Imaging neurological disease
a neurodegenerative disease and imaging technology, applied in the field of radiopharmaceutical imaging of the brain, can solve the problems of compromising the utility and applicability of ‘normal’ average values reported, unable to establish a meaningful normal database built on data from more than one camera type, and unable to apply ‘correction factors’ with considerable effort,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0090]Embodiments of the present invention is illustrated by the non-limiting Examples detailed below. Examples 1 and 2 are theoretical Examples, whereas Examples 2-5 are based on clinical data.
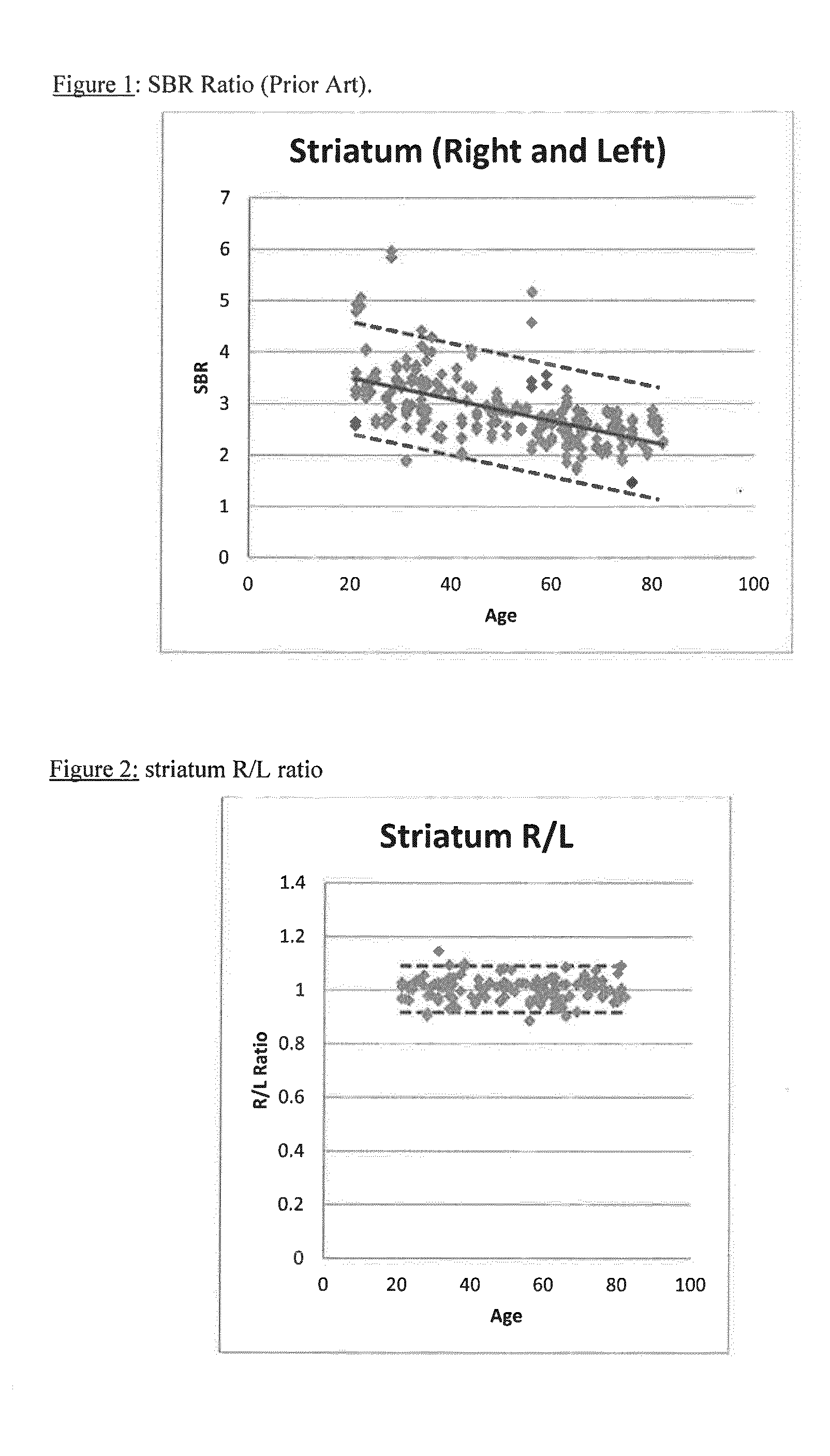
[0091]Example 1 is a comparative Example which shows the calculation of SBR using data from: (i) a range of camera manufacturers (Group A); (ii) a single manufacturer (GE; Group B) and (iii) a patient. The variation in Group A is so wide that there is almost no value in it for comparison with patient data. Even with Group B, the normal range is too wide to be useful for comparative purposes. This demonstrates the difficulties with the current methodology.
