Covering network group broadcast protocol technology
An overlay network and multicast technology, applied in the field of computer communications, to ensure stability, facilitate tracking and management, and have high latency sensitivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
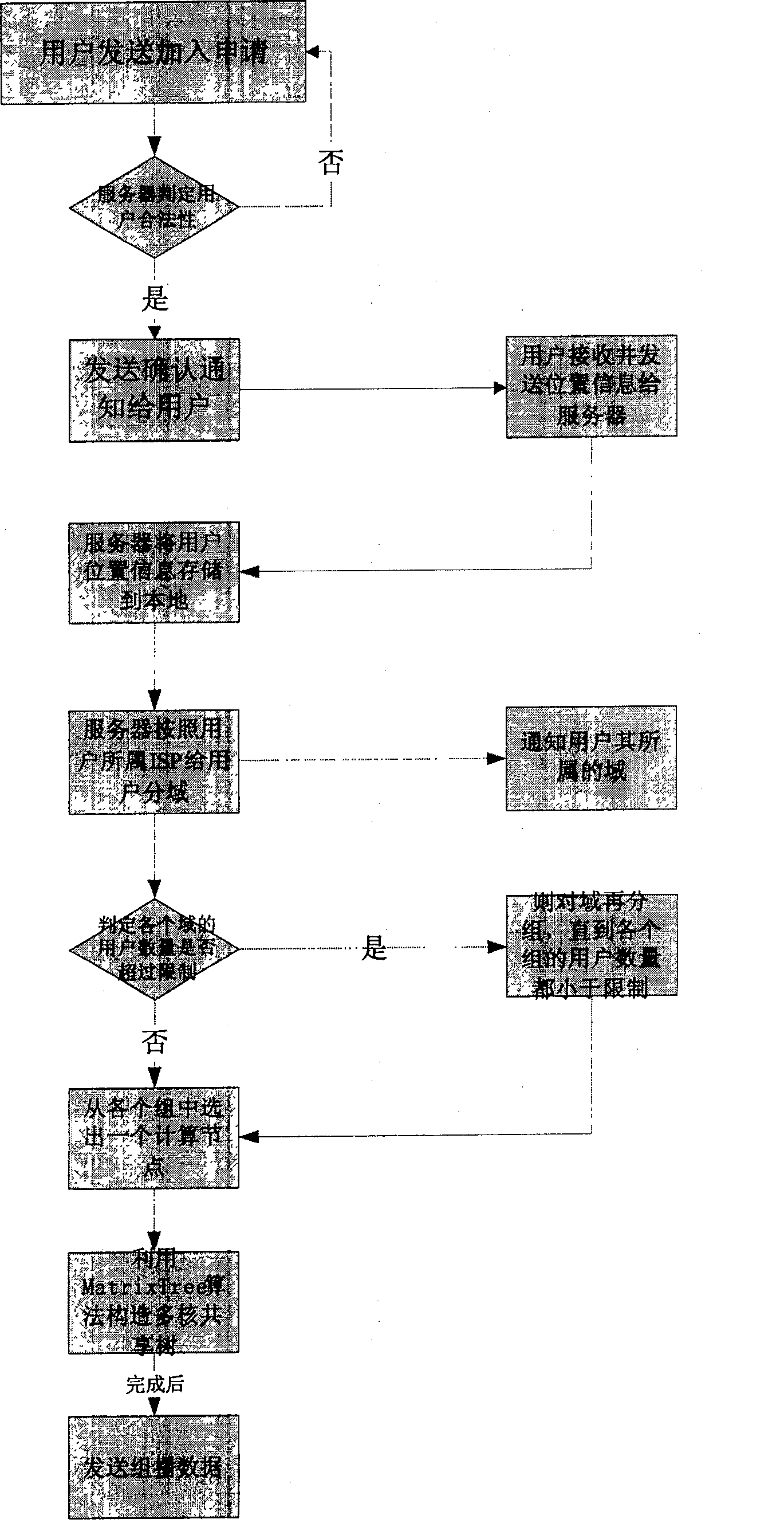
[0043] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 Shown, the specific technical steps adopted by the present invention to solve its technical problems are as follows:
[0044] Step 1. The host user who joined the multicast group sends a joining application, and the server judges the user's legitimacy; otherwise, it returns;
