Power-fail protection method based on two continuous logical blocks for non-volatile memory
A non-volatile, power-down protection technology, applied in the protection of storage content to prevent loss, redundancy in operation for data error detection, response error generation, etc. , hidden dangers and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving reliability and safety, ensuring consistency and integrity, and improving service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
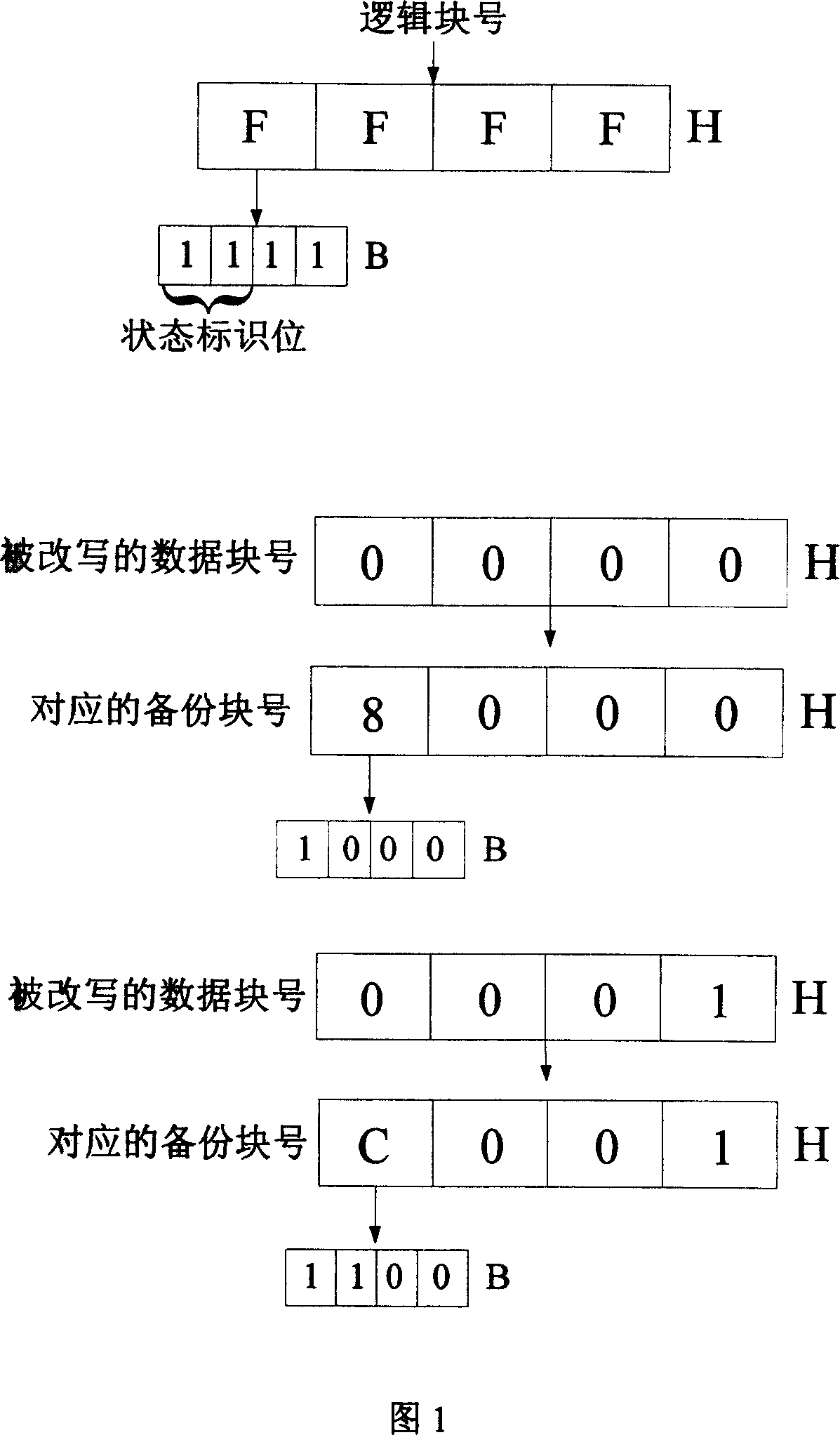
[0042] In this embodiment, two data blocks with consecutive logical addresses are taken as an example to specifically introduce the process of data protection and recovery after power failure. In this embodiment, the logical block number is represented by two bytes, that is, four hexadecimal numbers, and the user's PIN code is stored in the rewritten data block. In this embodiment, select two data blocks that have been erased in the Flash storage area as the backup block, and set the high two bits of the logical block number of the backup block as the status flag, and represent the backup block and the backup block by rewriting the status flag. Correspondence of the data blocks to be rewritten.
