Plasmid having three complete transcriptional units and immunogenic compositions for inducing an immune response to HIV
A technology of immunogenicity and composition, which is applied in the field of plasmids and immunogenic compositions to improve the immune response of preventive and therapeutic antigens, and can solve the problems of carrier instability and the possibility of increasing repetitive sequence recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0241] Example 1. Selection and modification of HIV genes
[0242]Those skilled in the art will appreciate that sequence information from many viruses and bacteria is available in the art. More specifically, the sequence information can be used to clone the genes used to express the polypeptides in the plasmids of the invention. Information on many sequences from HIV and other pathogens is available from the Los Alamos National Laboratory's HIV Sequence Database and the United States National Library of Medicine's National Biotechnology Available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894).
[0243] In one embodiment of the invention, the following HIV genes were selected for inclusion in an exemplary single DNA plasmid expressing a large portion of the HIV genome: the gag gene from the HXB2 isolate and the pol gene from the HXB2 isolate. The complete HXB2 sequence is listed in the GenBank computer database under accession...
example 2
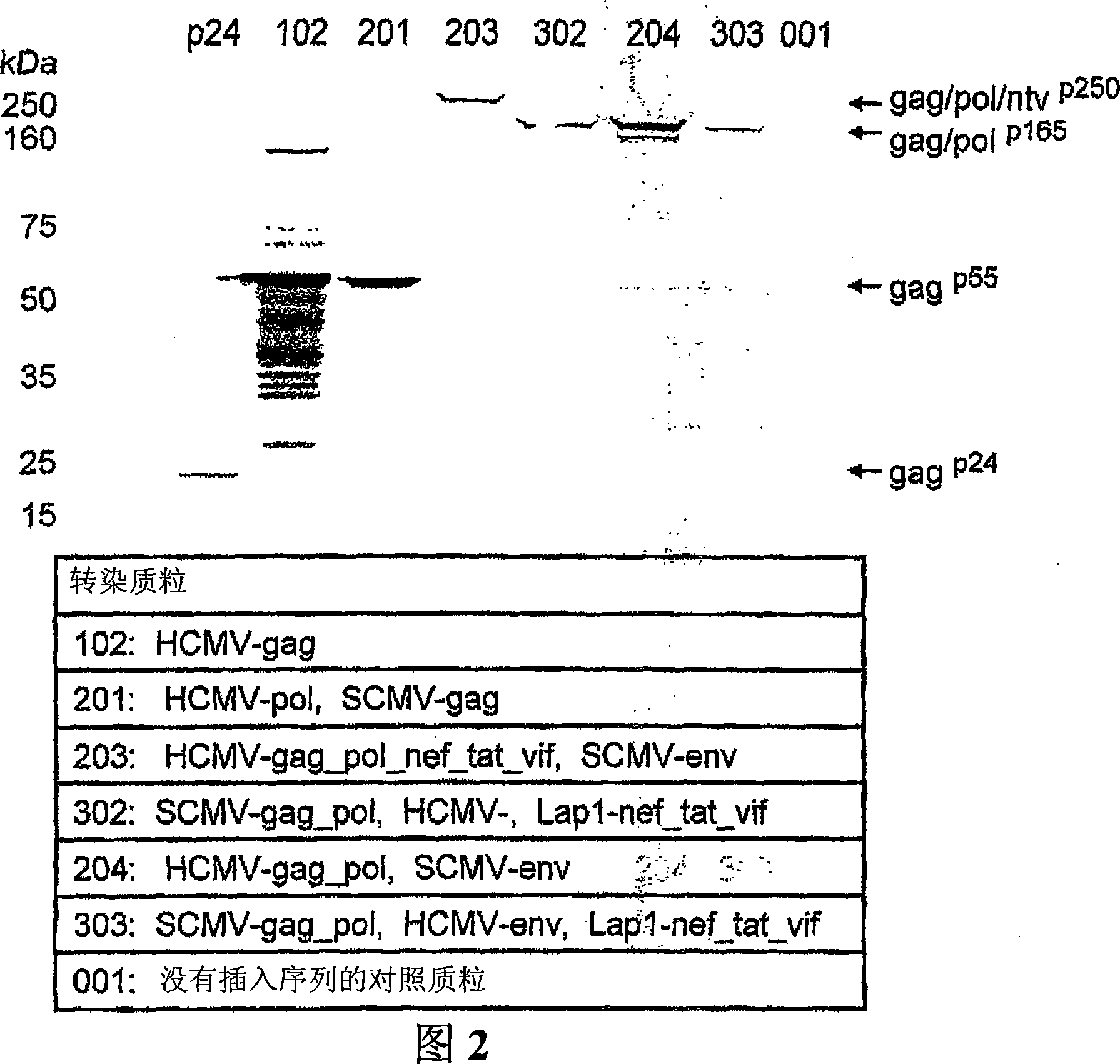
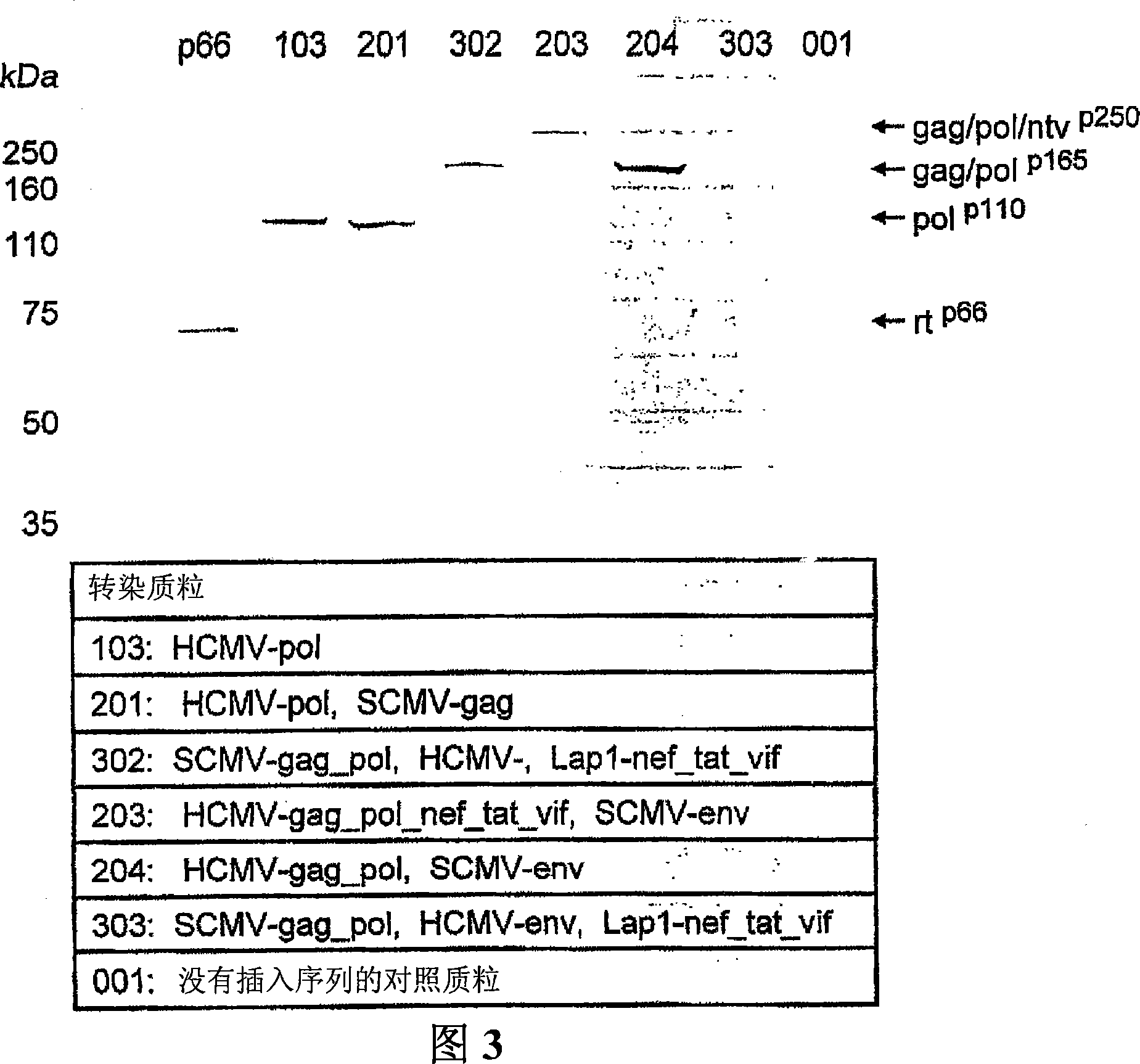
[0254] Example 2. Construction of single, double and triple transcription unit plasmids
[0255] The plasmids detailed in these examples are listed in Tables 1 and 2.
