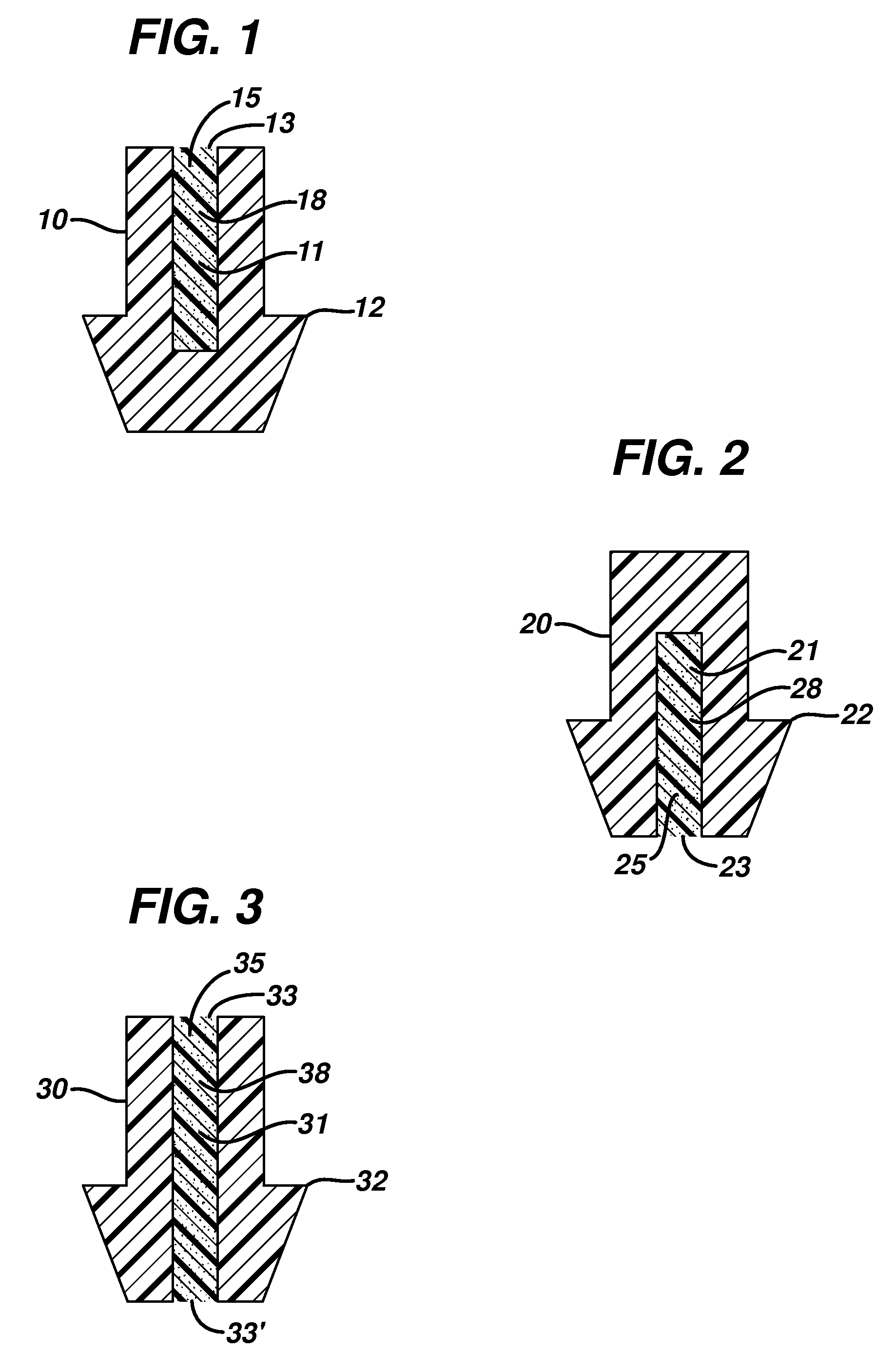
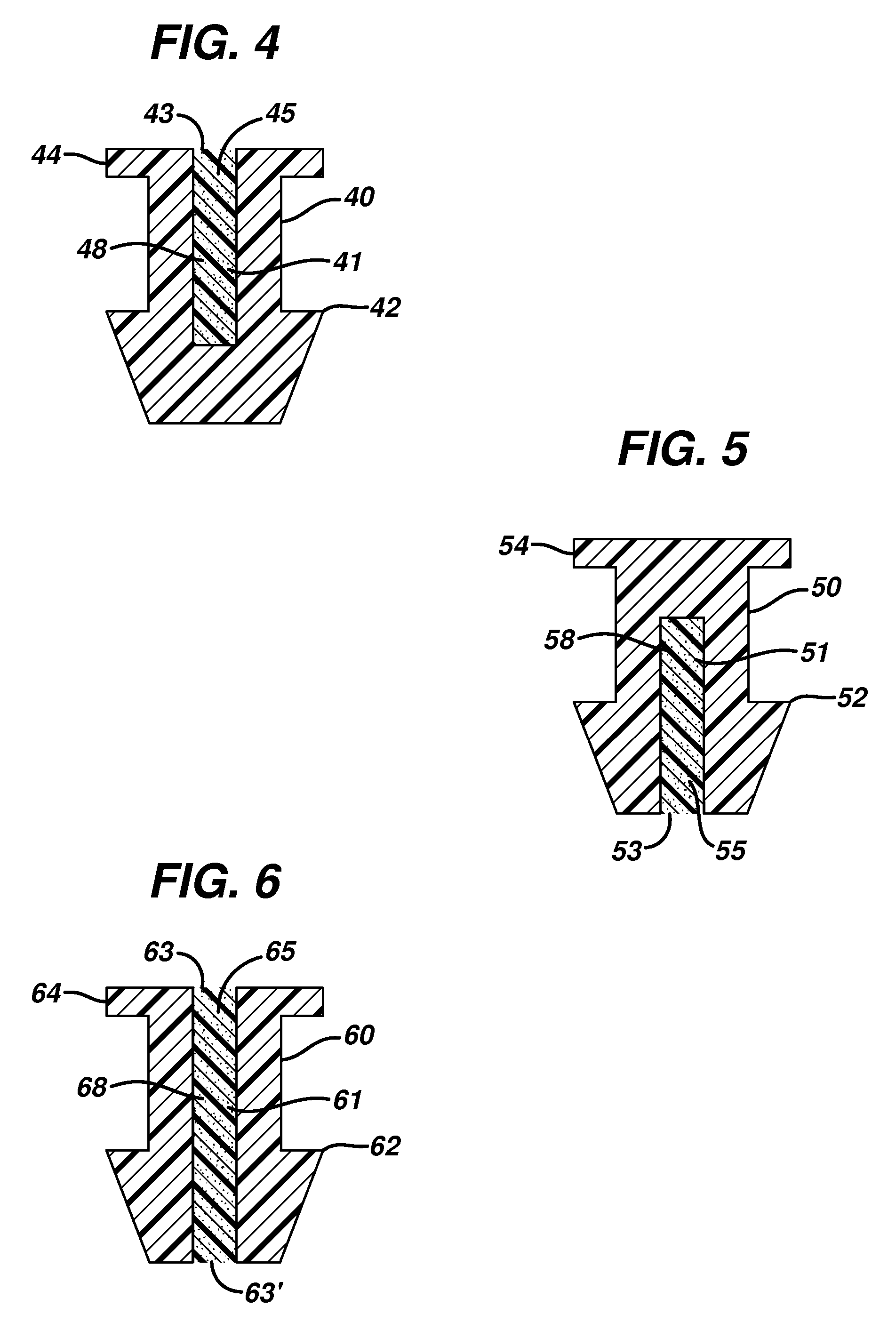
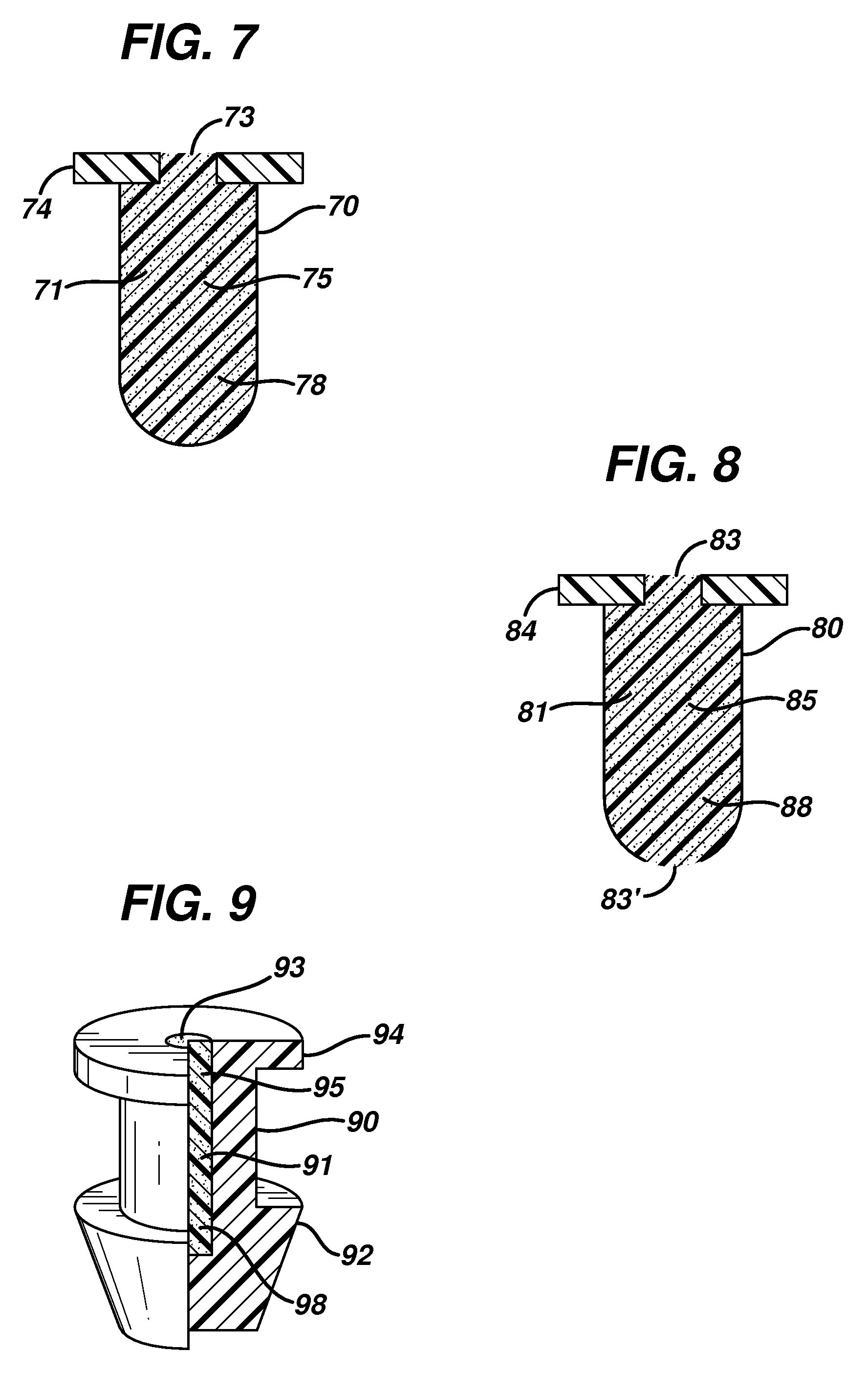
Punctal plugs for the delivery of active agents
a technology of active agents and plugs, applied in the field of punctal plugs, can solve the problems of complex use, ineffectiveness, and ineffectiveness of infection risk, and achieve the effect of improving the safety of patients and reducing the risk of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0066]A 1.50 g amount of epsilon polycaprolactone with an average Mw of approximately 14,000 and an average Mn of approximately 10,000 by GPC (available from Aldrich) was combined with 1.50 g EVA (EVATANE™, Arkema), and 1.00 g of bimatoprost (Cayman Chemicals), each with a purity of greater than approximately 97%. The mixture was then placed in a twin-screw