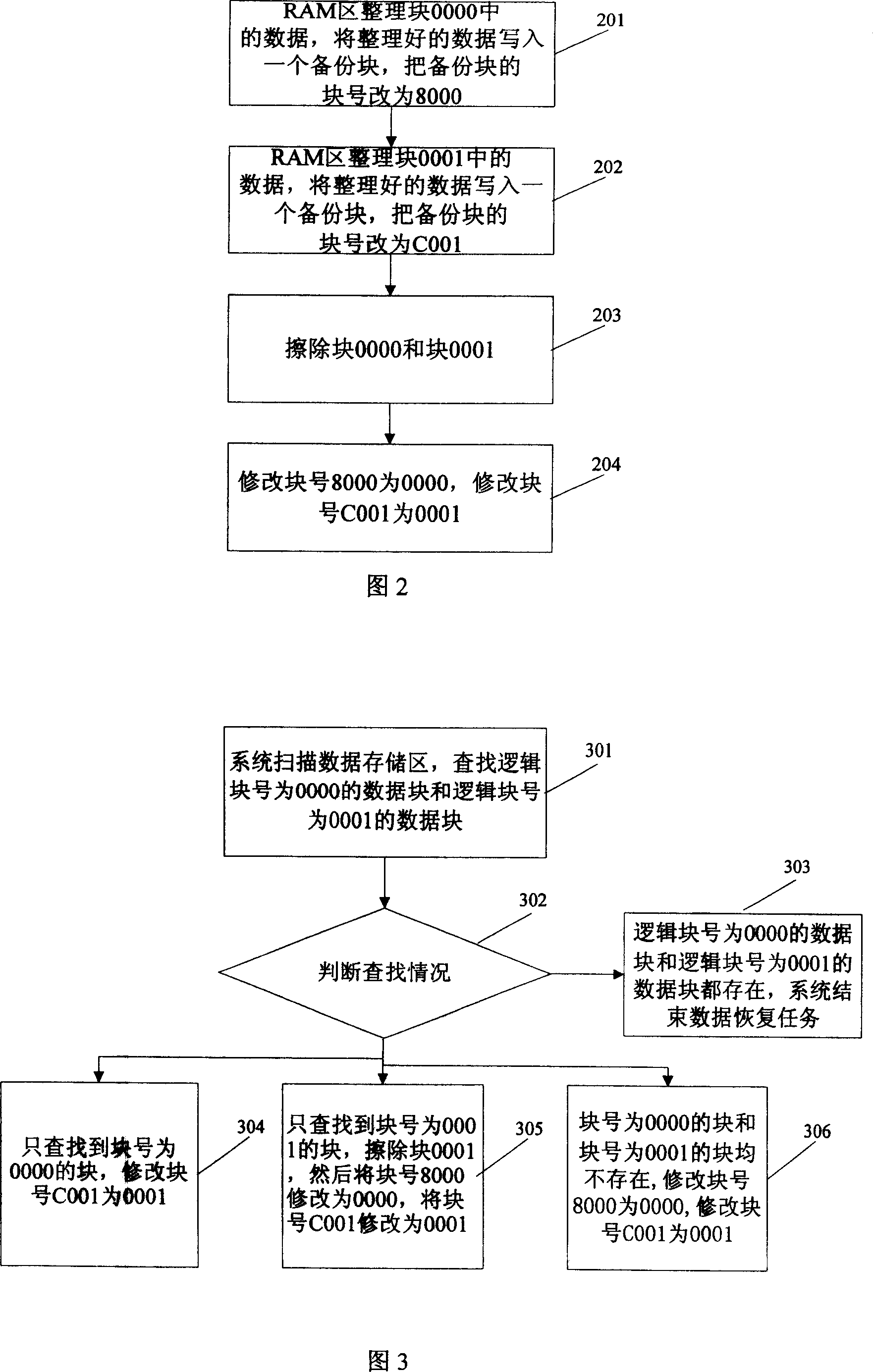
[0043] As shown in Figure 1, in the present embodiment, the block number of the data block that is rewritten is 0000 and 0001, utilizes the characteristic that Flash stores simultaneously, promptly when a Flash memory area is in clean state (was erased, But there is no write operatio...
