Copolymers of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene having reduced extractable content and improved solution clarity
a technology of hexafluoropropylene and vinylidene fluoride, which is applied in the field of copolymers of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene having reduced extractable content and improving solution clarity, can solve the problems of not being able to reproduce the polymers tested with any degree of certainty, not being able to describe such properties, and not being able to achieve industrial use. practical process,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Into a 7.5 liter, stainless steel reactor were charged 4.913 kg of deionized water, 0.230 kg of a 1 wt % solution of a mixture of perfluoroalkanoate salts, and 0.004 kg of paraffin wax. The mixture was purged with nitrogen and agitated for 30 minutes. The reactor was sealed and heated to 80 degrees Celsius. The reactor was charged with 0.415 kg of vinylidene fluoride, 0.215 kg of hexafluoropropylene (a ratio of 66 vinylidene fluoride / 34 hexafluoropropylene), and 0.010 kg of ethyl acetate. The pressure was at 4895 kPa. The reaction conditions were stabilized at 80 degrees Celsius, and then the polymerization was begun by introducing 0.040 kg of an initiator emulsion consisting of 2 wt % di-n-propyl peroxydicarbonate and 0.15 wt % mixed perfluoroalkanoate salts dispersed in deionized water. The pressure dropped upon initiation and it was then maintained at 4825 kPa. The polymerization was maintained by the addition of the initiator emulsion at the rate of 0.176 kg per hour, and by the...
example 4
Into a 293 liter stainless steel reactor were charged 200.0 kg of deionized water, 1.00 kg of a 10 wt % solution of a mixture of perfluoroalkanoate salts, and 0.015 kg of paraffin oil. The reactor was evacuated and heated to a temperature of 91 degrees Celsius during the charging, and agitation was used. To the reactor were added 12.6 kg of vinylidene fluoride, 0.8 kg of hexafluoropropylene (a weight ratio of 94 vinylidene fluoride / 6 hexafluoropropylene), and 0.5 kg of ethyl acetate, which brought the reactor pressure to 4480 kPa. During the pressurization, when the pressure reached 3445 kPa, a feed of initiator emulsion consisting of 2 wt % di-n-propyl peroxydicarbonate and 0.15 wt % mixed perfluoroalkanoate salts dispersed in deionized water was begun and was maintained at 9.0 kg / h until 4.6 kg of initiator emulsion had been added. The rate of further initiator emulsion addition was adjusted so as to maintain a total monomer feed rate of 27.0 kg / h. A monomer mixture in the ratio 9...
