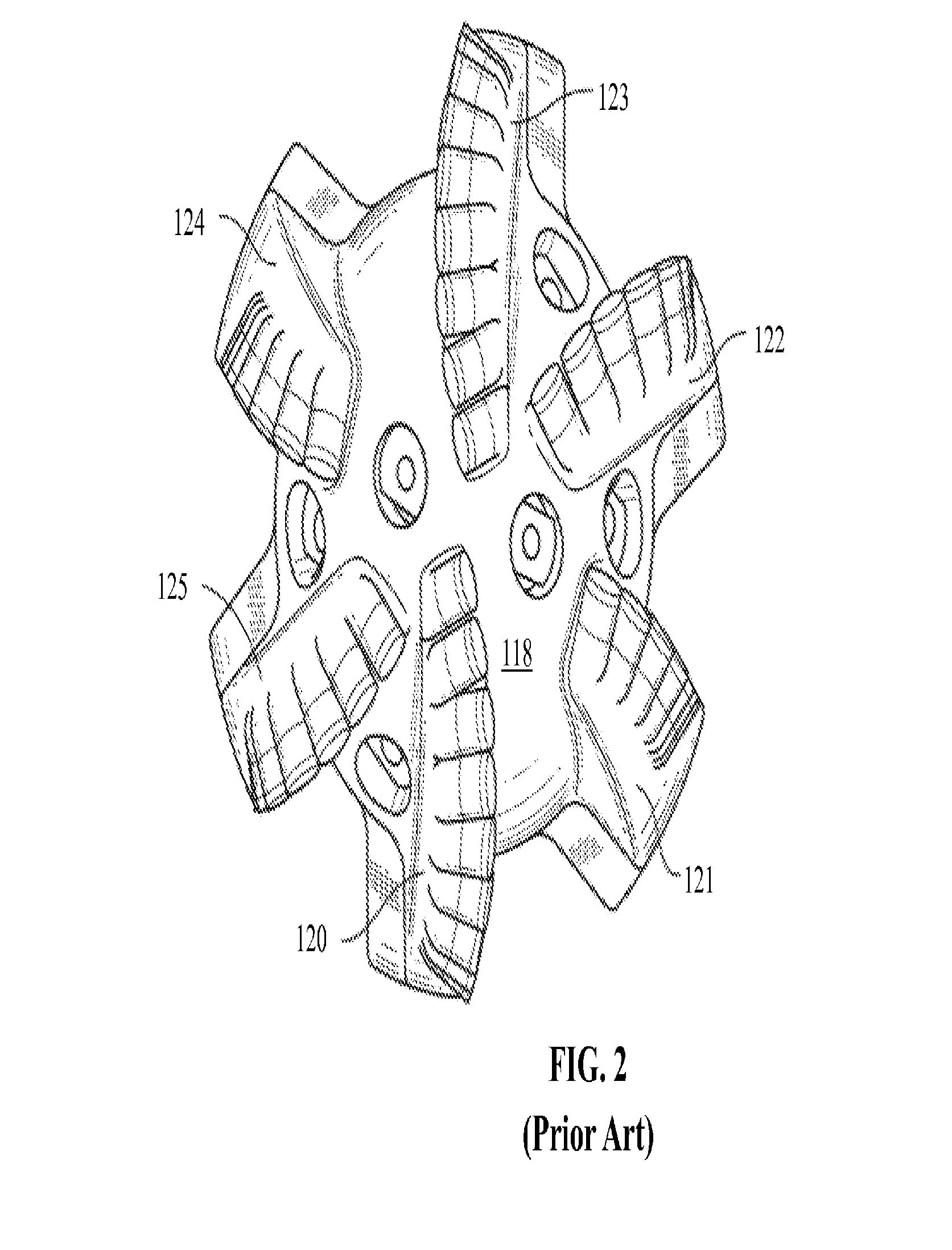
[0046]In one aspect, embodiments disclosed herein relate to rolling cutters and methods of retaining such rolling cutters on a drill bit or other cutting tools. In some embodiments, rolling cutters may be retained on a fixed cutter drill bit by a retention pin or a WC sleeve and the side surface of a rolling cutter pocket, thus allowing the entire cutting face of a rolling cutter to be exposed. According to other embodiments, rolling cutters may be retained on a fixed cutter drill bit by only the side surface of a rolling cutter pocket.
[0047]Generally, cutting elements described herein allow at least one surface or portion of the cutting element to rotate as the cutting elements contact a formation. As the cutting element contacts the formation, the cutting action may allow portion of the cutting element to rotate around a cutting element rotational axis extending through the cutting element. Rotation of the cutting structure may allow for a cutting surface to cut the formation usin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| arc angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| arc angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com