[0045] Step 2. Send a confirmation notification to the user, the user sends his location information to the server, and the server stores the information locally, and the location information includes: the IP address of the host, the name of the ISP to which it belongs, and some basic information of the host user;
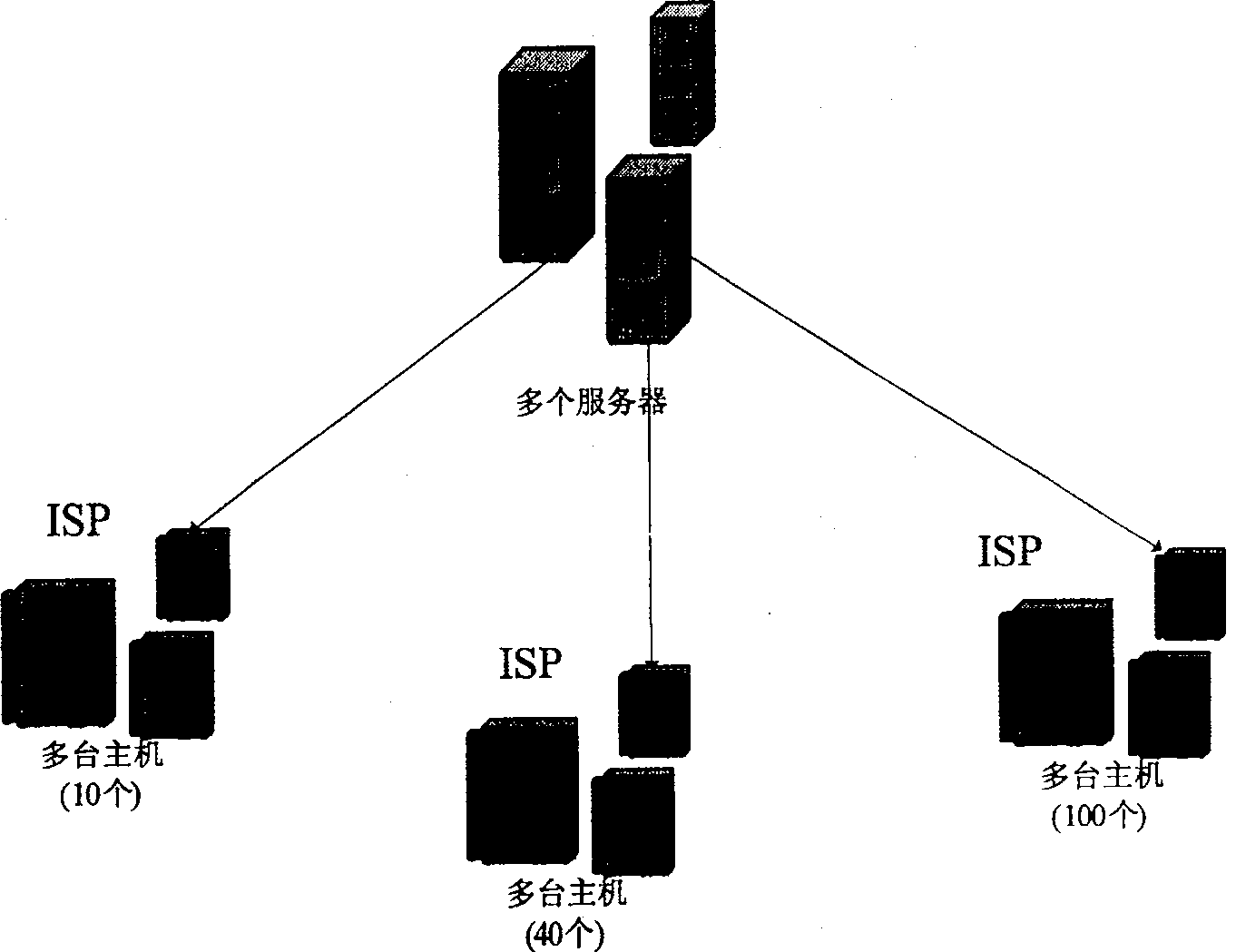
[0046] Step 3. After the joining nodes are stabilized, the server starts to group all nodes according to the ISP domain organization method. The server first divides each node into each large domain according to the different ISP of each node. All nodes in each domain belong to the same ISP management, and each domain is grouped again according to the network...
