Intelligent identification method of metallurgical mine phase
A technology for intelligent identification and ore phase, applied in the field of metallurgy, which can solve the problems of indistinguishable size and distribution of pores in sintered ore, difference in identification results, and high labor intensity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
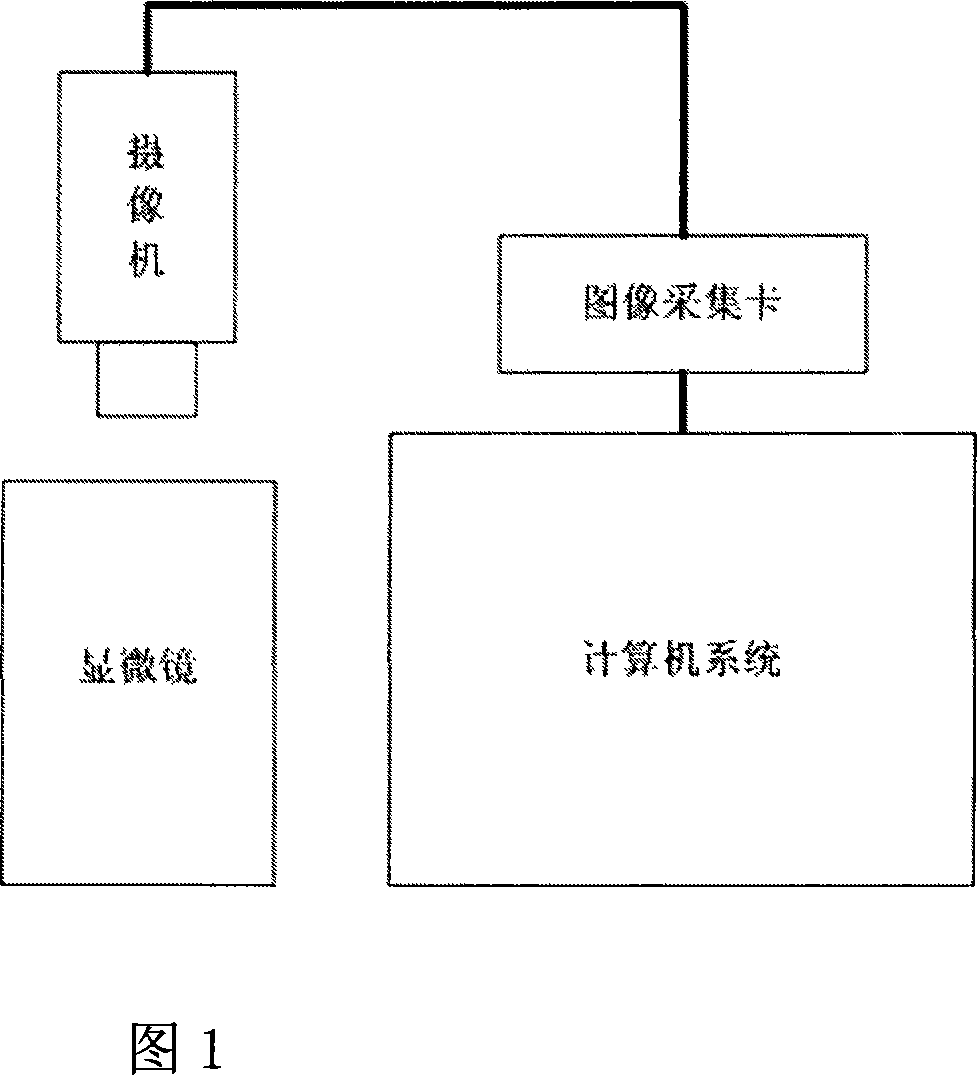
Image
Examples
Embodiment
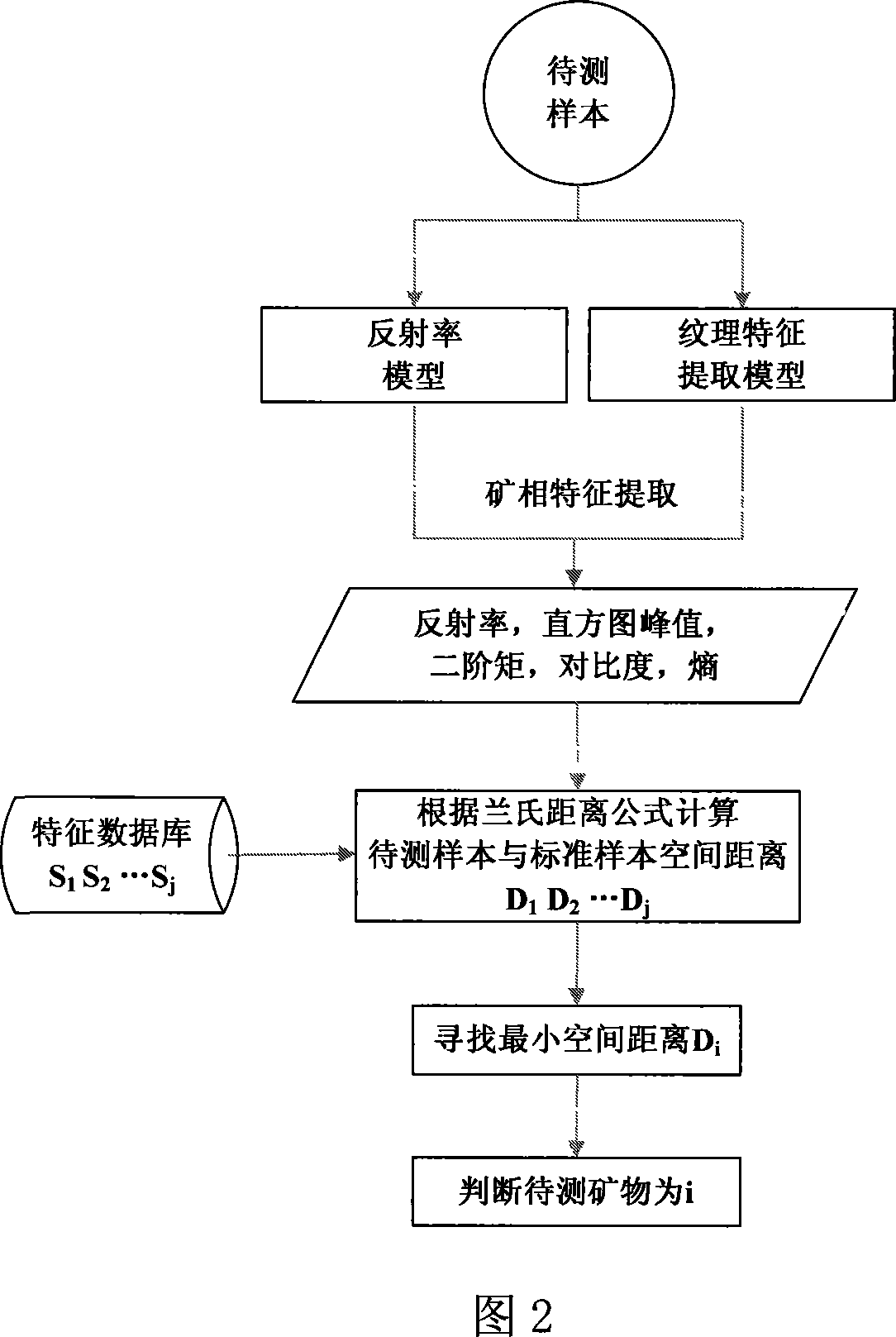
[0115] 1. Establish standard mineral phase database
[0116] mineral
name
the peak
Interval 1
the peak
Interval 2
the peak
Interval 3
second moment
contrast
entropy
calcium ferrite
22~25
20
18~18.5
41~51
7~8
45~49
98~102
74~83
77~85
136~138
127~128
113~116
0.0884
0.0465
0.1781
4.8475
3.5724
6.0078
5.1680
4.3092
3.3286
[0117] 2. Extract the characteristics of the ore sample to be tested (as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4)
[0118] mineral
name
the peak
Interval 1
the peak
Interval 2
the peak
Interval 3
second moment
contrast
entropy
to be tested
mineral
20.7
7~8
43~44
1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com