Sequential protein isolation and purirication schemes by affinity chromatography
A protein separation, protein technology, applied in the field of protein separation, can solve the problems of lack of specificity and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
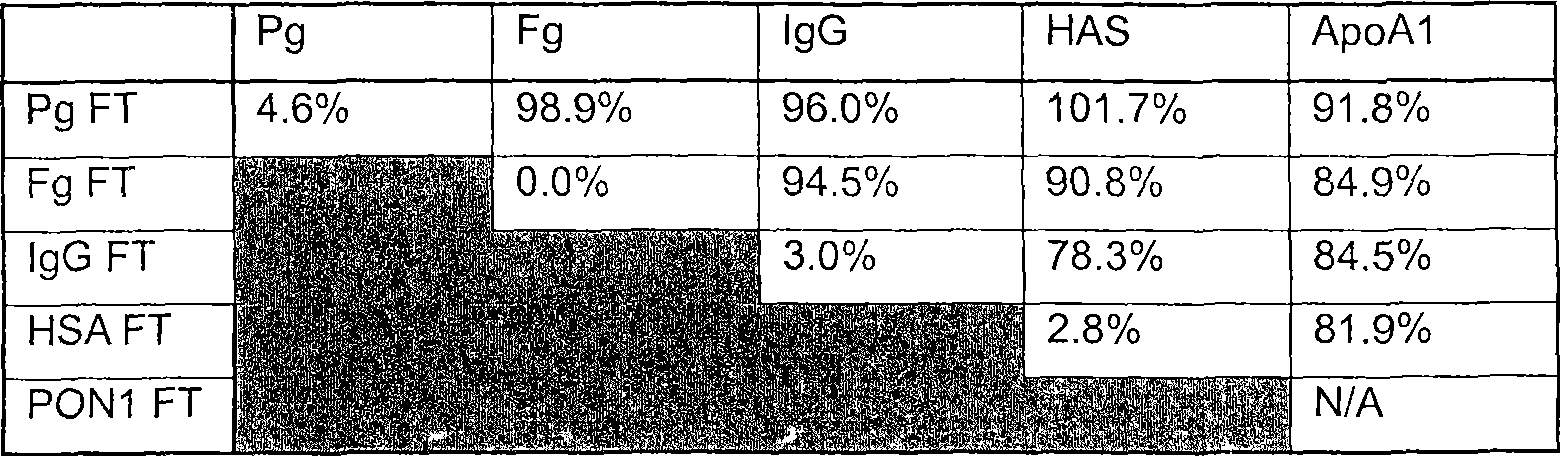
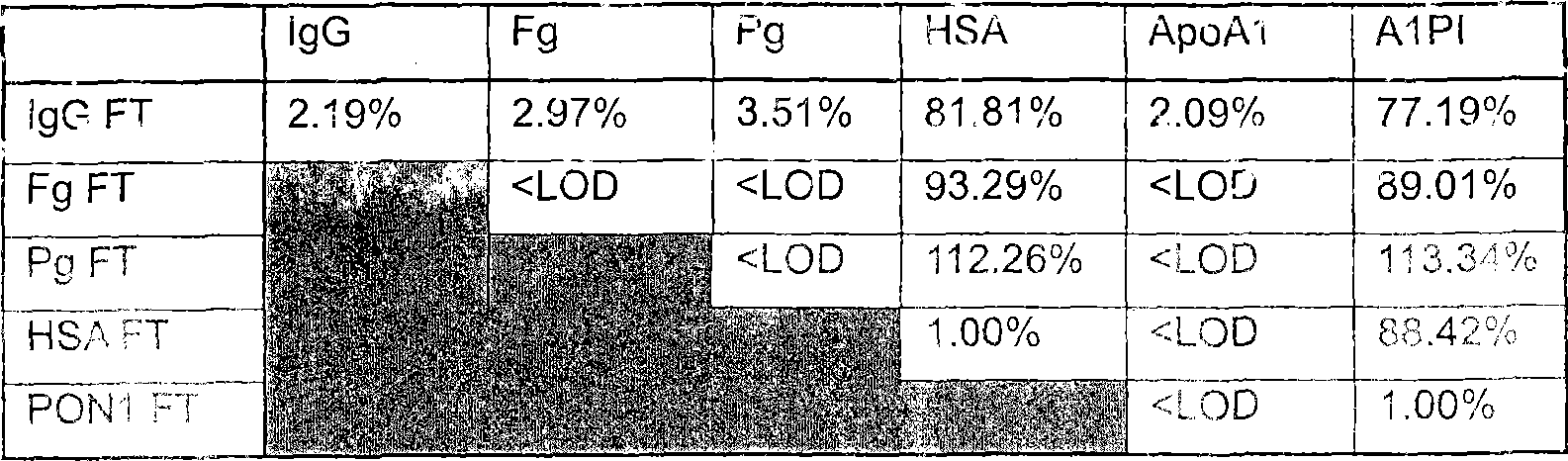
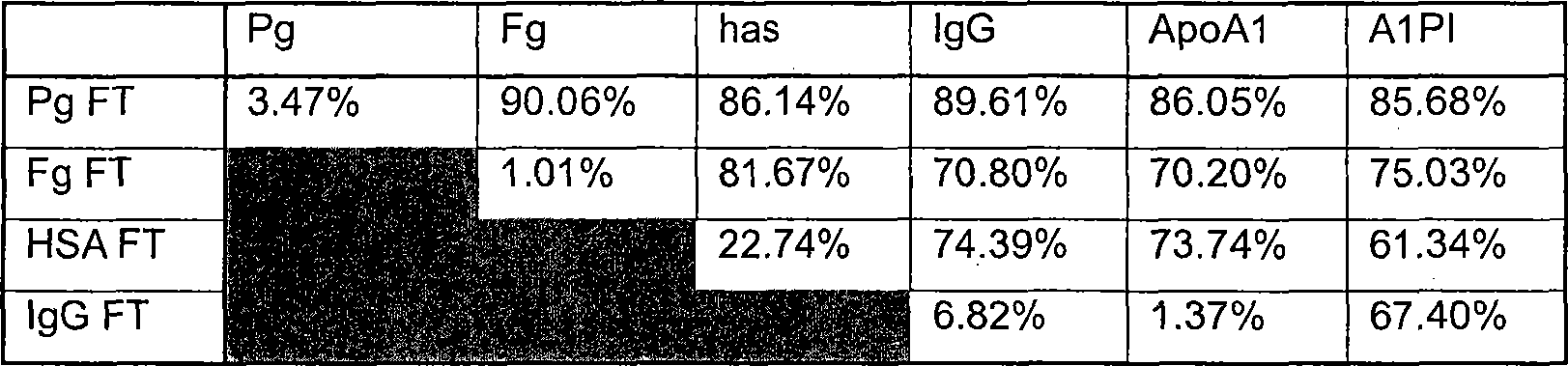
[0085] Embodiment 1: Definition of Straight-line Cascade Sequence Schemes 1-7
[0086] The linear cascade is composed of five affinity columns: albumin (HSA), fibrinogen (Fg), IgG, plasminogen (Pg) and PON1 / ApoA1. First, the columns were run sequentially in four different sequences to determine the sequence most suitable for linear cascading. To simplify ongoing sample analysis, only the undiluted flow-through was collected as the load for the next column in the sequence. Specifically, this helps keep the concentration of background proteins constant throughout the experiment. It also simplifies the comparison of output to input at each column. Samples of the load and each flow-through were analyzed to monitor the recovery of target and non-target proteins in the flow-through. Each column was tested using these values to determine its ability to capture the target protein with minimal downstream target protein hold-up. Use the sequence that best fits this criterion as th...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2: Affinity capture of plasma proteins
[0133] The following column order was used in this experiment:
[0134] vWF / FVIII→plasminogen→fibrinogen→IgG→UF / DF→HSA→UF / DF.
[0135] Plasma preparations: Four liters of frozen pooled plasma were obtained from -20°C storage.
