Structured material having apertures and method of producing the same
a structured material and aperture technology, applied in the direction of synthetic resin layered products, bandages, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of poor skin health, leakage of conventional cover materials used in personal care absorbent articles, and inability to provide high viscosity fluids, etc., to achieve fast and efficient menses handling, high viscosity, and high viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
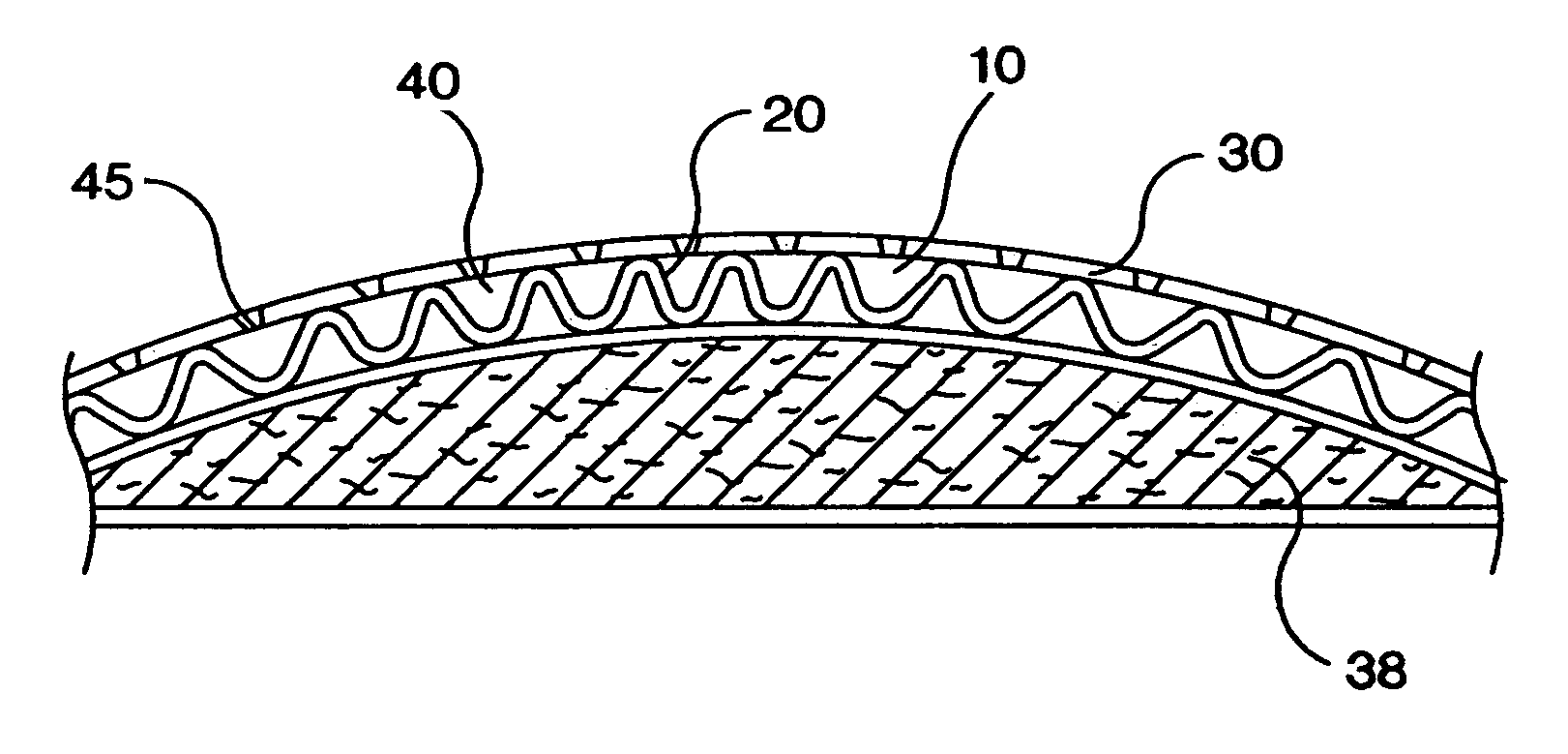
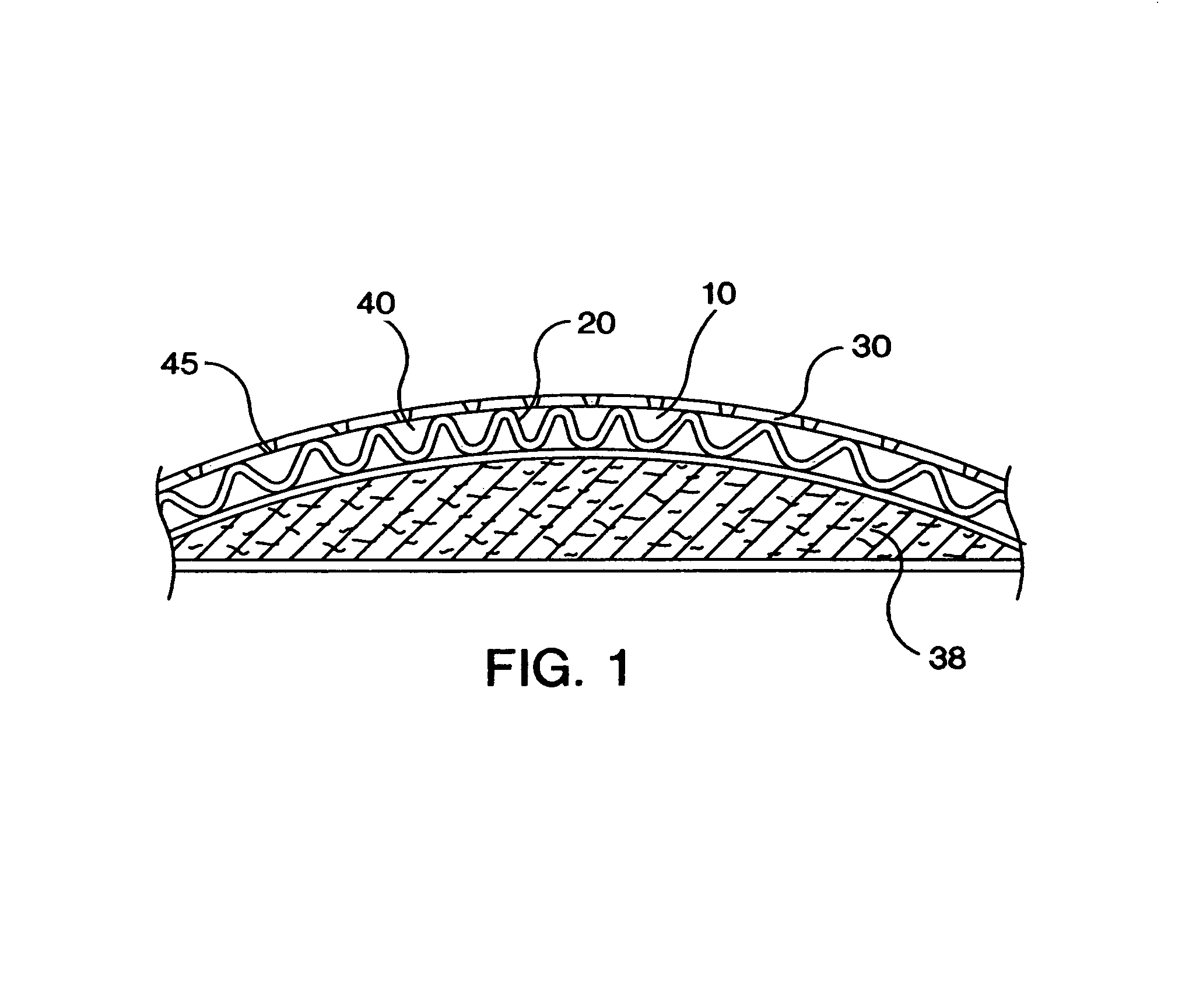
[0111]Several structured composite materials 10 were produced in accordance with the process of this invention and evaluated to compare the properties of each material with those of conventional model cover materials. A 100 gsm CaCO3 filled linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) film, made using 45% by weight of m-LLDPE and 55% by weight CaCO3, is oriented in the machine direction using a machine direction orientor to three times its original length and then bonded to a nonwoven surge material. The bond pattern used was a S-weave bond pattern. The film layer of the composite material has a low shrinking temperature and is apertured during the bonding process by burning off the polymers in the bond areas. As the apertured composite material is heated, the film layer shrinks, thus producing the structure 40 of the apertured structured composite material 10.
