Bus transaction reordering in a computer system having unordered slaves
a computer system and slave technology, applied in the field of computer architecture, can solve the problems of inability to advance, data tenures to occur out of order with respect to address tenures, system is most prone to deadlocks and livelocks, etc., to achieve greater bus utilization, simplify implementation, and increase bus utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
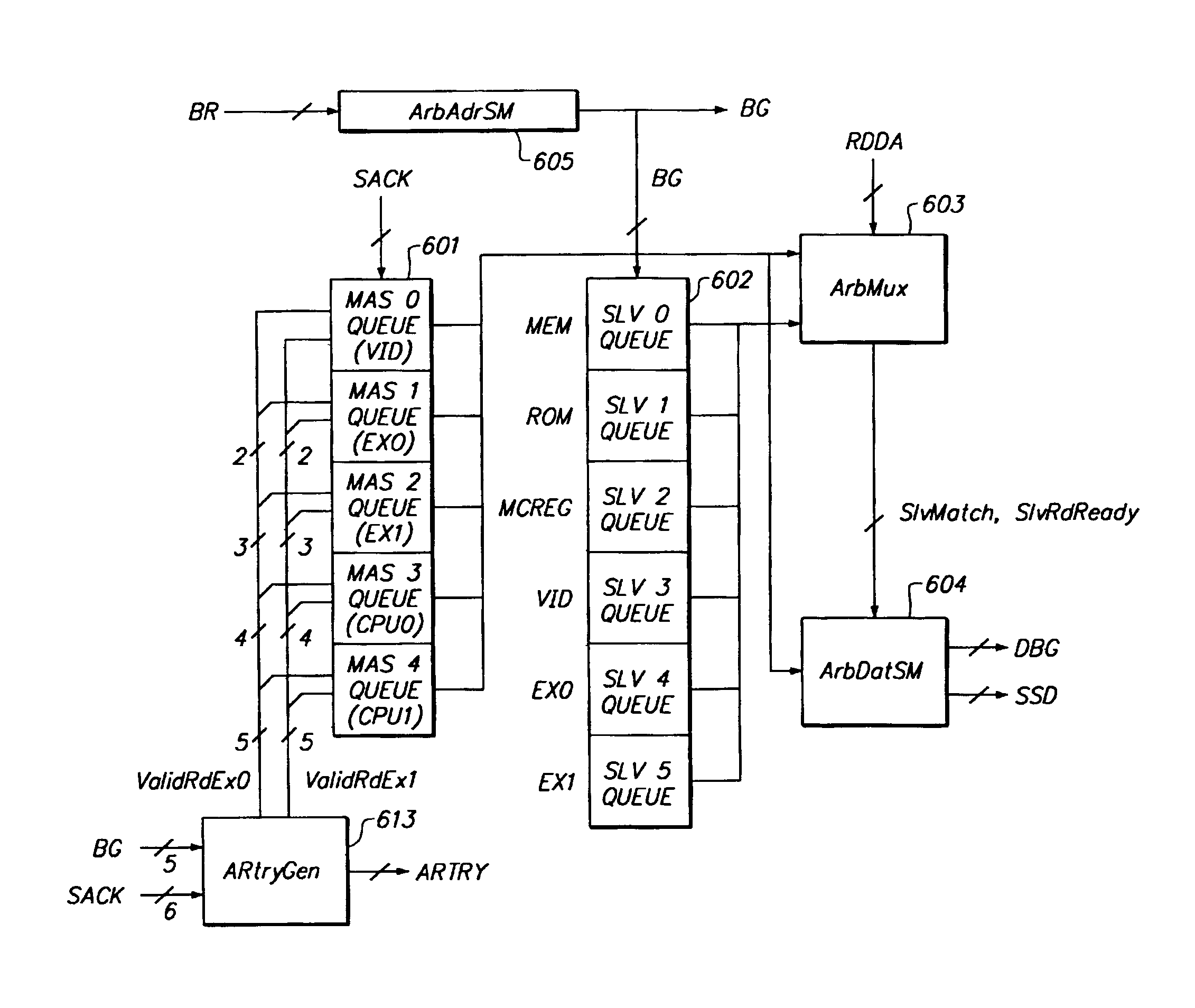
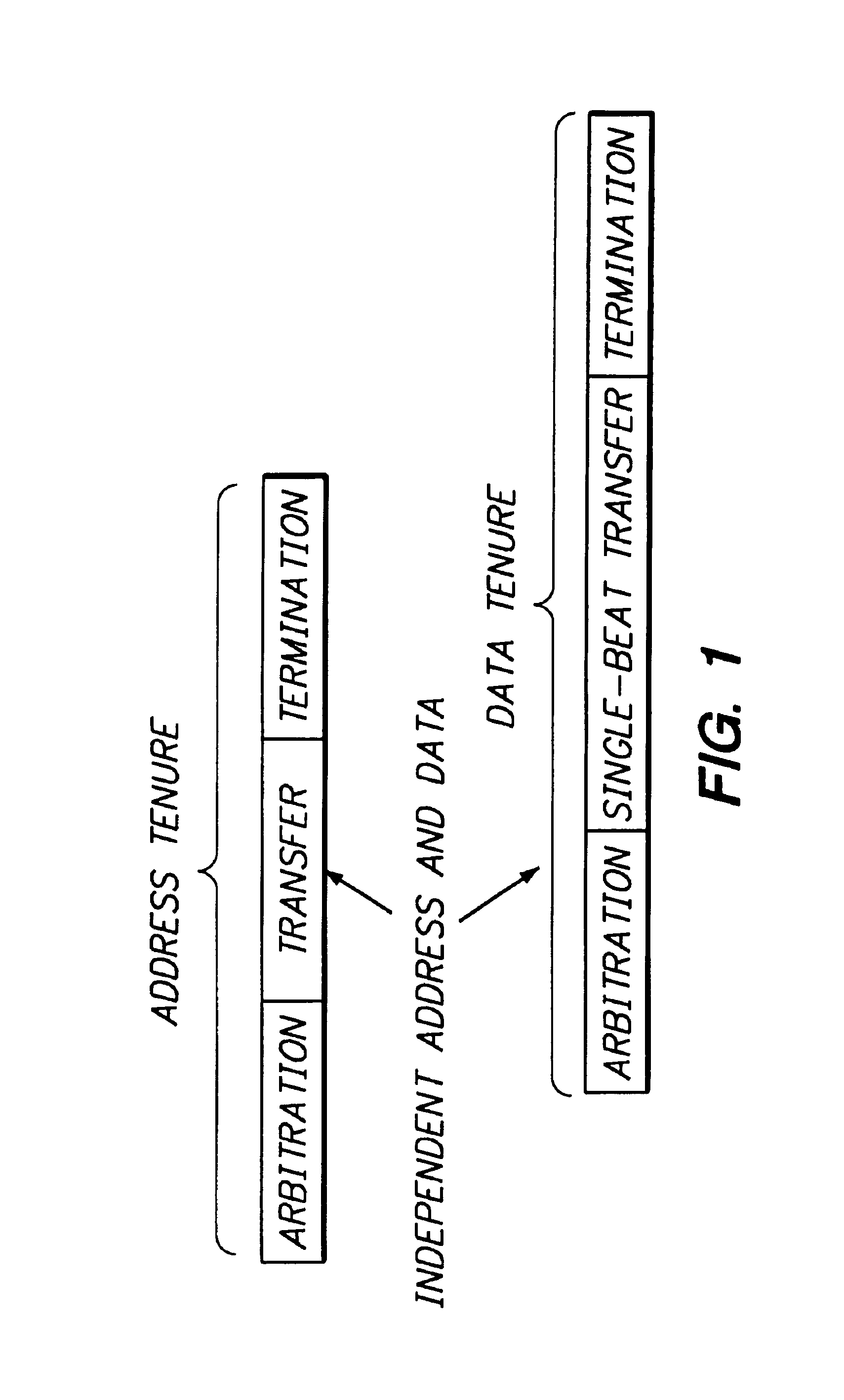
[0046]In the following description, the system architecture of a computer system in which the present invention may be used will first be described, including a description of the MPC601 bus, the ARBus, which is a superset of the MPC601 bus, a system arbiter and an expansion bridge. Deadlock avoidance will then be described, beginning with a description of the types of deadlocks and livelocks that may occur in the system, followed by a description of specific deadlock and livelock situations for both a system having a single expansion bridge and a system having two or more expansion bridges. Rules will be identified for avoiding deadlock. These rules will then be summarized, both for the case of a single expansion bridge and for the case of two or more expansion bridges. Finally, the manner in which the rules are implemented in the system will be described.
