Distributed photodiode structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
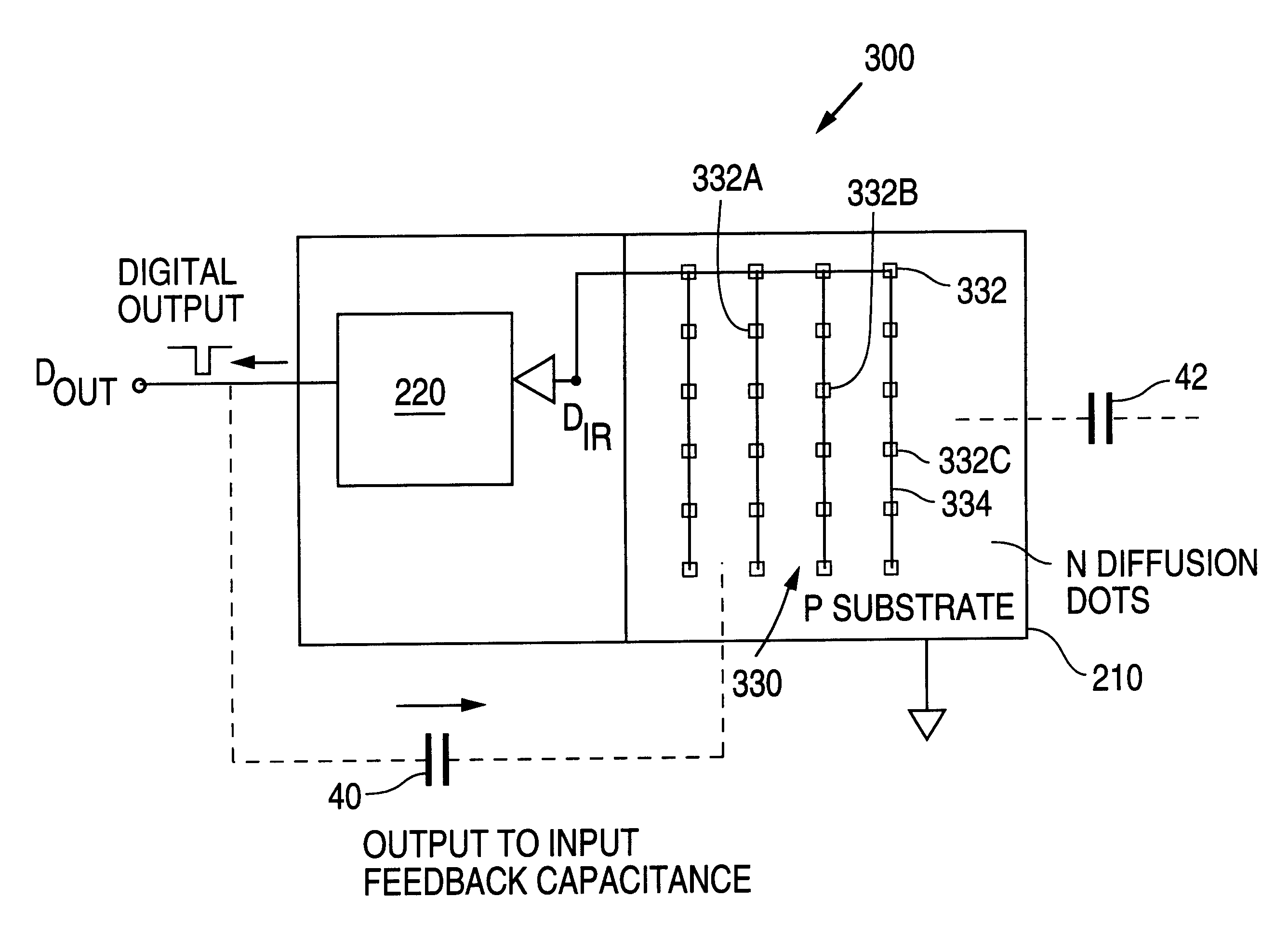
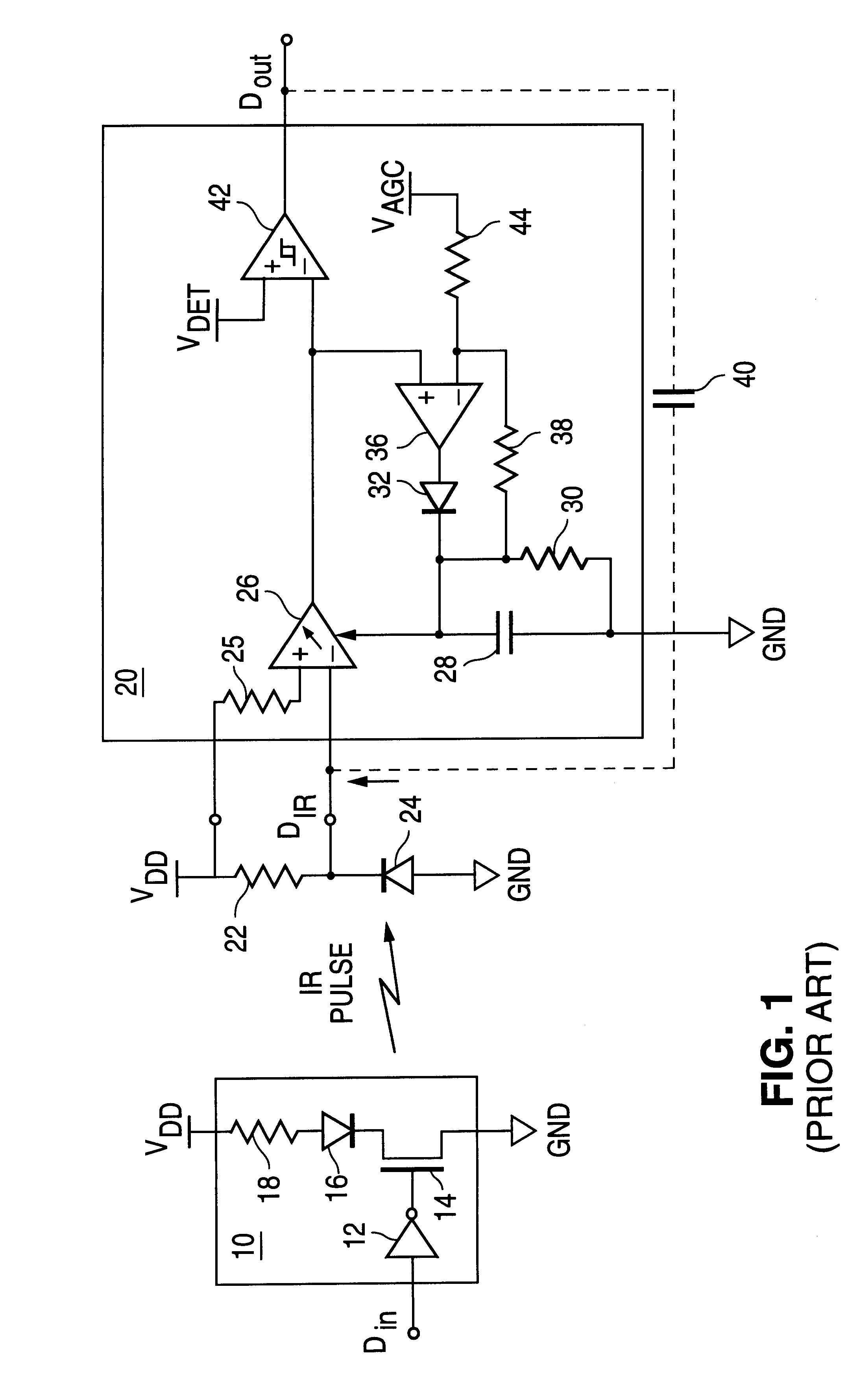
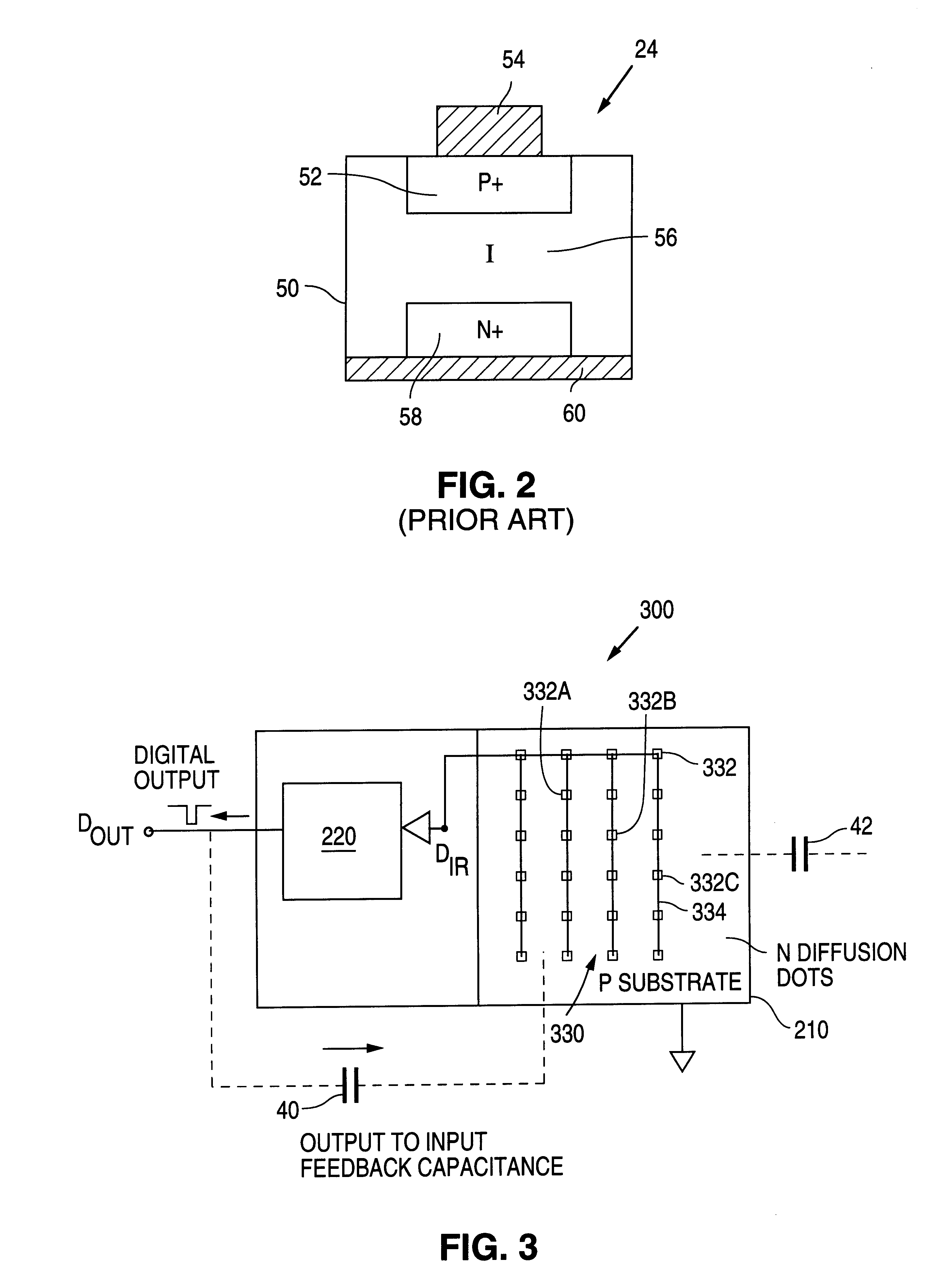
Because of the cost associated with assembling the transceiver module into a single package, it is desirable to integrate the photodiode and the receiver circuit on a single silicon substrate. However, constructing an IrDA receiver or transceiver with an integrated photodiode has typically not been either cost effective or sufficiently optically sensitive to have the range to meet, for example, the IrDA lowspeed specification.
In general, IrDA receivers typically use discrete photodiodes with areas of 3.4 to 25 square millimeters in order to produce the minimum signal level, typically 30 nA to 220 nA, required by the minimum detect threshold of an IrDA receiver at a range of 1 meter. A receiver or transceiver IC typically has an area of 2 to 10 square millimeters depending upon the IC fabrication process technology employed and the complexity of the circuit design.
Although PN photodiodes can be constructed using a standard IC fabrication process, the resulting photodiodes typically s...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap