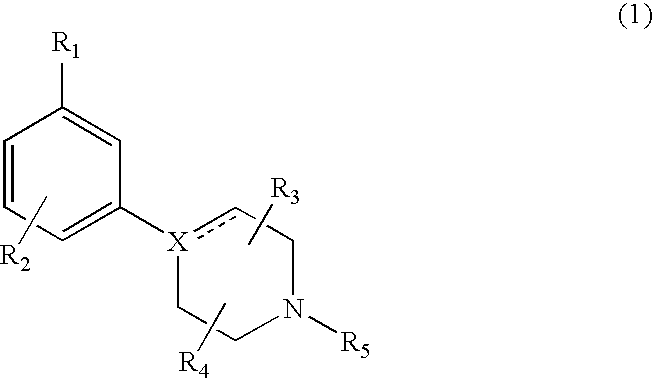
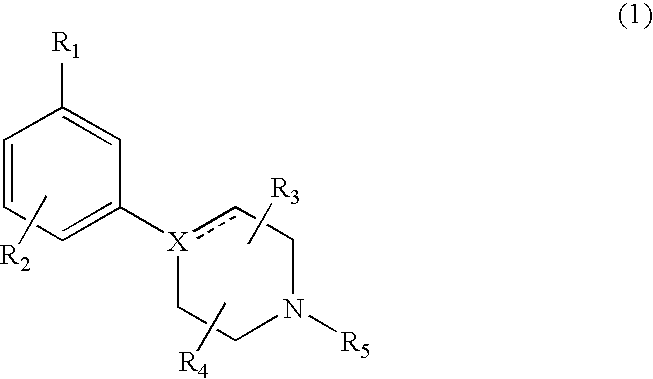
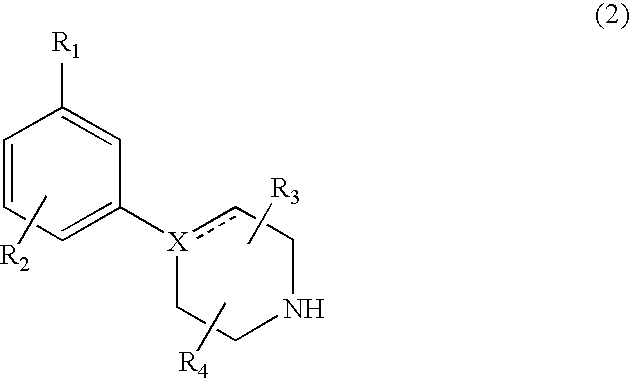
Modulators of dopamine neurotransmission
a dopamine neurotransmission and modulator technology, applied in the field of new substituted 4(phenyl nalkyl)piperazines and 4(phenyl nalkyl)piperidines, can solve problems such as inability to obtain, and achieve the effects of improving rehabilitation, improving mental and motor function, and reducing tremors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
1-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-4-propyl-piperazine
[0090]A mixture of 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzotrifluoride (0.2 g, 0.85 mmol), n-propyl piperazine (0.15 g, 1.17 mmol), sodium tert-butoxide (0.134 g) dppf (14 mg) and [Pd2(dba)3 (10 mg) in dioxane (5 ml) was heated under argon at 100° C. for 24 h. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was taken up in Et2O (40-50 ml) and washed with brine (15-20 ml). The organic fraction was dried (MgSO4), filtered and evaporated to dryness. The crude material was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel using CH2Cl2:MeOH (9:1 (v / v)). The amine was converted into the HCl-salt and recrystallized from ethanol / diethylether; m.p. 268° C. (HCl); MS m / z (rel. intensity, 70 eV)) 307 (M+, 6), 279 (33), 277 (98), 70 (bp), 56 (40). Rf=0.35 (EtOAc)
example 2
1-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-4-propyl-piperazine
[0091]A suspension of 1-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-piperazine (100 mg) and ground K2CO3 (200 mg) was stirred in CH3CN (30 mL) at room temperature. A solution of 1-bromo-propyl (52 mg) in CH3CN (5 mL) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at 50° C. overnight. The reaction mixture was filtered and the volatiles were evaporated in vacuum. The oily residue was chromatographed on a silica column with MeOH: CH2Cl2 (1:9 (v / v)) as eluent. Collection of the fractions containing pure product and evaporation of the solvent afforded the title compound (85 mg). MS m / z (relative intensity, 70 eV) 306 (M+, 25), 277 (bp), 234 (23), 206 (23), 179 (23).
example 3
1-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-4-ethyl-piperazine
[0092]Beginning with 1-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-piperazine and iodoethane, the title compound was recovered by the procedure described in Example 2. MS m / z (rel. intensity, 70 eV)) 292 (M+, bp), 277 (88), 234 (33), 206 (55), 179 (49).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| DA autoreceptor agonist properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| DA autoreceptor agonist properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com