[0112]During the bonding process, the film layer was positioned against the pattern roll and the nonwoven surge material was posi...
example 2
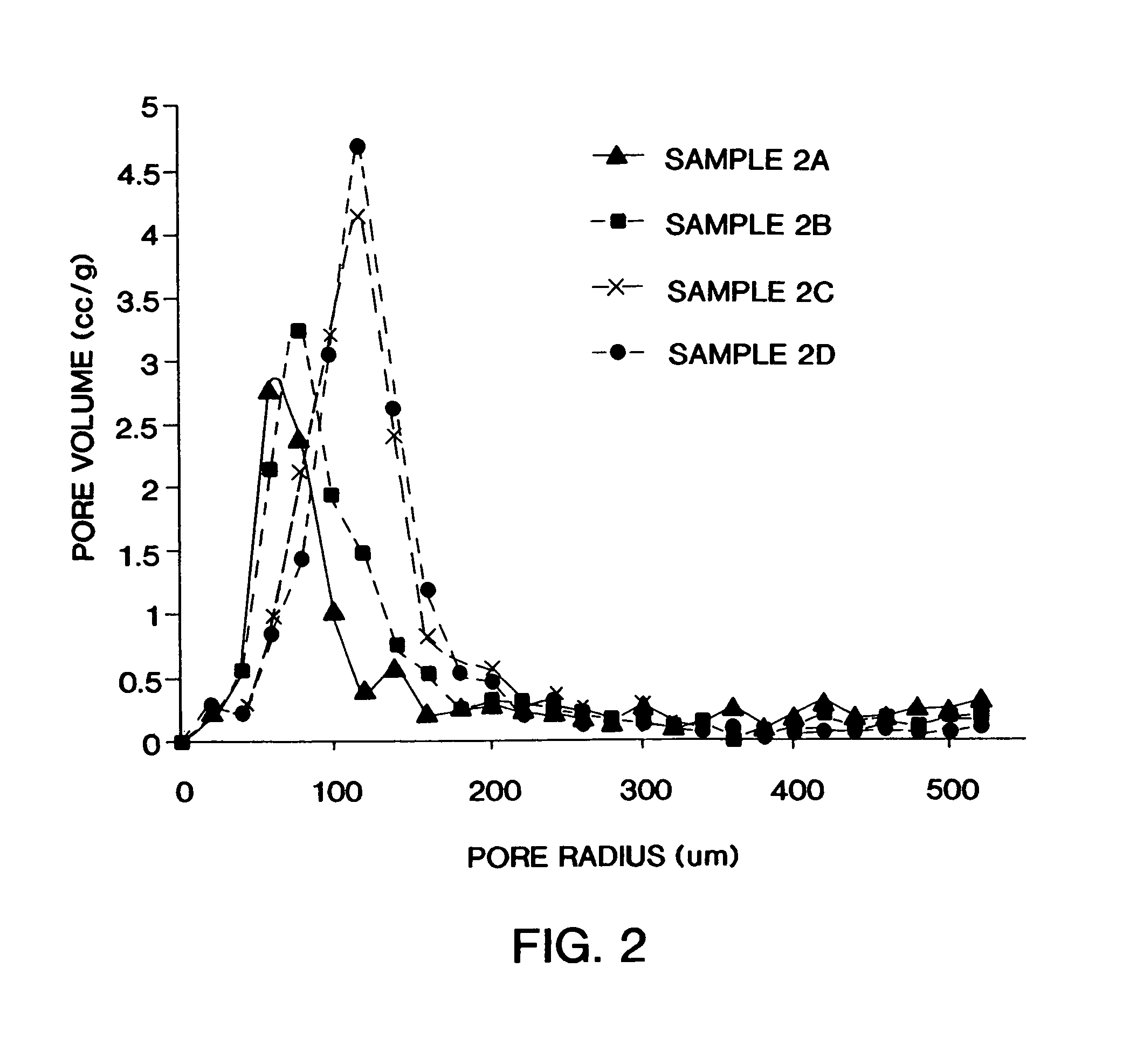
[0119]Several samples of structured composite materials 10 were produced according to this invention having a first layer 20 made of a polypropylene polymer and a slit apertured second layer 30 made of an ethylene-propylene copolymer 30. Sample 1 was made with a non-shrinking first layer 20 and a slit apertured second layer 30 having slits 44 with a machine direction orientation. Sample 2 was made with a non-shrinking first layer 20 and a slit apertured second layer 30 having slits 44 with a diagonal orientation. Sample 3 was a composite cover material having a first layer 20 of polypropylene polymer and a second layer 30 of ethylene-polypropylene copolymer. The polypropylene polymer was made by the Exxon Mobil Chemical Company under the trade designation Exxon 3155 and the copolymer was made by Union Carbide under the trade designation 6D43. Each sample was treated with 0.3% Ahcovel surfactant add-on and tested for menses and rewet performance. The control code for the test was a s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com