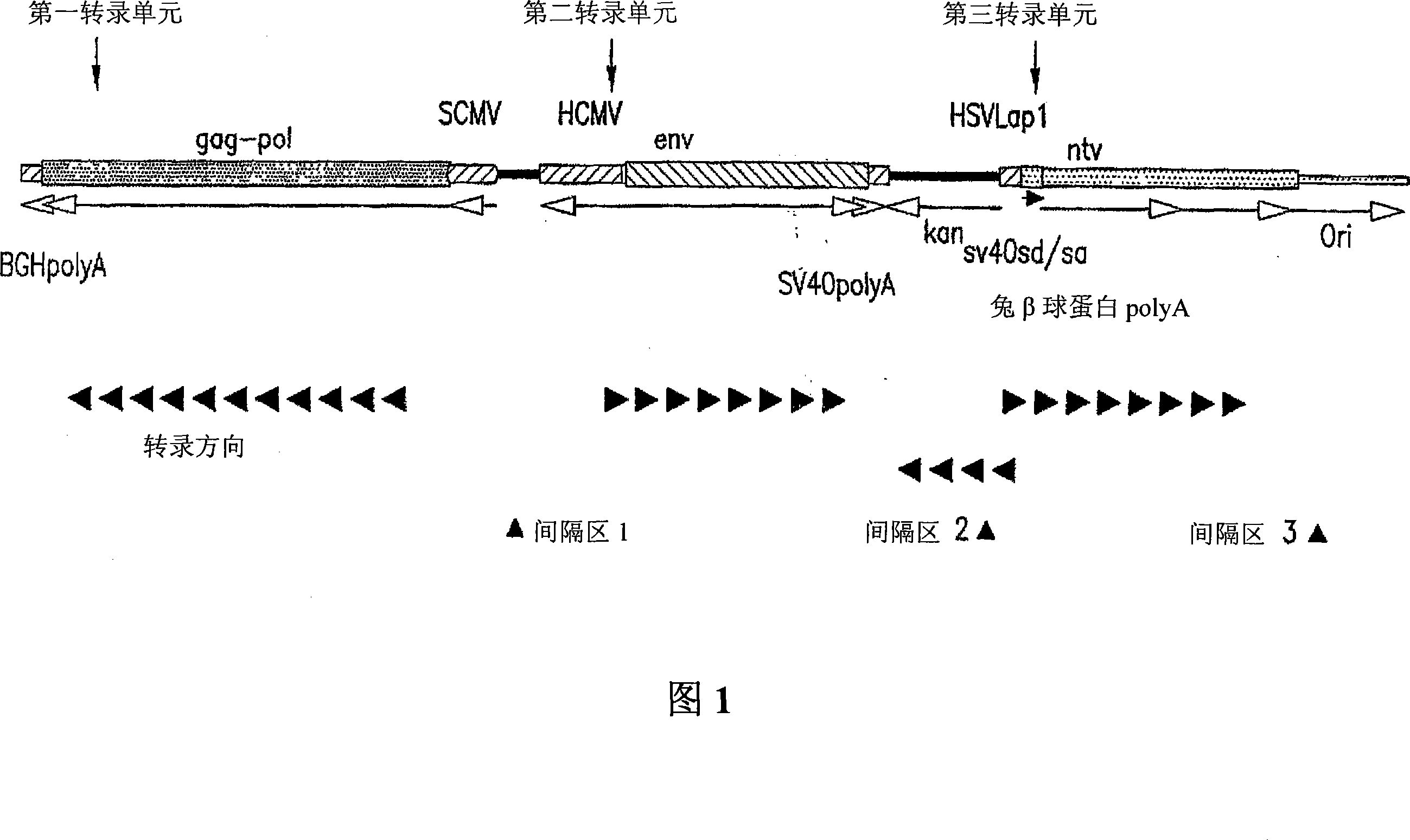
[0256] Construction of triplet transcription unit expression cassettes in circular double-stranded DNA plasmids with the aid of multiple components. See Figure 1. The first component is a first transcription unit for expression of the polypeptide in eukaryotic cells, which consists of the simian cytomegalovirus (SCMV) promoter, a cloning site and bovine growth hormone (BGH) poly-A signal. The second component is a second transcription unit for expressing polypeptides in eukaryotic cells, which consists of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) immediate early promoter, a cloning site and SV40 polyadenylation (poly A) signal . Separating the first and second transcription units is a spacer 1 . The third component is a third transcription unit for expression of polypeptides in eukaryotic cells and consists of the h...
example 3
[0257] Example 3. Triple transcription unit plasmid containing six HIV genes
[0258] As an illustration of the use of triple transcription unit plasmid DNA vectors, vectors capable of co-expression of three eukaryotic open reading frame plasmids were formed. The triple transcription unit plasmid DNA vector was formed by inserting the following selected genes encoding HIV-1 antigens into the triple transcription unit expression cassette described in Example 2. All cloning techniques were performed according to conventional techniques (Sambrook et al., 1989).
[0259] First, an HIV-1 gag-pol fusion gene is inserted into the Pmel-Xhol cloning site between the SCMV site of the first transcription unit and the BGH poly-A site. The gag gene was derived from a HXB2 isolate, and similarly, the pol gene was also derived from a HXB2 isolate. The complete HXB2 sequence is listed in the GenBank computer database under accession number K03455. Those skilled in the art will appreciate t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com