Manufacturing method of active matrix substrate, active matrix substrate and liquid crystal display device
a technology of active matrix substrate and liquid crystal display device, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, instruments, electrical devices, etc., can solve the problem that liquid crystal cannot be supplied with sufficient voltage, and achieve the effect of excellent properties and preferable application properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
(First embodiment)
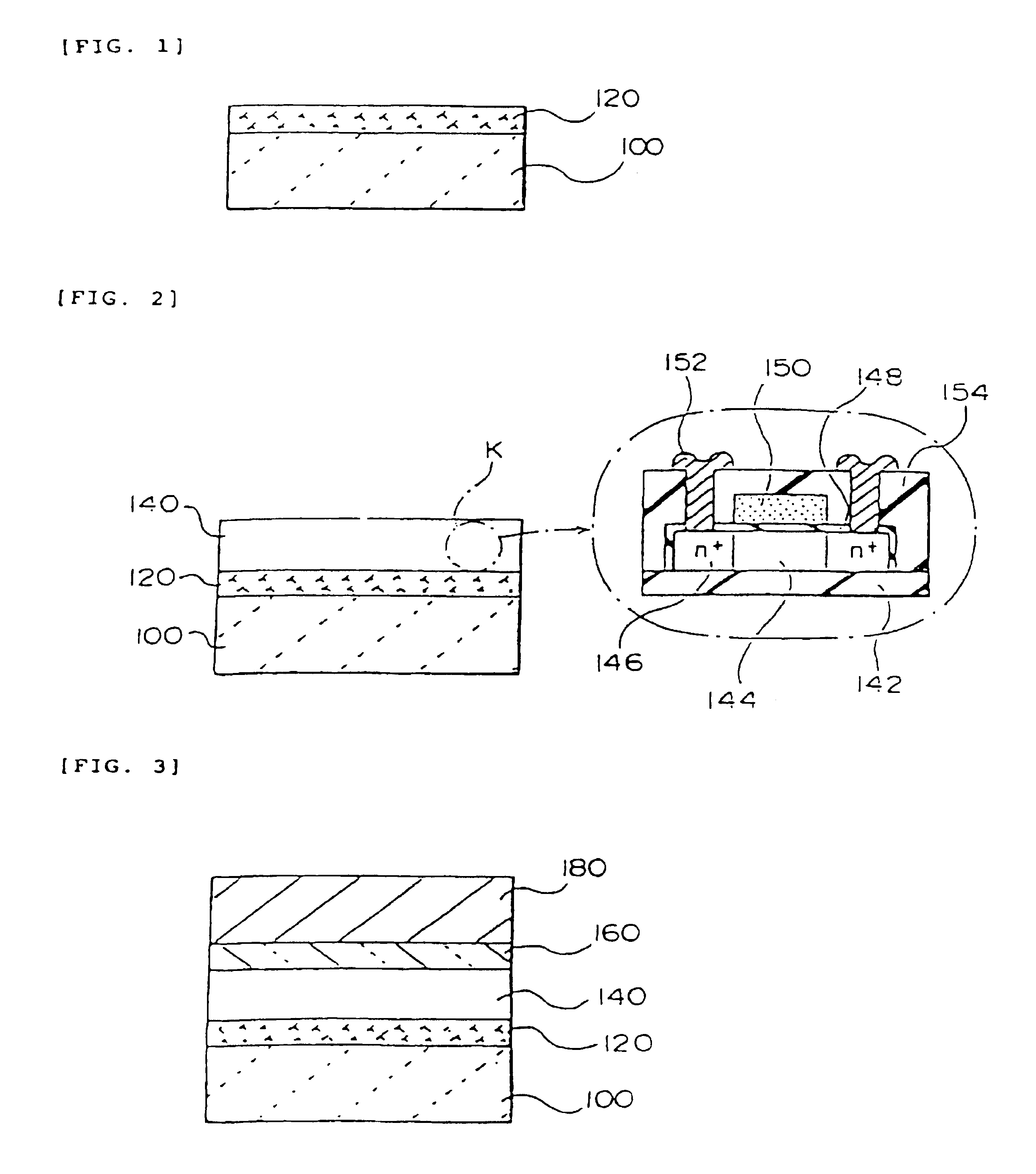
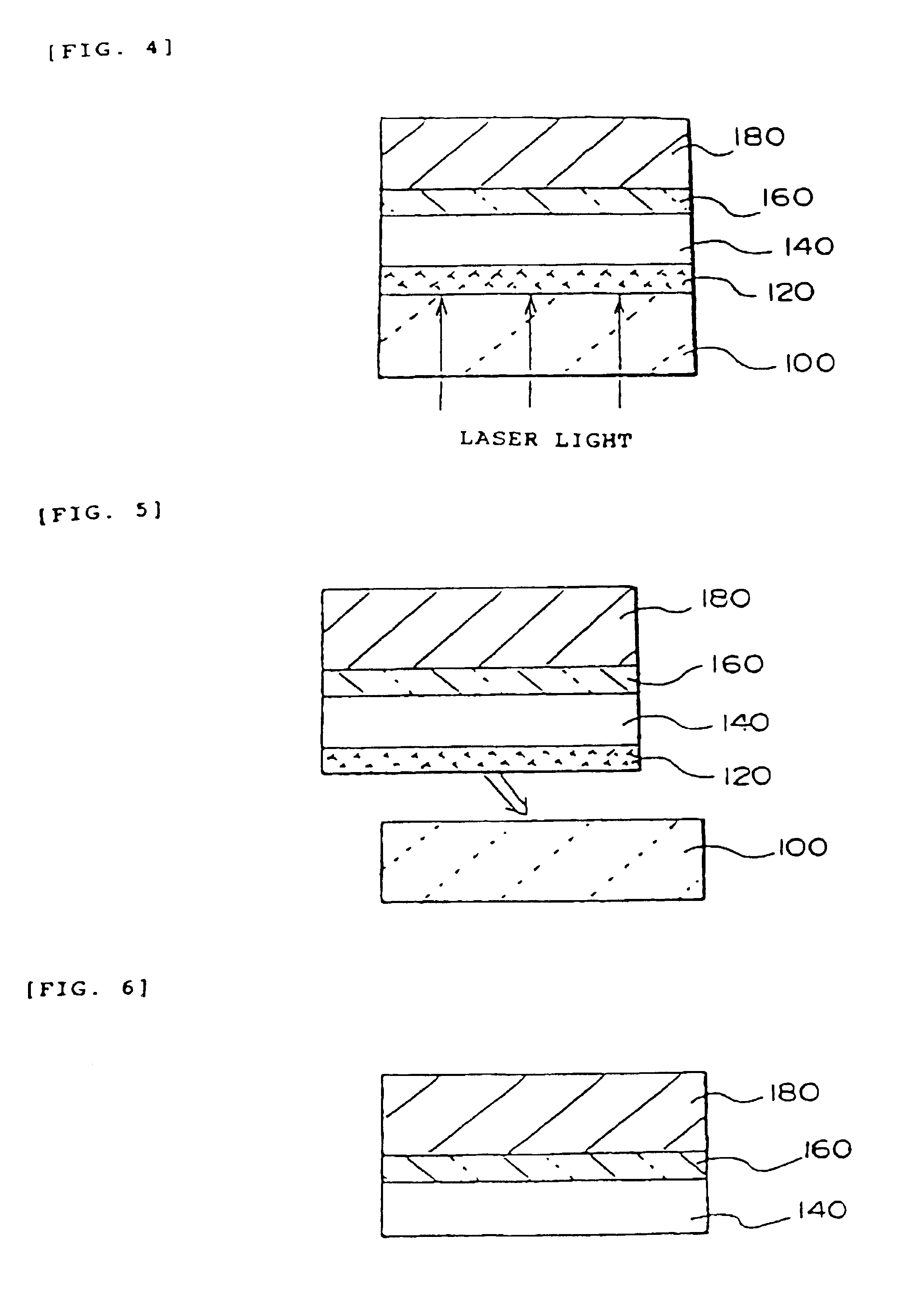
[0181]In this embodiment, an example of the process for manufacturing an active matrix type liquid crystal display device comprising an active matrix substrate, as shown in FIGS. 7, 8 and 9, using the thin film device transfer technique is described.