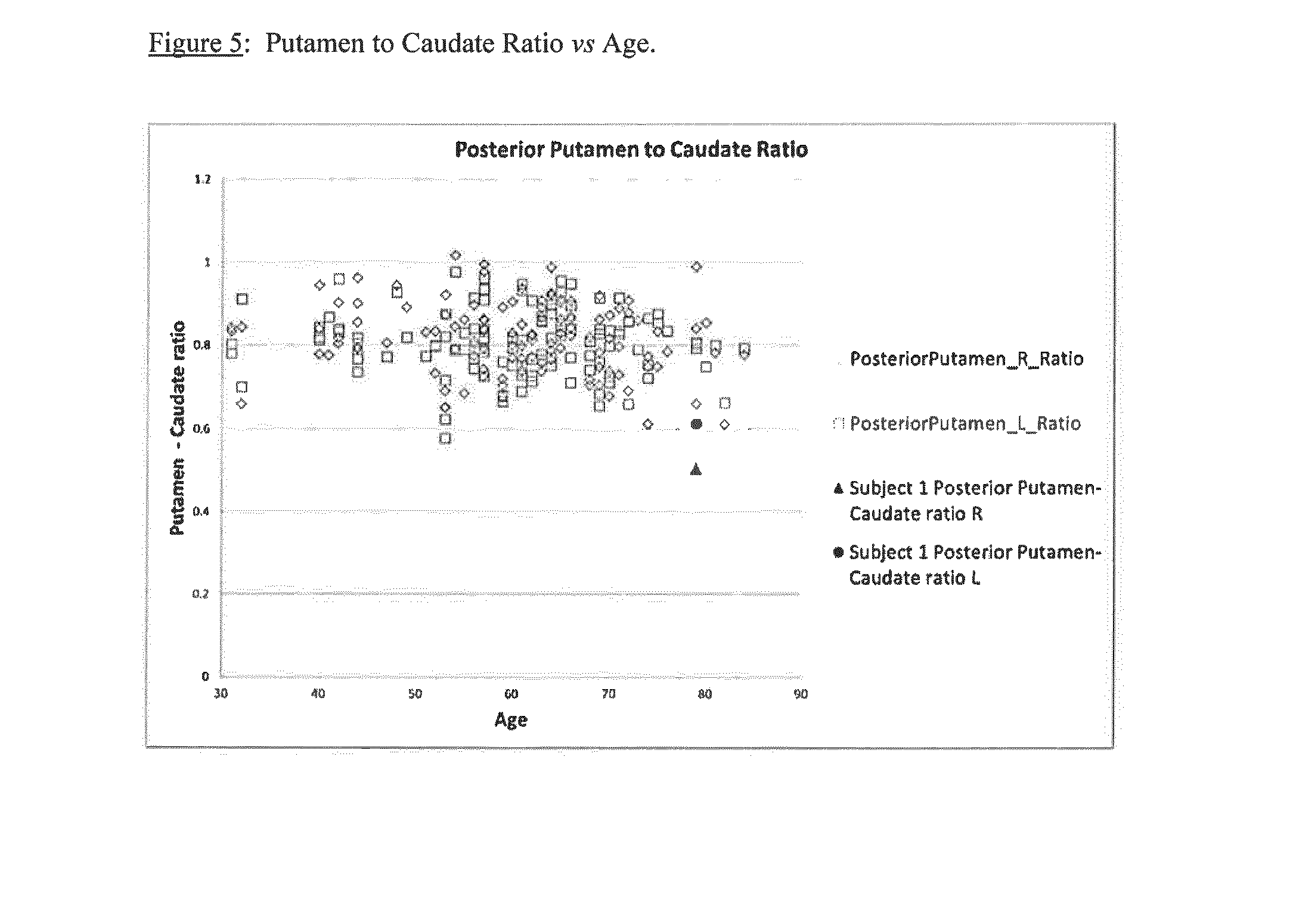
[0092]Example 2 applies the method of the present invention. In the normal population, for each individual subject the values for left and right are likely very close: a normal subject with striatum right=1.78 and striatum left=3.05 is inconceivable even though these represent −1 standard deviation and +1 standard deviation from the normal me...
example 1
Striatal Binding Ratios: Normal Range
Comparative Example
[0117]The European Association of Nuclear Medicine RESEARCH4LIFE© initiative (“EARL”) has been compiling a database of DaTSCAN images of normal human subjects since 2007 (see http: / / earl.eanm.org / cms / website.php?id= / en / projects / enc-dat.htm). The ENCDAT database includes 150 normal subjects—with data from a range of camera types. SBR was calculated for the 150 normal subjects (Group A):
SBR=(countdensitytargetROI-countdensityreferenceROI)countdensityreferenceROI[0118]where:[0119]SBR=specific binding ratio or striatum binding ratio,[0120]ROI=region of interest.