Embodiment 2
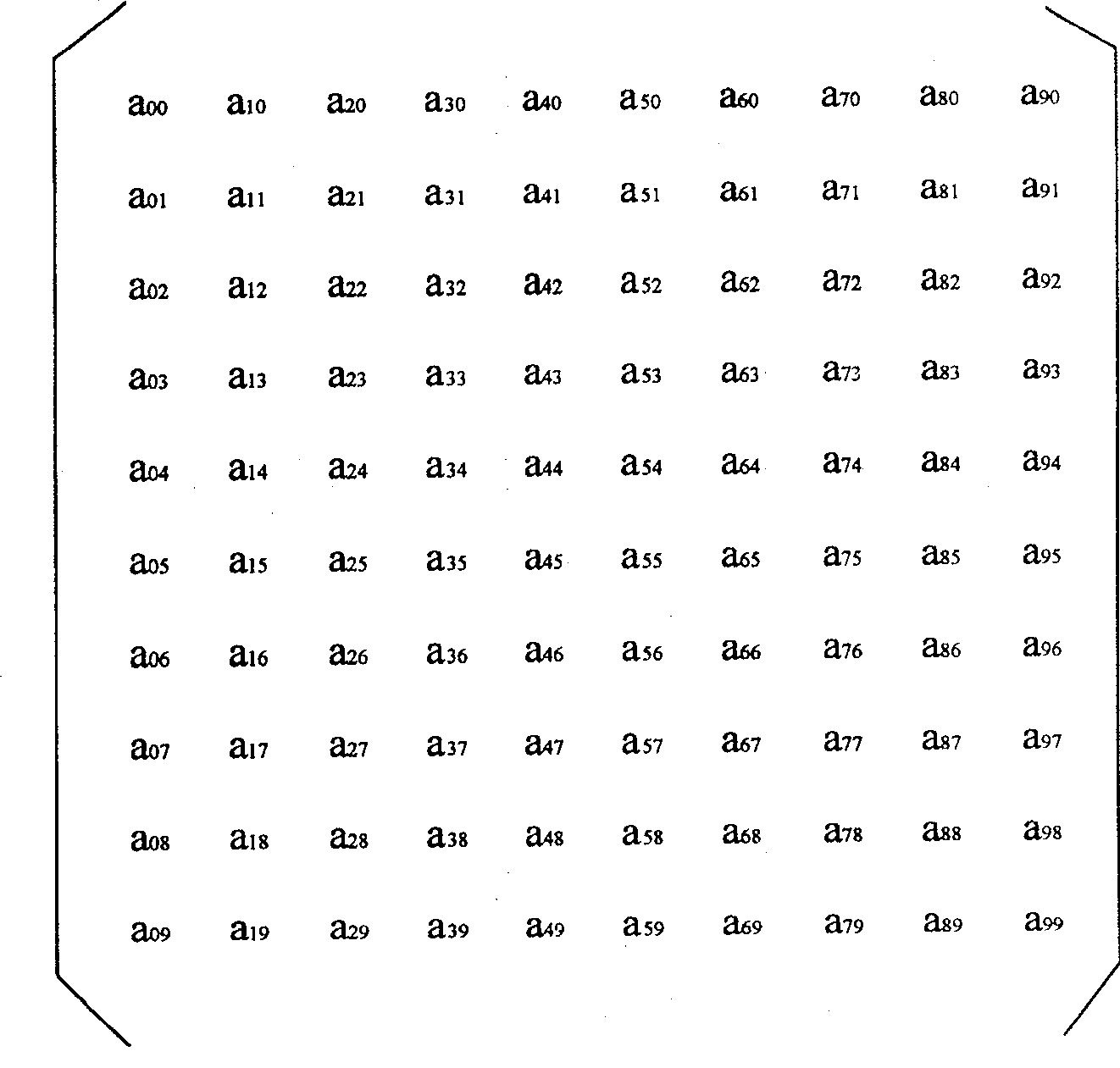
[0052] Embodiment 2: First, according to the characteristics of the current Internet network service, the present invention organizes multicast members according to ISP domains. Before the multicast group is established, all nodes that want to join the multicast group will send a join request to the data source server, and through this join request server can ask each node to add its ISP and basic network information, which is convenient for the multicast group Member classification reorganization. After a period of time, when the users joining the nodes are relatively stable, the server begins to group all members; the server first divides them into large domains according to the different ISPs of each node (such as image 3 ), all nodes in each domain are managed by the same ISP. Each domain is grouped again according to the network topology and the number of multicast members. If the number is small, all multicast members in the entire domain will be grouped together; Mul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com