(Configuration of liquid crystal display device)
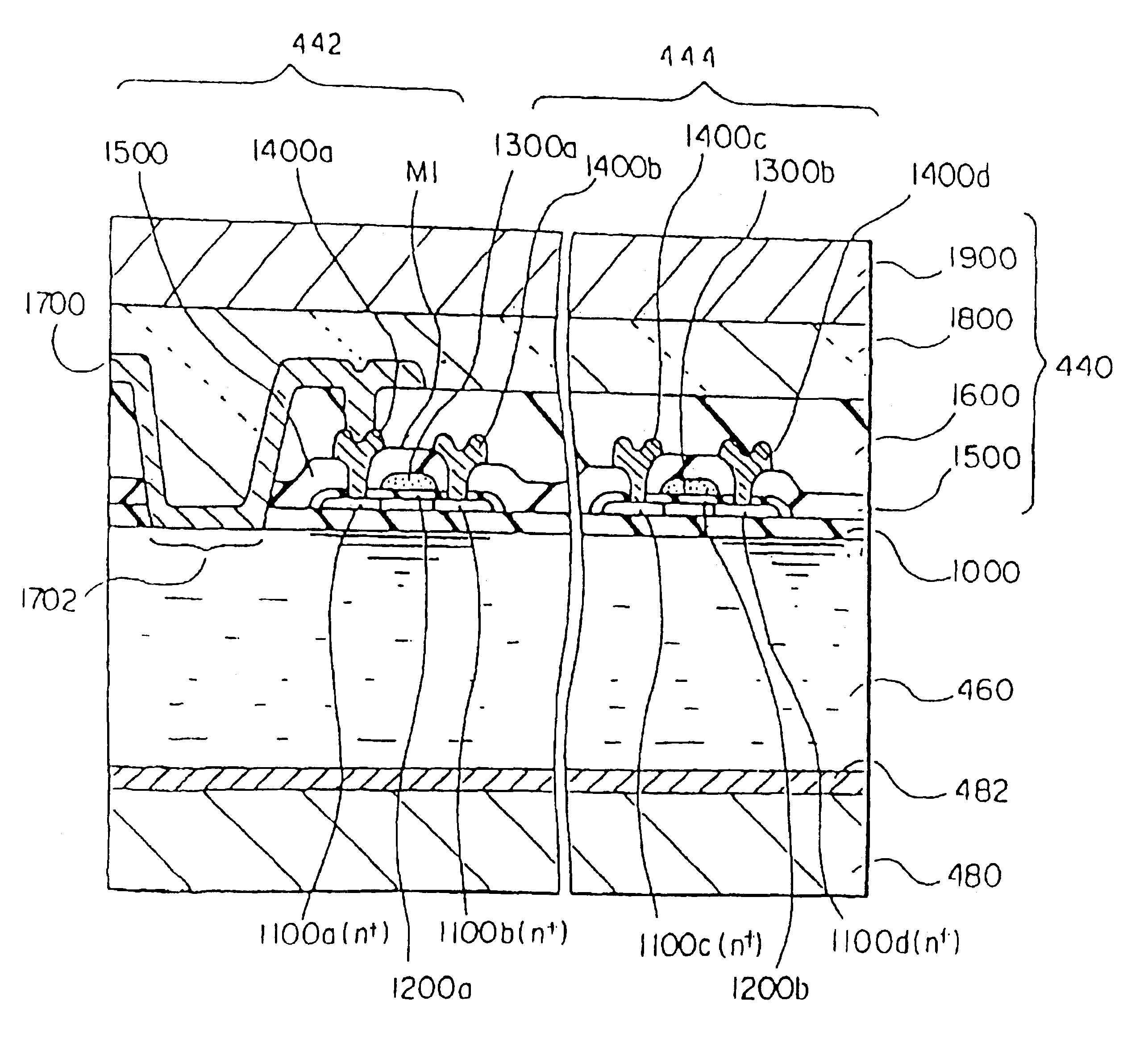
[0182]As shown in FIG. 7, an active matrix type liquid crystal display device comprises backlights 400, a polarizer 420, an active matrix substrate 440, a liquid crystal 460, an opposite substrate 480, and a polarizer 500. In the present invention, when a flexible substrate is used as each of the active matrix substrate 440 and the opposite substrate 480, a lightweight active matrix type liquid crystal panel having flexibility and resistance to shock can be realized as a reflective liquid crystal panel by using a reflecting plate in place of the illumination light sources 400.
[0183]The active matrix substrate 440 used in this embodiment is an active matrix substrate with a...
second embodiment
(Second embodiment)
[0215]FIGS. 18 and 19 are sectional views showing a device in accordance with a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0216]This embodiment is characterized in that the step of forming a color filter and a light shielding film (for example, a black matrix) is added after the step of forming the pixel electrode made of ITO or a metal to form an active matrix substrate with the color filter and the light shielding film (for example, a black matrix).
[0217]The case where the black matrix is used as the light shielding film is described below.
[0218]As the structure of an ordinary thin film transistor, a structure in which the color filter and the black matrix are formed on the pixel electrode cannot be used because the liquid crystal layer and the pixel electrode are separated.
[0219]However, in the present invention, a device is reverse to a normal device due to transfer, and thus the contact region between the pixel electrode and the liquid crystal layer is forme...
third embodiment
(Third embodiment)
[0224]FIG. 20 shows a section of the principal portion of a liquid crystal display device in accordance with a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0225]The liquid crystal display device shown in FIG. 20 is characterized in that a terminal (external connection terminal) 1404 (made of ITO or a metal) for connecting a driver IC 4200 is formed on the active matrix substrate through the same manufacturing steps as the pixel electrodes.
[0226]Namely, in the active matrix substrate, where the external connection terminal (for example, a terminal for connecting liquid crystal driving IC) is required, this terminal must be exposed to the surface.
[0227]Therefore, in the region where the external connection terminal is provided, the underlying insulation film (intermediate layer) and the insulator layer such as interlayer insulation film are moved.
[0228]However, the surface of the external connection terminal 1404 need not be exposed only in the same step as formation o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| light transmittance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| light transmittance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com