Method for extracting timing parameters using a cardio-mechanical sensor
a timing parameter and sensor technology, applied in the field of conditioning signals, can solve the problems of not always available noninvasive echocardiography measurement equipment, difficult to predict the trend of the time, and difficult to predict the time of the tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
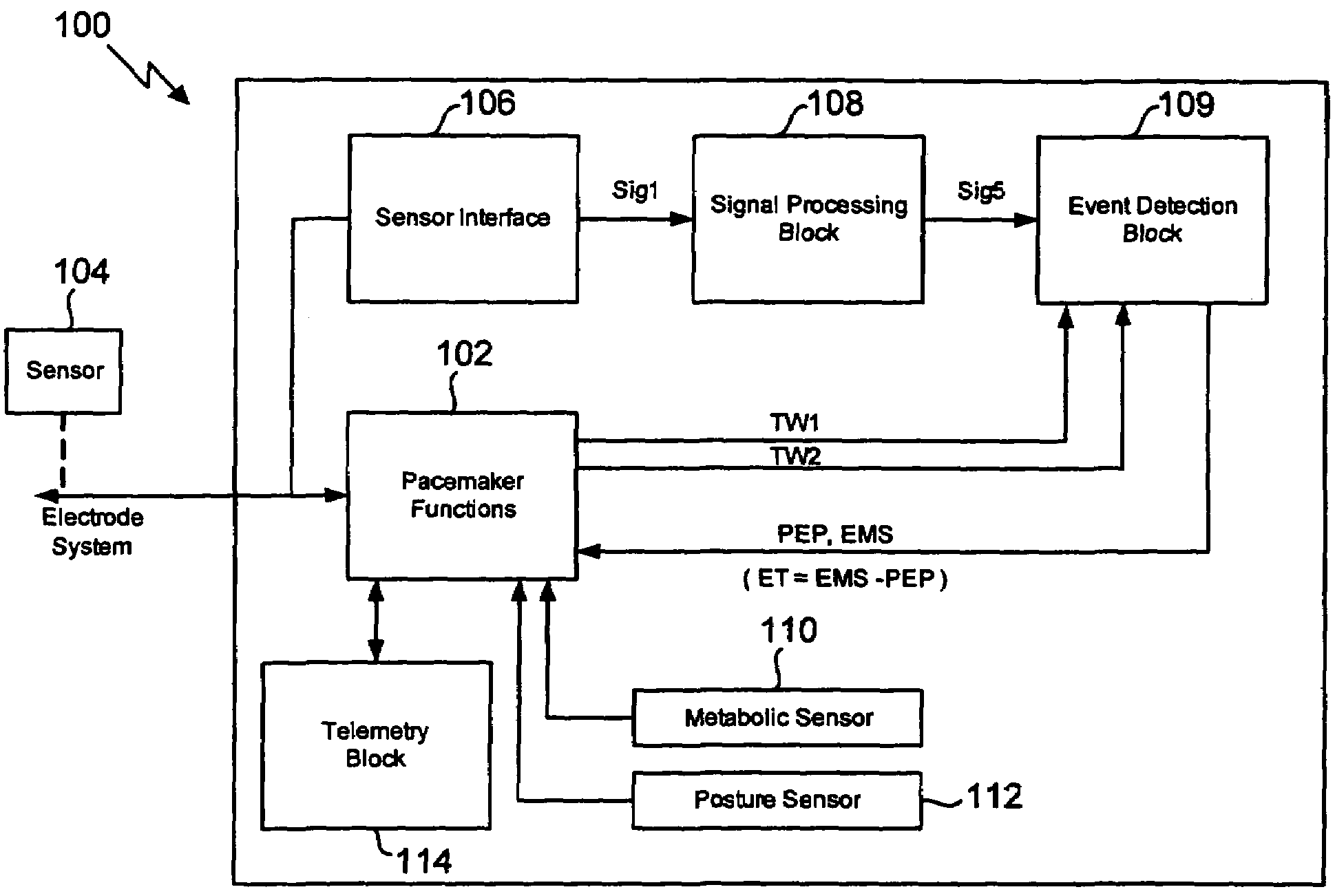
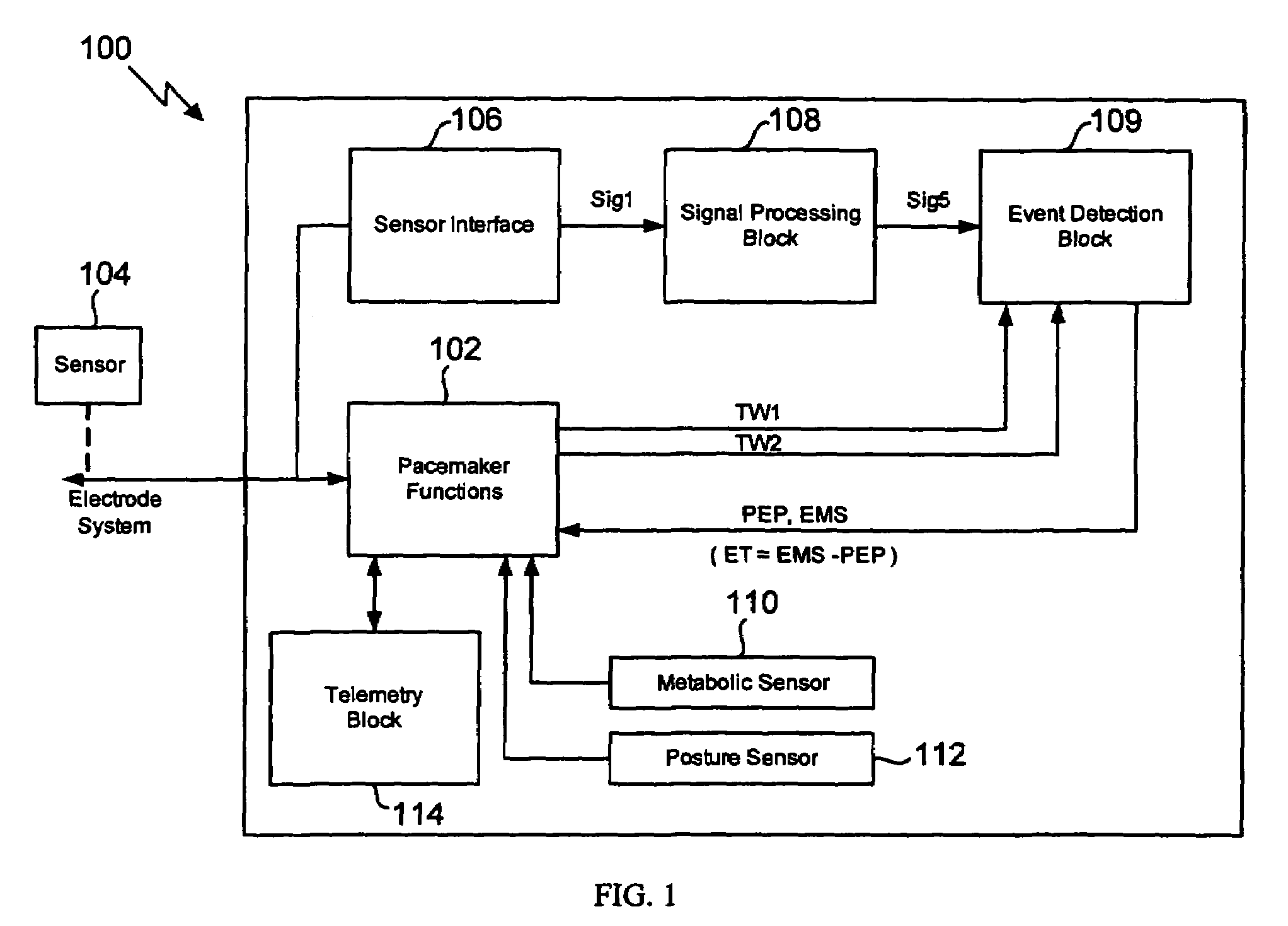
[0026]The invention involves measuring pre-ejection period (PEP) and left ventricular ejection time (LVET) to determine the ejection fraction (EF) and to trend the data over time. This provides an advantageous monitoring of a patient's cardiac function in a minimally invasive manner with a minimum of disruption to the patient.
