Stable semiconductor storage device with pseudo storage unit
A technology of pseudo memory cells and storage devices, which is applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, information storage, etc., and can solve the problems of prolonging the design and development cycle, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
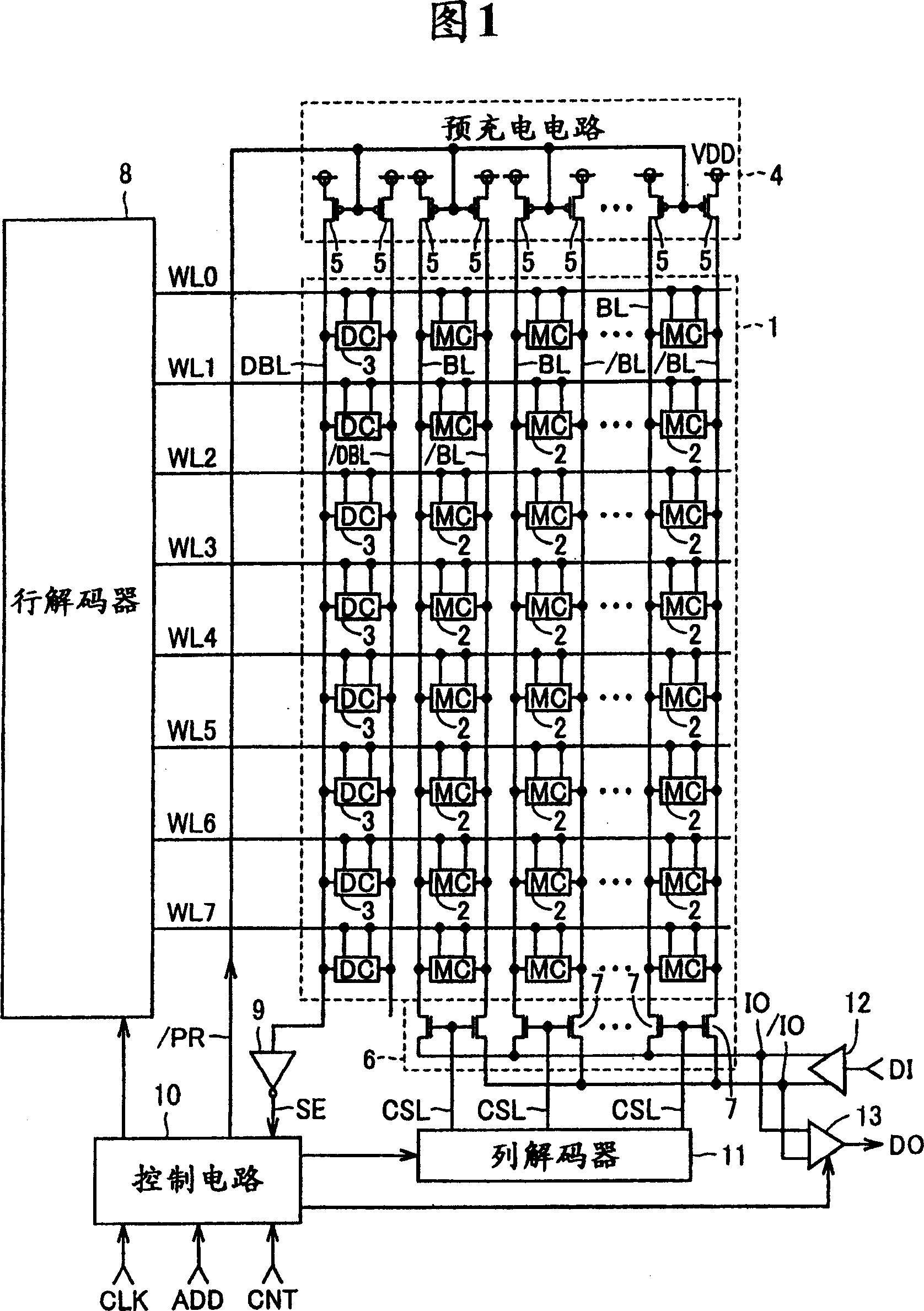
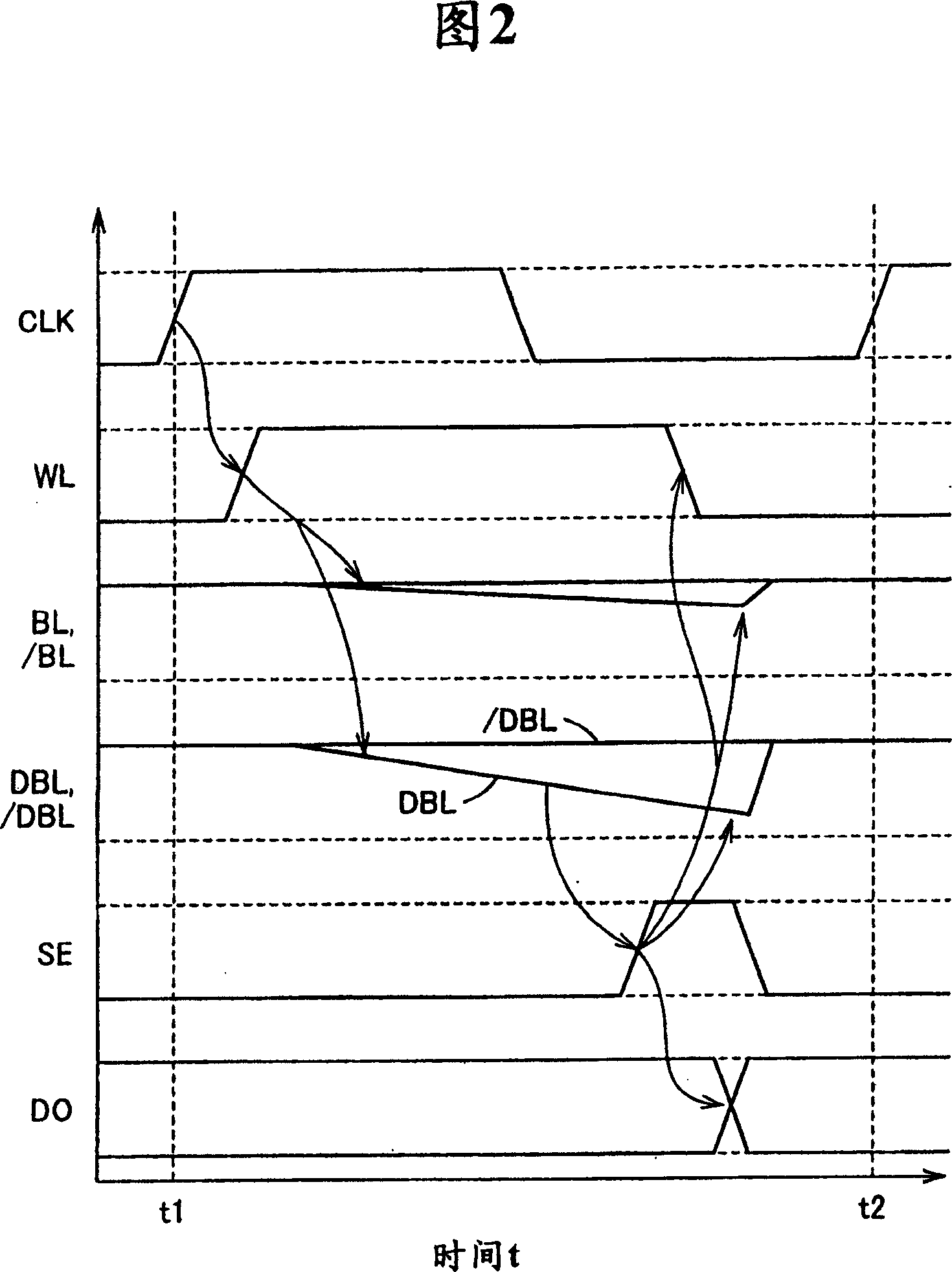
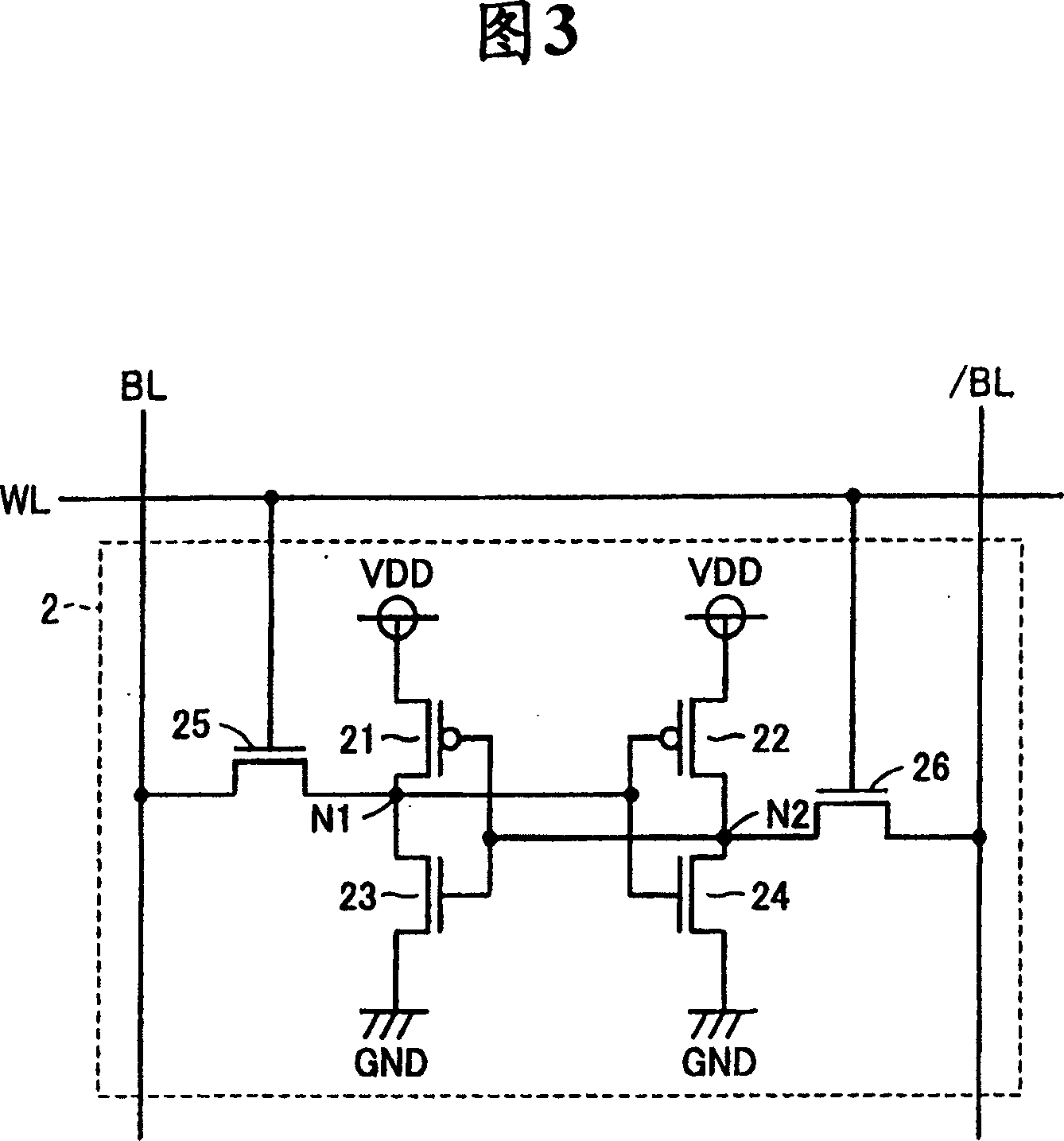
[0034] FIG. 1 is a circuit block diagram showing the overall configuration of an SRAM according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In FIG. 1 , the SRAM includes a memory cell array 1 , a precharge circuit 4 and a column selection gate 6 . The memory cell array 1 includes: a plurality of memory cells (MC) 2 configured in multiple rows (8 rows in the figure) and multiple columns, 8 word lines WL0-WL7 respectively arranged corresponding to the 8 rows, and 8 word lines WL0-WL7 respectively arranged corresponding to the multiple columns A plurality of bit line pairs BL, / BL. Each memory cell 2 is connected to a corresponding word line WL and a corresponding pair of bit lines BL, / BL, and stores one data signal.