Embodiment 2
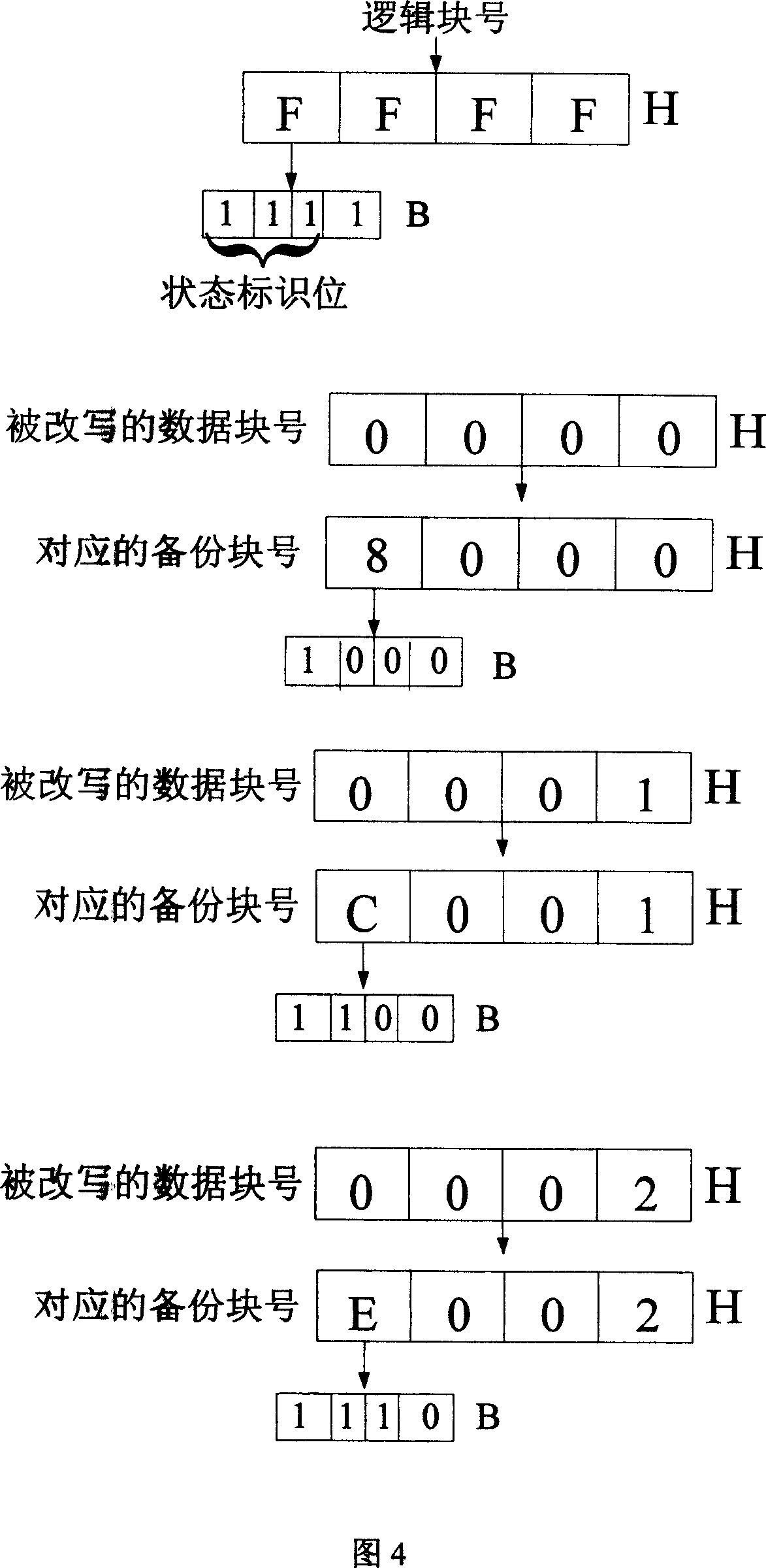
[0059] In this embodiment, three data blocks with consecutive logical addresses are taken as an example to specifically introduce the process of data protection and recovery after power failure. In this embodiment, the logical block number is represented by two bytes, and the key data of the user is stored in the rewritten data block. In this embodiment, the three data blocks that have been erased in the Flash storage area are also selected as the backup block, and the high two bits of the logical block number of the backup block are set as the status flag, and the backup block is represented by rewriting the status flag The corresponding relationship with the rewritten data block.
[0060] As shown in Figure 4, in this embodiment, the block numbers of the rewritten data blocks are 0000, 0001, 0002, the storage block with the logical block number FFFF is used as the backup block, and the upper three bits of the logical block number are set to Status flag. When the upper thre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com