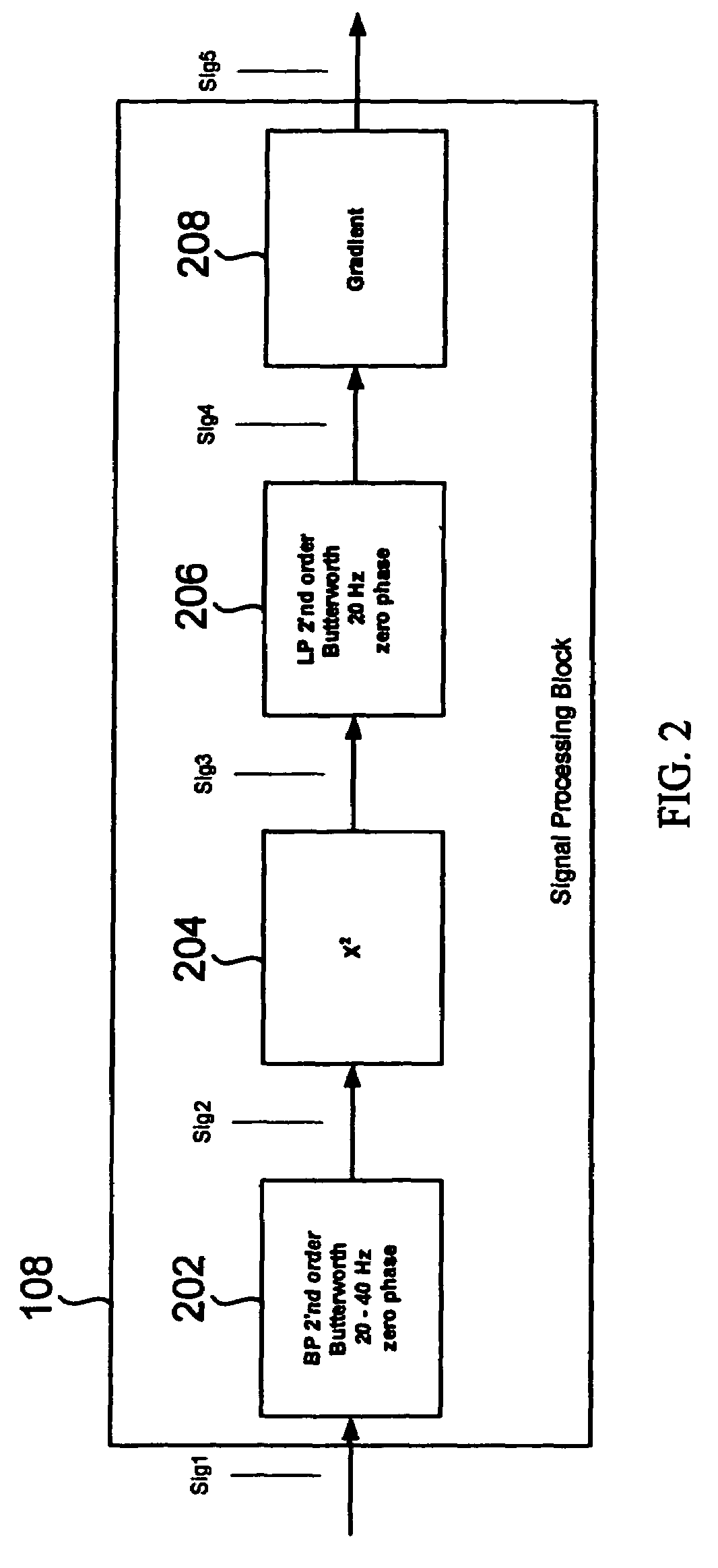
[0027]The invention achieves a robust detection of the opening and closing of the aortic valve of a heart chamber by processing the measured raw signal from an implanted sensor. It was found that a robust detection of the opening and closing of the aortic valve can be achieved by analyzing the signal energy (power) in a frequency range much higher than the heart rate. The signal processing of the invention is insensitive to circadian signal morphology changes for a patient. In one embodiment of the invention, the time derivative of the raw signal rather than the raw signal itself is processed as the high frequency parts are enhanced in the time derivative.
[0028...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com