Stereoscopic display
a stereoscopic display and parallax technology, applied in the field of parallax stereoscopic displays, can solve the problems of difficult to provide a haptic interface, inability to display stereoscopic videos including moving images, and inability for viewers to enter the display space, so as to reduce the effective pitch, increase the number of horizontal pixels, and reduce the effect of effective pitch
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0060
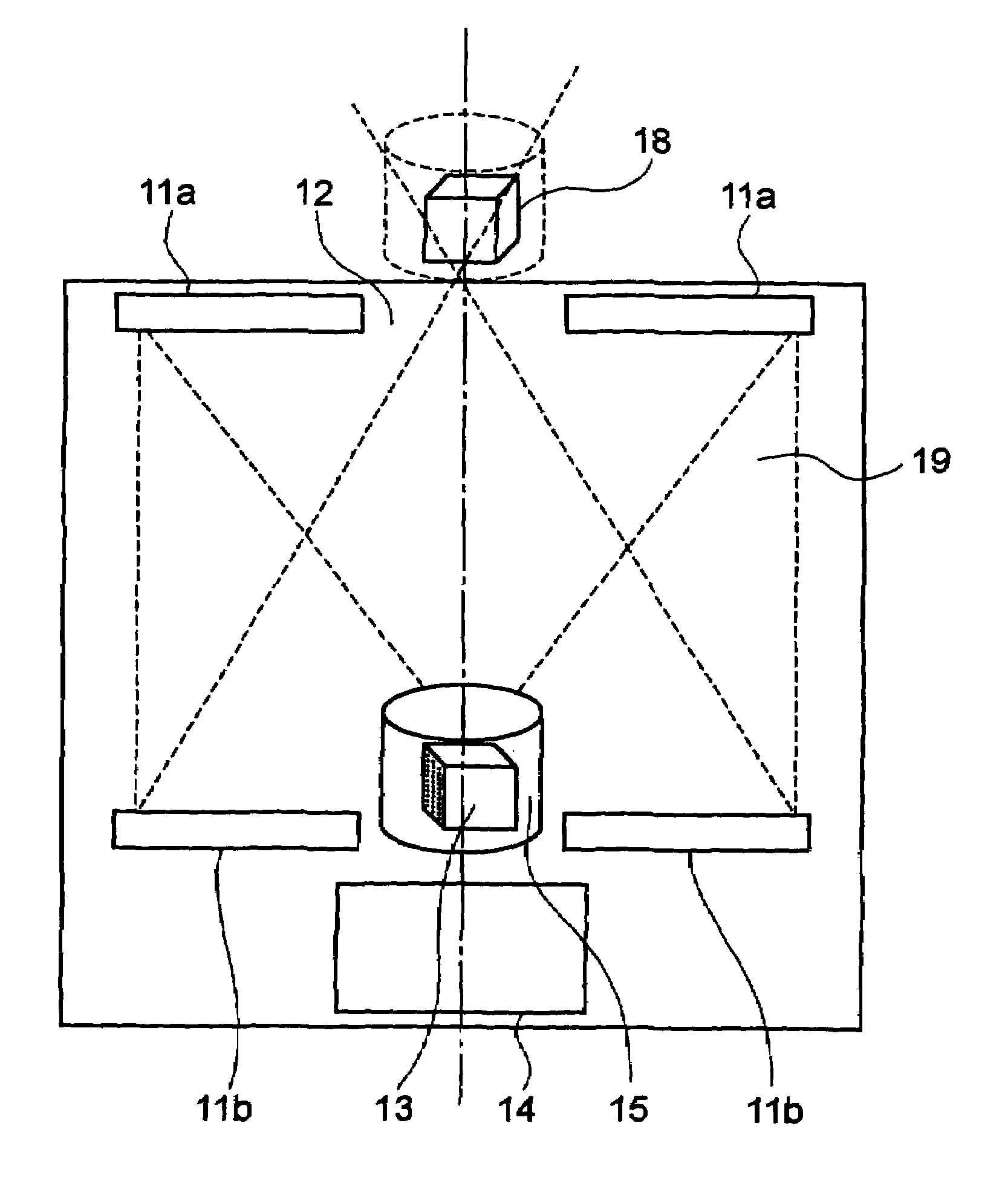
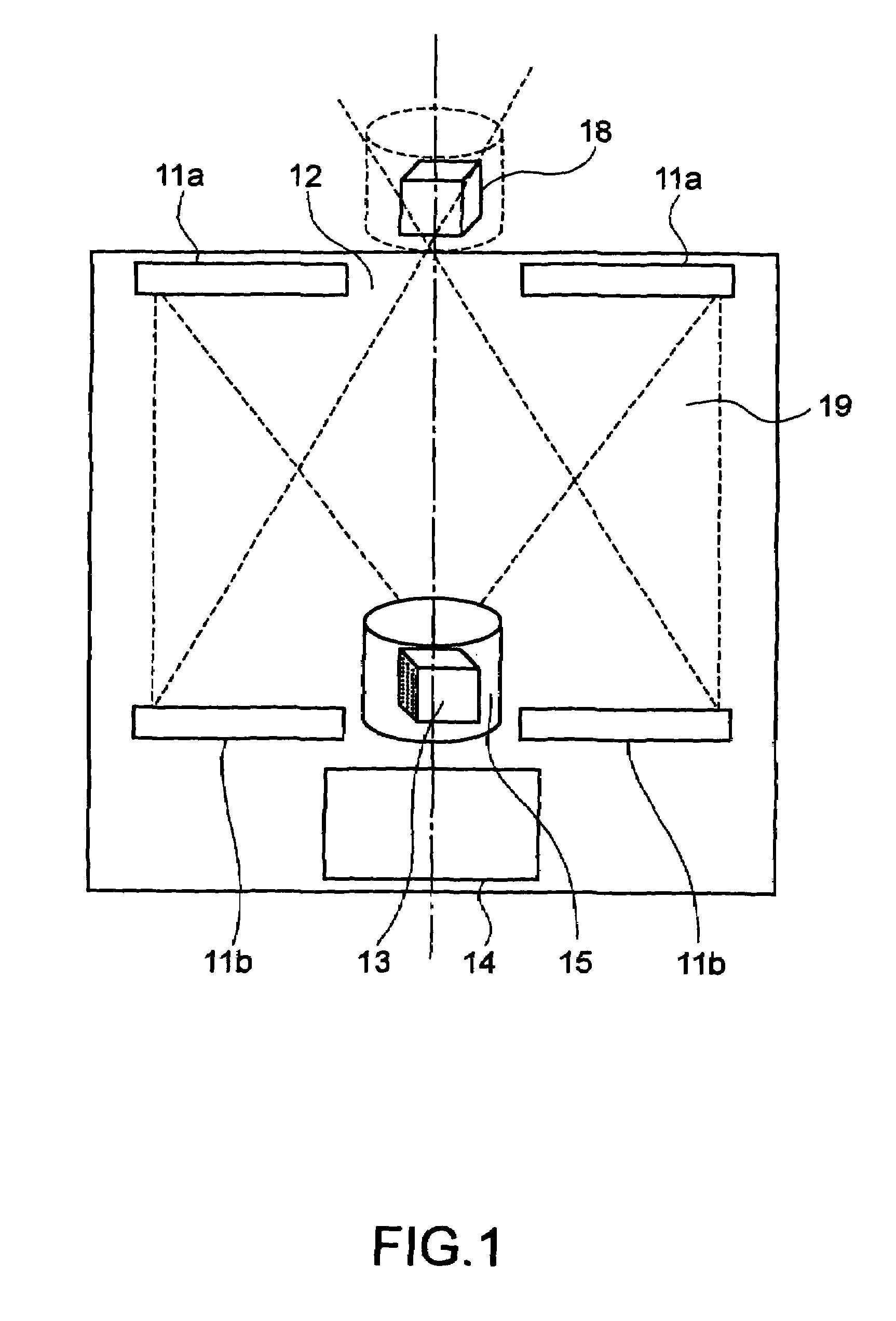
[0061]FIG. 1 is a schematic showing a construction in which a reflective image-forming optical system is used as an image-forming device and a cylindrical parallax barrier 15 and a rotating cylindrical light-emitting array are used together as a multi-viewpoint-light-beam forming device.
[0062]In the reflective image-forming system, two Fresnel mirrors 11a and 11b, which are reflective optical elements which serve as convex lenses, are disposed such that the Fresnel mirrors 11a and 11b oppose each other. Apertures 12 are formed in the Fresnel mirrors 11a and 11b at the central regions thereof. A stereoscopic image 13, which is reproduced by a multi-viewpoint light beam group formed by the light-emitting array and the cylindrical parallax barrier 15, is placed close to the lower aperture, and a conjugate image 18 is formed at a position close to the upper aperture. Accordingly, the conjugate image 18, which is to be observed by a viewer, is formed by the lower Fresnel mirror 11b,...
second embodiment
[0075
[0076]FIG. 8 is a schematic showing a construction in which a reflective image-forming optical system is used as an image-generating device, a cylindrical slit-formed unit and a rotating light-emitting array are used together as a multi-viewpoint-light-beam-group forming device, and a polarization selecting element and a phase plate are disposed between the multi-viewpoint-light-beam-group forming device and a conjugate image.