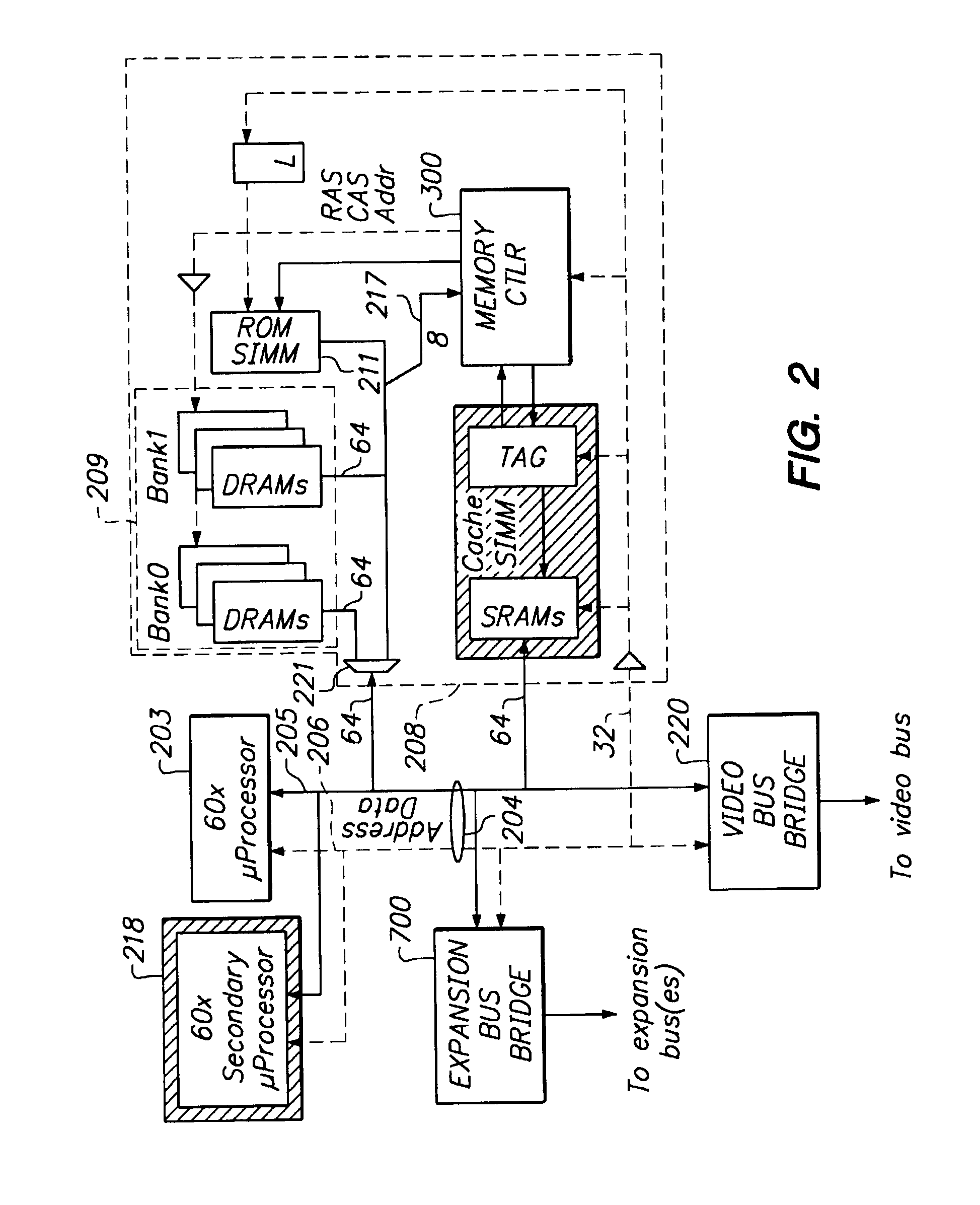
[0047]Referring now to FIG. 2, the present invention may be used in a computer system of the type shown. A CPU 203 (for example ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com