Brain imaging data for n=37 normal subjects acquired on GE cameras in the ENCDAT database was used for the calculation of SBR (Group B). SBR for an illustrative patient from the ENCDAT database is also shown:
TABLE 1SBR Striatum rightSBR Striatum leftNormal A (±1 SD)2.88 ± 0.652.88 ± 0.69Normal B (±1 SD)2.41 + / − 0.632.42 + / − 0.63
FIG. 1 shows the variation of SBR with age for ...
example 2
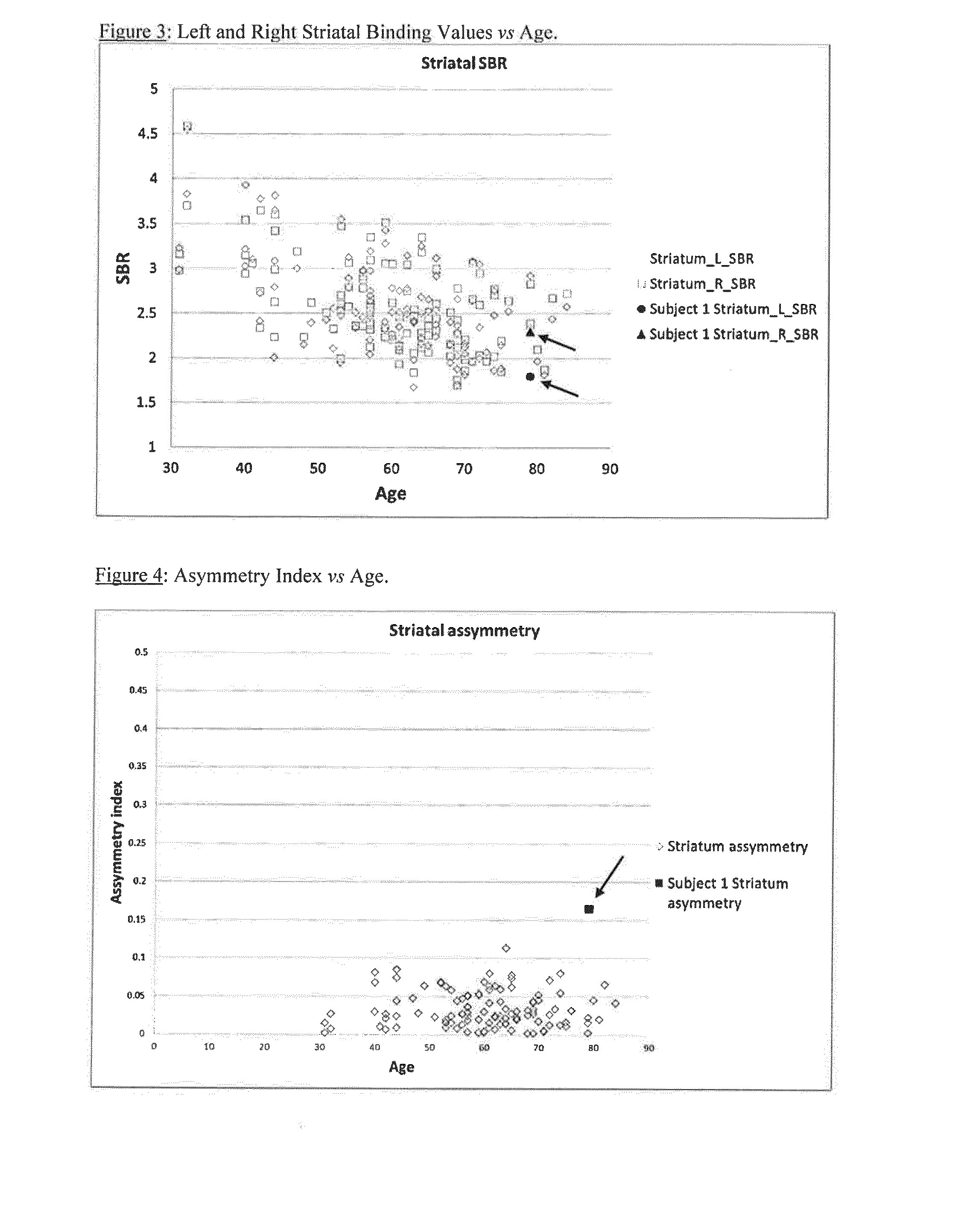
Striatal Left / Right Binding Ratio
[0121]Using the method of the present invention, the data from Example 1 was used to calculate a striatum right:left ratio:
TABLE 2StriatumSBR rightSBR leftRight:leftNormal2.88 + / − 0.652.88 + / − 0.691.00 + / − 0.04(+ / −1 SD)Normal range1.78-3.041.79-3.050.96-1.04(+ / −1 SD)
Table 3 below uses SBR data for normal subjects from the ENC DAT database. Three subjects from each of five different sites are shown, but the overall average is based on data from 11 sites:
TABLE 3Anterior PosteriorSBRSBRStriatum Caudate PutamenputamenPutamenStriatum Striatum R:LR:LR:LR:LR:LSiteRLratioratioratioratioratio14.934.791.031.011.041.011.113.233.221.001.030.990.961.073.153.091.021.051.001.000.9323.293.251.010.981.031.031.032.652.581.031.021.021.001.083.163.111.020.971.041.001.1832.742.601.051.051.051.001.182.692.940.920.890.930.911.001.911.881.021.031.000.981.0544.064.031.011.050.980.970.992.562.331.101.151.061.011.203.573.281.091.111.071.061.0752.702.621.031.071.000.991.022.372...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com