micro-compounder Model No. 20000 from DACA Industries, Inc. that was fitted with a 0.25 mm die and compounded for 15 min. at 120 rpm and 67° C. Following compounding, the mixture was extruded into fibers at 75° C.
[0067]The fibers were cut into approximately 1.5 mm in length sections and inserted into the opening of Sharpoint ULTRA™ plug, available from Surgical Specialties. 70 plugs with drug and 30 placebo each of a 0.6 mm length were made and 70 drugs with drug and 50 placebo each of a 0.8 mm length were made. To insert the fiber, each plug was positioned under a stereomicroscope and tweezers were used to insert a fiber into th...
example 2
[0068]A plug made according to the method of Example 1 that is 0.6 mm in length and a fiber having a diameter of approximately 0.2 mm and containing 25% w / w was placed in a glass vial with 1 cc of phosphate buffered saline having a pH of 7.4. The vial was placed in an incubator at 37° C. and gently agitated. Aliqouts of 1 cc were collected at intervals at 3, 8, and 24 hours and then weekly and analyzed for drug content via HPLC. FIG. 11 is a graph depicting the results of the analysis.
example 3
[0069]A plug made according to the method of Example 1 that is 0.9 mm in length and a fiber with an approximately 0.6 mm diameter and containing 25% was placed in a glass vial with 1 cc of phosphate buffered saline having a pH of 7.4. The vial was placed in an incubator at 37° C. and gently agitated. Aliqouts of 1 cc were collected at intervals as set forth in Example 2 and analyzed for drug content via HPLC. FIG. 12 is a graph depicting the results of the analysis.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com