Message forwarding method and device
A message forwarding and message sending technology, which is applied in the field of network communication, can solve the problems of failing to meet the low-latency requirements of LLQ messages, increasing the forwarding delay, and increasing the implementation complexity of the queuing system, so as to reduce the implementation complexity, Avoid delay and avoid coupling effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Referring to shown in Figure 4, the LLQ message forwarding process in the primary queuing system mainly includes the following steps:
[0067] Step 401: After receiving the LLQ message, first judge whether the LLQ queue is empty, that is, judge whether the number of messages in the LLQ queue is 0, if the LLQ queue is empty, then perform step 402; otherwise, perform step 405.
[0068] Step 402: Determine whether the LLQ message meets the enqueue condition, if so, execute step 403; if not, directly discard the LLQ message, and end the processing of this flow.
[0069] Step 403: Judging whether the LLQ message meets the dequeuing condition, if so, go to step 404; otherwise, go to step 405.
[0070] Step 404: Send the LLQ message directly, and then end the processing of this flow.
[0071] If the transmission fails, the LLQ message is pushed back into the LLQ queue for buffering.
[0072] Step 405: Put the LLQ message into the LLQ queue for queuing.
[0073] The processi...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Before introducing the LLQ packet forwarding process in this embodiment in detail, the two-level queuing system used in this embodiment will be described below.
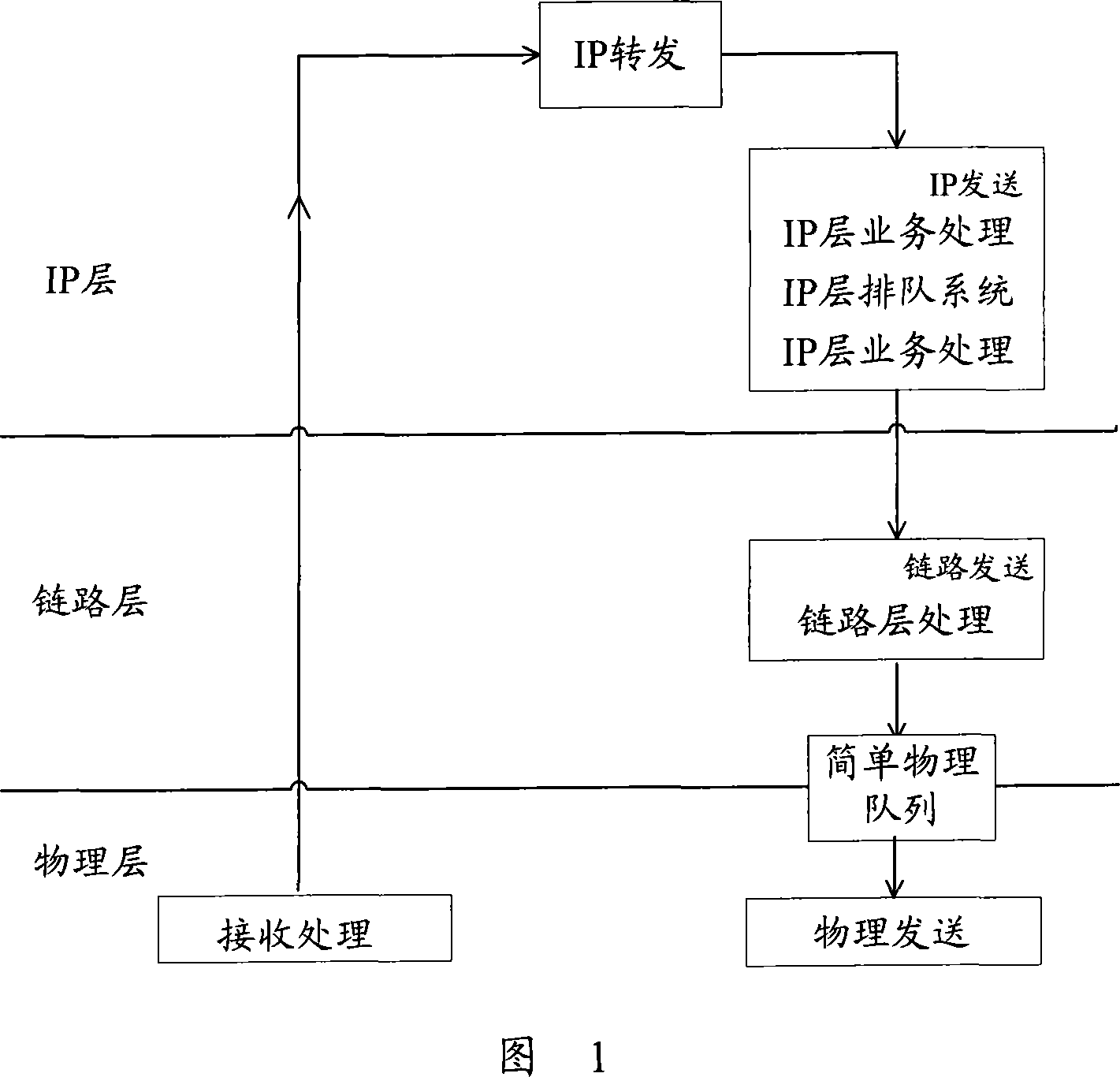
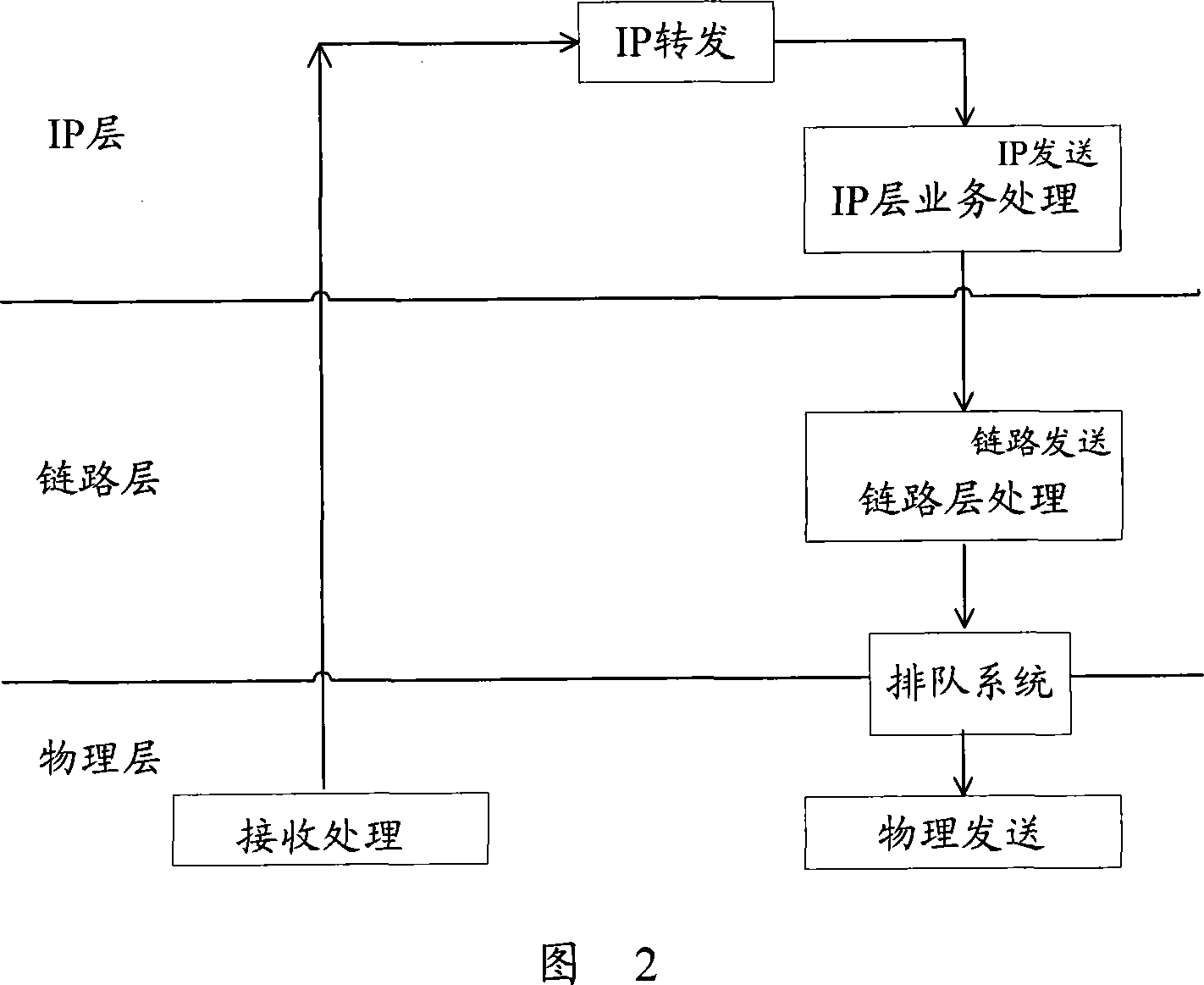
[0077] FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a two-stage queuing system in this embodiment. Wherein, the IP layer queuing system is a general queuing system, which is consistent with the IP layer queuing system in FIG. 1 , including a high-priority LLQ queue and multiple low-priority DQ queues.
[0078] The physical layer queue in Figure 5 is an extension of the physical layer queue in Figure 1, which uses two queues, LLQ and DQ, to replace the original message cache. Among them, the LLQ queue is used to cache the packets with the LLQ flag; the DQ queue is used to cache the packets with the DQ flag. Priority scheduling is performed between the two queues, that is, as long as there are messages in LLQ, the messages in LLQ are sent first; only when LLQ is empty, messages in DQ are sent. In this way, priority transm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com