examples 5 to 12
Copolymers of examples 5 to 8 are made similarly to copolymers of Examples 1 or 2, and copolymers of examples 9 to 12 are made similarly to copolymers of Examples 3 or 4 and are shown in Table I.
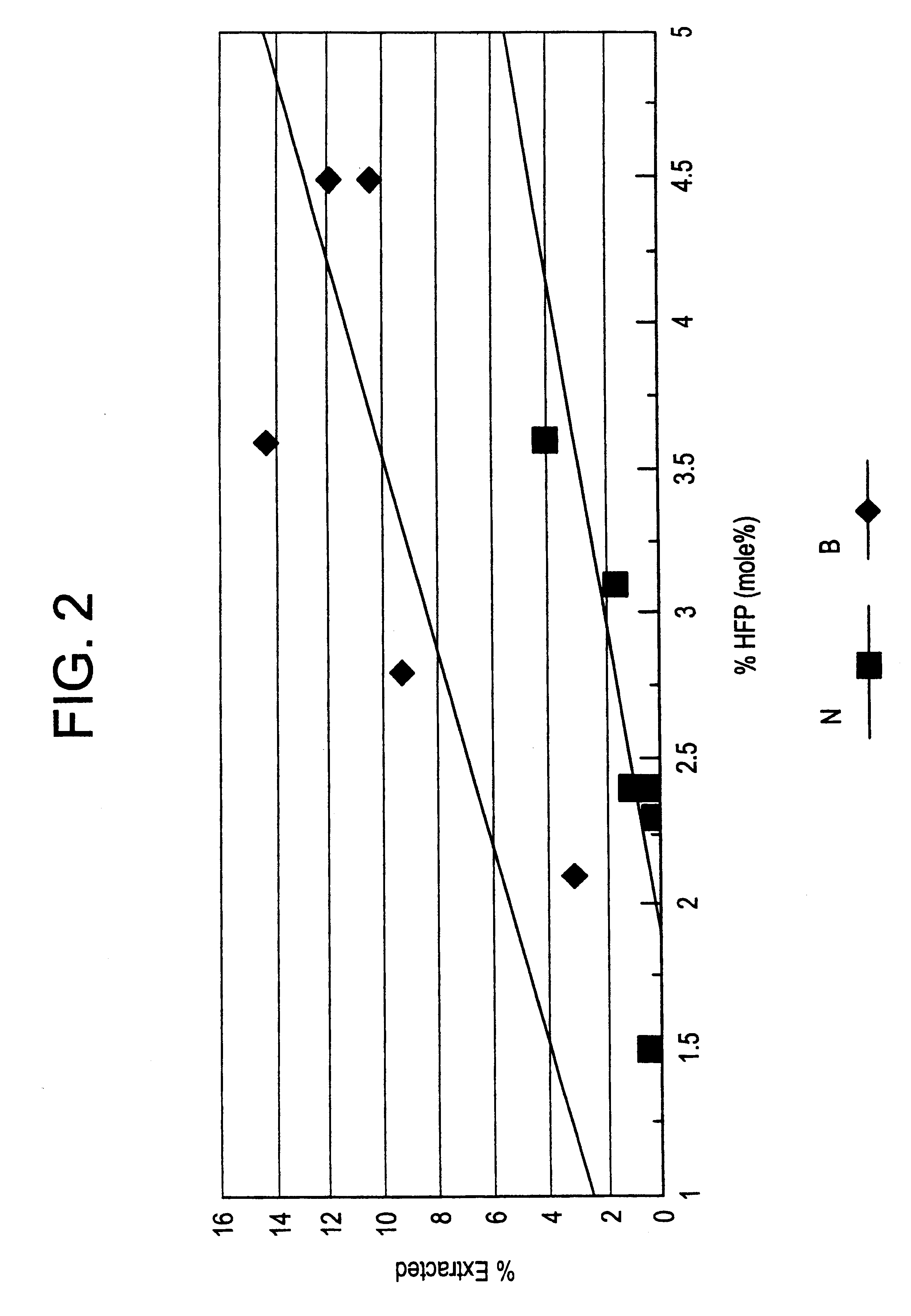
Evaluation of the Solution Properties of the Examples
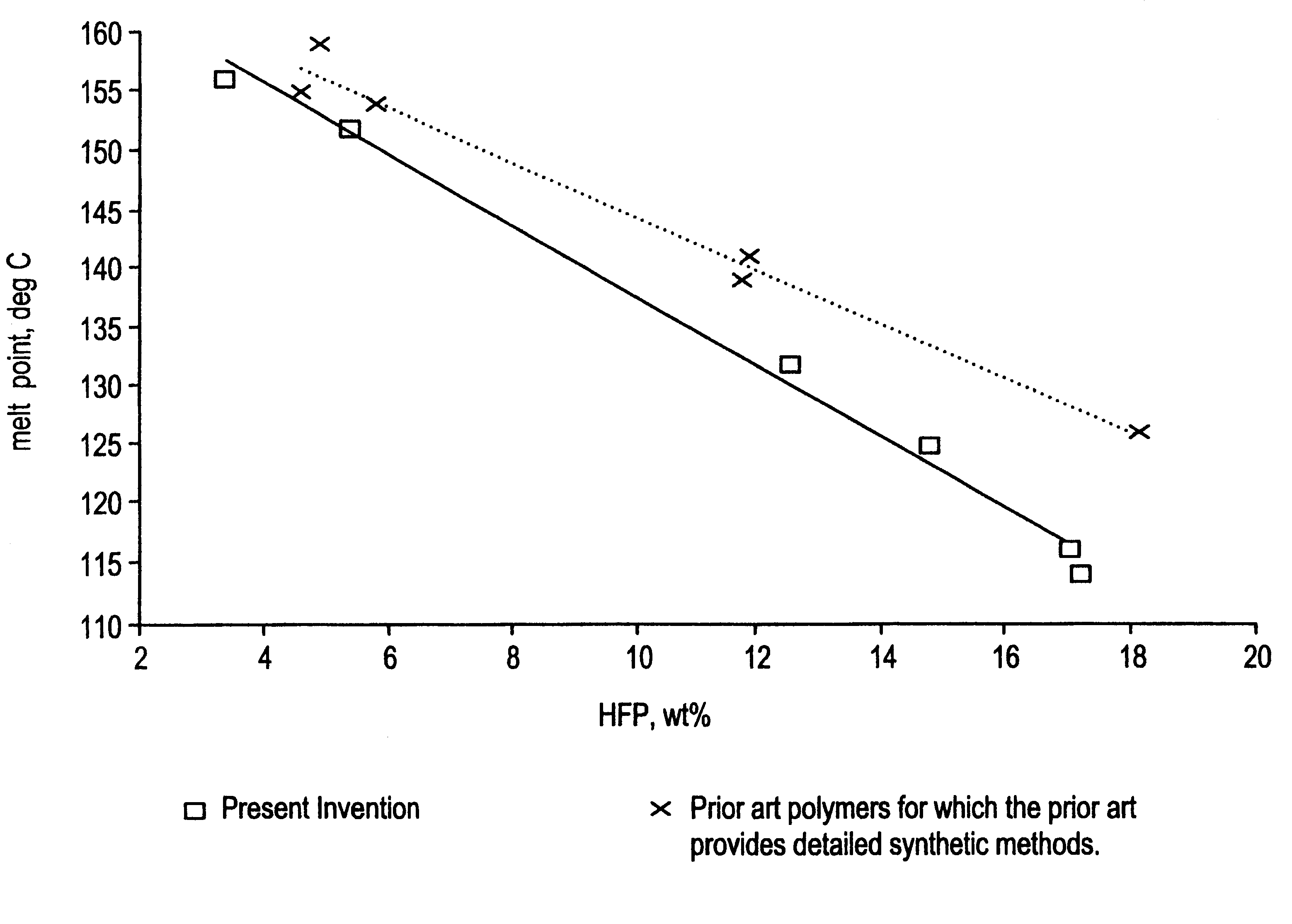
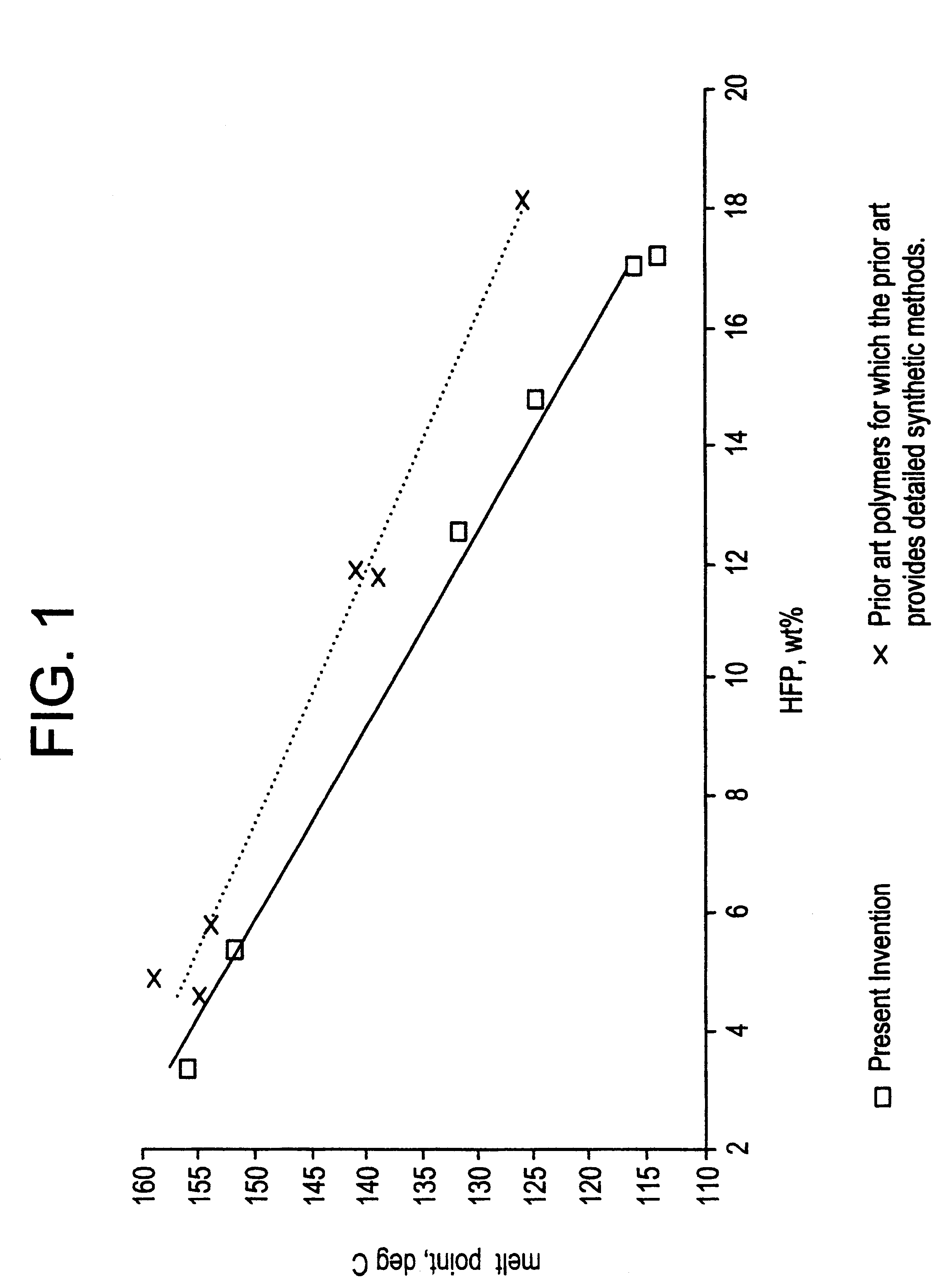
The term "solution(s) having improved clarity and fluidity" as used in the specification and claims of this application means as shown in Table II for Examples 2 and 12, that there will be a difference across a range of solvents between copolymers of the same HFP content at the same solution concentration and temperature whereby solutions of the copolymers of the present invention tend to remain clear and fluid for longer periods than solutions of copolymers made by a typical process described in the prior art.
The solution properties of examples 2 and 12 are shown in Table II. Mixtures of the indicated weight percent were prepared, using heat when necessary to dissolve the polymer completely and form a clear solution. Solutions were then a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| DSC melting points | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com