[0077]The stereoscopic display according to the present embodiment includes a stereoscopic image 81 reproduced by a multi-viewpoint light beam group, image-forming optical elements 82a and 82b which form the reflective image-forming device and serve as convex lenses, a reflection / polarization selecting element 83 which separates polarized light used to form a conjugate image 88, a phase plate 84, and a mirror 85. An upper polarizing element 86 is provided as necessary so that reflection of external light at the reflection / polarization selecting element 83 ...
third embodiment
[0086
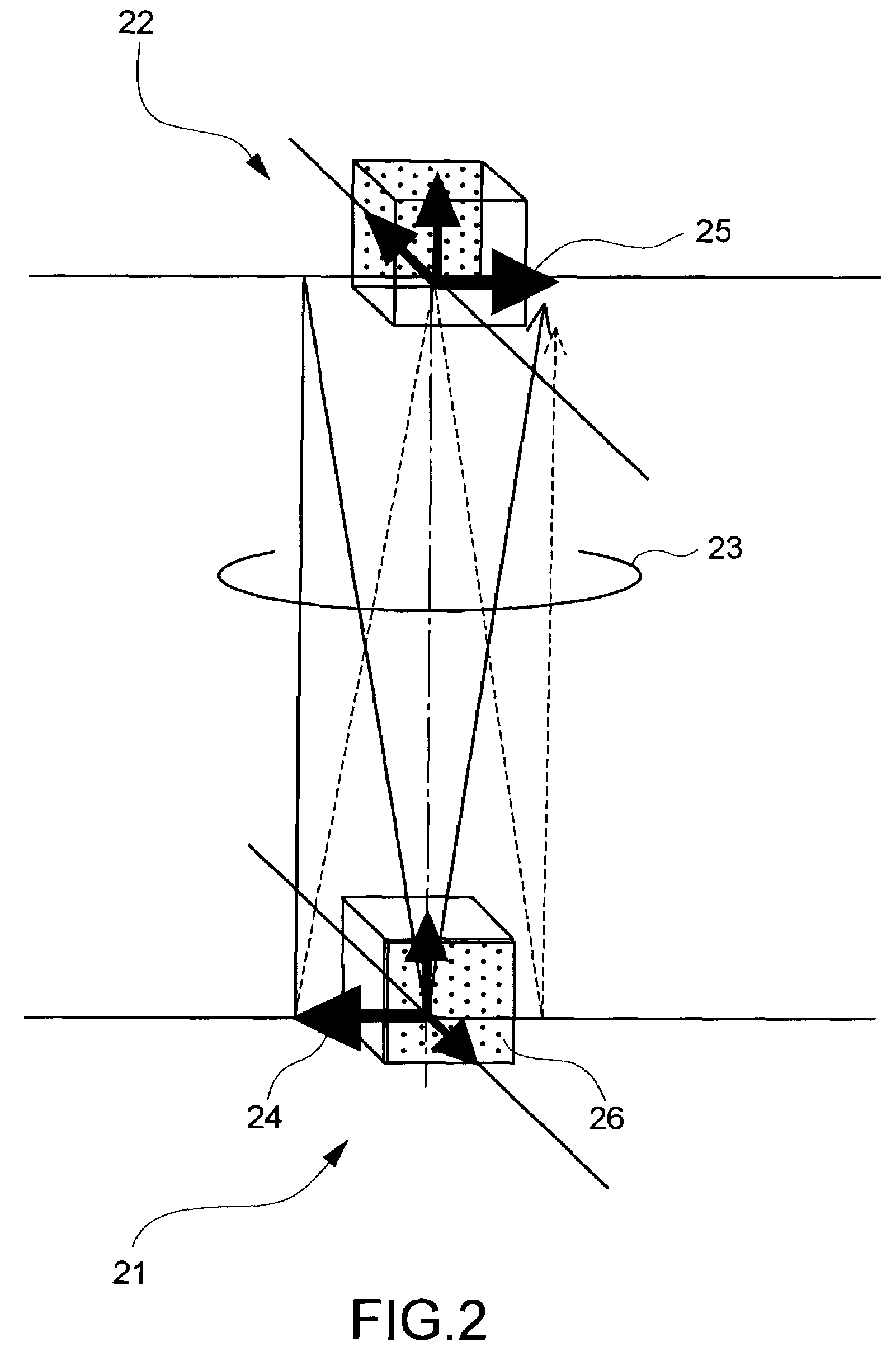
[0087]FIG. 10 is a schematic of a multi-viewpoint-light-beam generating device used in the present embodiment. FIG. 11 is a perspective view of a cylindrical light-emitting array shown in FIG. 10.
[0088]The multi-viewpoint-light-beam generating device 100 includes a cylindrical parallax barrier 102 disposed at the periphery and a cylindrical light-emitting array 101 disposed inside the cylindrical parallax barrier 102. As shown in FIG. 11, the cylindrical light-emitting array 101 is formed such that two-dimensional light-emitting-array elements 111 are arranged so as to cover almost the entire periphery thereof.
[0089]The two-dimensional light-emitting-array elements 111 are preferably formed of thin-film light-emitting elements. A single light-emitting-array element includes 768×128 pixels, and twelve light-emitting-array elements are disposed at the periphery of the cylindrical body. More specifically, the light-emitting-array elements are formed of active-matrix, thin-film, or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com