[0136] Plasma pools were thawed at 37.0°C ± 2°C in a water bath. Once the plasma is thawed, quickly remove it from the water bath. Plasma was adjusted to 20 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl using a 50x dilution of 1 M Tris, pH 7.5 and a 40x dilution of 2M NaCl. Plasma was mixed well and filtered using SartoPure 300 PP2 (8 micron) sterile filters.
[0137] a. Von Willebrand Factor / Factor VIII (vWF / FVIII) Affinity Capture
[0138] A 7 cm x 10.6 cm packed bed column was prepared containing 410 mL of the affinity sorbent developed for the capture of vWF / FVIII affinity capture. The column is usually stored in a storage solution containing 0.1N NaOH when not in use for long periods of time. Was...
Embodiment 3
[0164] Example 3: Evaluation and Selection of Plasma Buffer Systems Used in the Linear Cascade Method
[0165] This experiment was performed to determine the most suitable buffer system for a linear cascade continuous plasma protein purification protocol. It was observed that the pH climbed up to two units above the plasma pH (pH ~ 7.5) during IgG column loading. Several pH changes were observed during IgG loading, which appeared to depend on the degree of protein depletion of the load. This means that certain plasma proteins have a buffering capacity and removal of these proteins from the loading solution may increase the probability of pH shifts. Buffer systems for plasma must maintain protein concentration and activity in plasma. The buffer system must maintain the pH within an acceptable range of approximately 7.5 ± 0.4 throughout the process.
[0166] To ensure that no pH changes occur during subsequent manipulations, plasma loads for subsequent manipulations must be b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com