[0035] In addition, memory cell array 1 includes 8 dummy memory cells (DC) 3 arranged in 8 rows and 1 column, and dummy bit line pairs DBL, / DBL. The dummy memory cell (DC) 3 is connected to the corresponding word line WL and the dummy bit line pair DBL, / DBL, and...
Embodiment 2
[0084] FIG. 23 is a circuit block diagram showing the overall structure of an SRAM according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, for comparison with FIG. 1 . Referring to FIG. 23 , the difference between this SRAM and the SRAM in FIG. 1 is that a redundant memory cell array 41 is added, and the row decoder 8 is replaced with a row decoder 42 .
[0085] The redundant memory cell array 41 includes at least one row (one row in the figure) of dummy memory cells 3 , a plurality of memory cells 2 and spare word lines SWL. The row decoder 42 is provided with a programming circuit for programming a row address signal of a bad memory cell row. For example, when at least one memory cell 2 in the first row is defective, the row address signal of the memory cell row in the first row is programmed. When the row address signal of the memory cell row of the first row is input, the row decoder 42 raises the spare word line SWL to the "H" level of the selection level instead of the word...
Embodiment 3
[0088] FIG. 24 is a circuit block diagram showing the overall configuration of an SRAM according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, for comparison with FIG. 1 . Referring to FIG. 24, the difference between the SRAM and the SRAM in FIG. 1 is that the memory cell array 1 and the pre-charging circuit 4 are replaced by the memory cell array 45 and the pre-charging circuit 46, respectively, and gate circuits 51-53 and "OR" gates are added. 54.
[0089] In the memory cell array 45 , two dummy memory cell columns are added to the end of the memory cell array 1 . One additional dummy memory cell column includes dummy bit line pair DBL, / DBL and 8 dummy memory cells 33 , and another added dummy memory cell column includes dummy bit line pair DBL, / DBL and 8 dummy memory cells 35 .
[0090] The precharge circuit 46 is to add 4 P channel MOS transistors 5 in the precharge circuit 4. The 4 P channel MOS transistors 5 are respectively connected to one end of the added 4 dummy bit l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com