Method for laser butt-welding copper or aluminum and carbon steel
A welding method and technology of carbon steel, applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, etc., can solve problems such as non-fusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
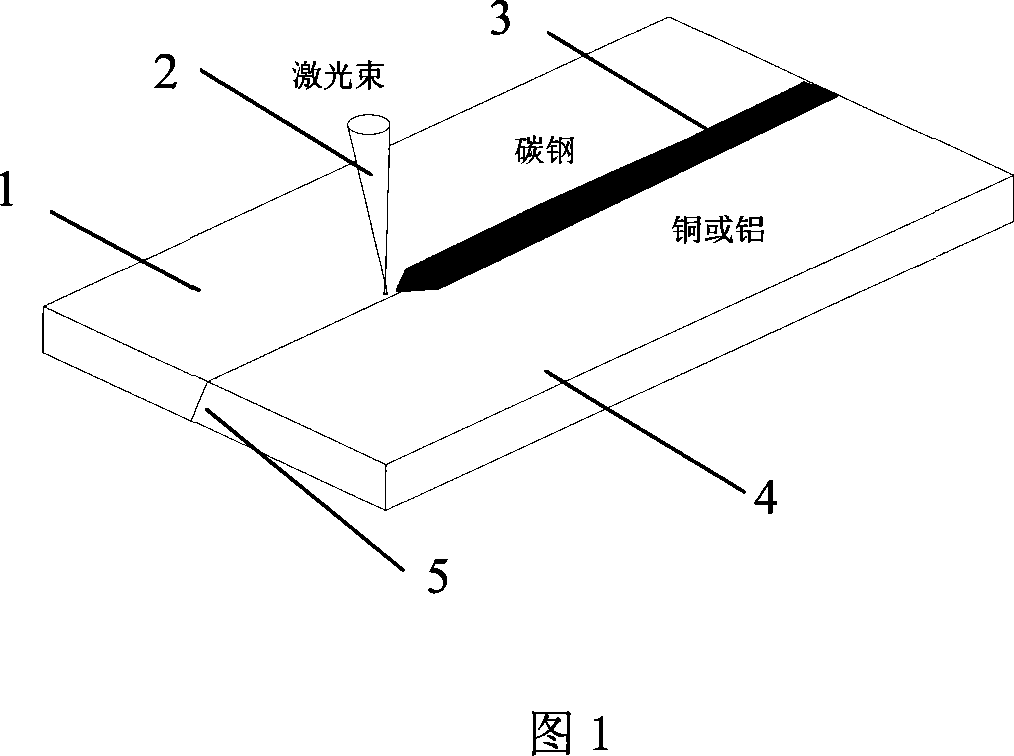
[0021] The dissimilar metal connection method of copper and carbon steel of the present embodiment: as shown in Figure 1, the butt joint form 5 of the inclined end face is adopted, so that the energy of the laser beam 2 can be absorbed by the carbon steel part 1 of low reflectivity at first and make the carbon The steel melts first; when a small hole is formed, the laser contacts with copper or aluminum, and the small hole has a wall focusing effect on the laser in it, and the absorbed energy is transferred to the side of the copper or aluminum plate through the small hole effect, so that the copper plate is melted, Thus a complete dissimilar metal weld 3 is formed.
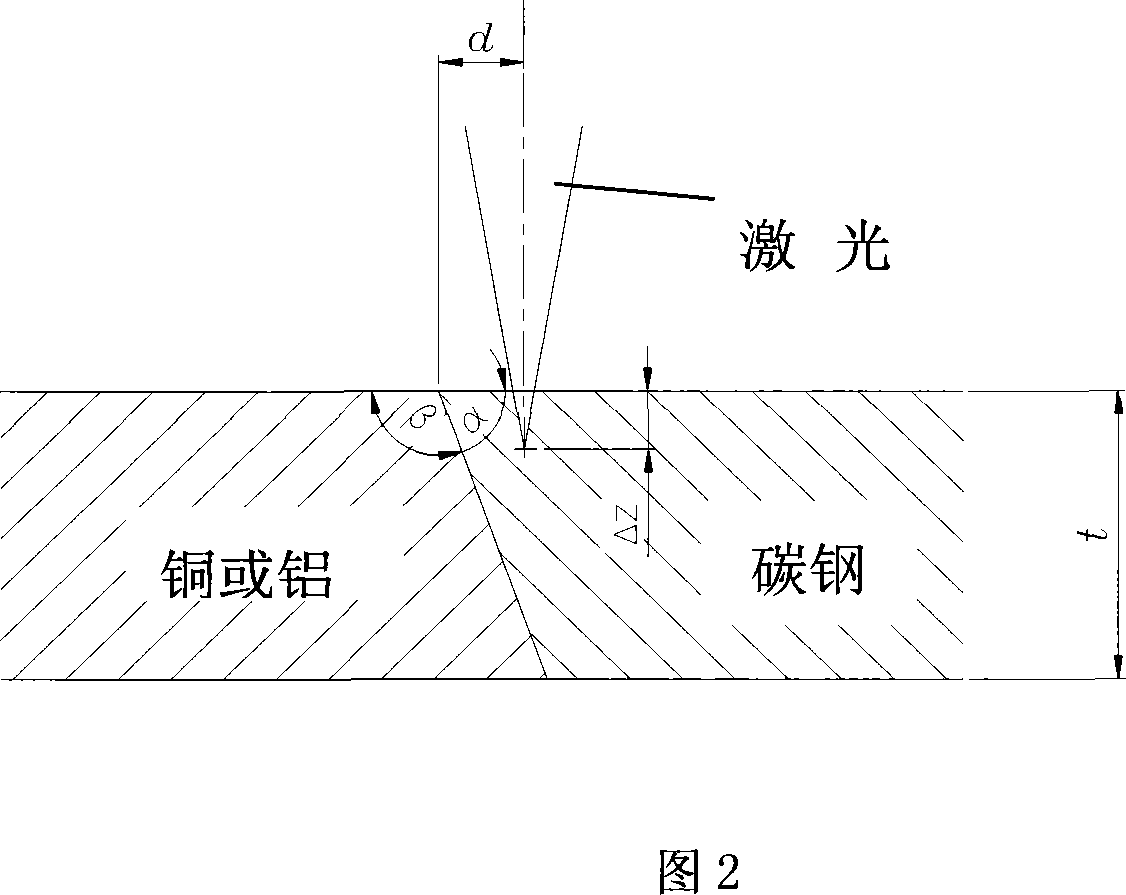
[0022] The materials of this embodiment are T2 copper and Q235 carbon steel, each with a plate thickness of 5mm. The plate processing is shown in Figure 2: the T2 copper side end surface is processed to 97°, and the Q235 steel side end surface is processed to 83°, that is, α=83° , using CO 2 The laser has an out...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The connection method of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0026] The materials of this embodiment are T2 copper and Q235 carbon steel, each with a thickness of 4mm. The plate processing is shown in Figure 2: the T2 copper side end surface is processed to 95°, and the Q235 steel side end surface is processed to 85°, that is, α=85° , using CO 2 The laser has an output power of 6.0Kw, the focus is adjusted to 2mm below the surface of the workpiece, and the welding speed is 1m / min. The two materials are butted, the laser beam is biased on the steel side, the distance from the carbon steel plate side is d=1.0mm from the center line of the butt joint, and the size of the test piece is 100×30×4mm.
[0027] The results of this example show that: the macroscopic view of the weld seam shows no macroscopic defects, there are no defects such as pores and cracks inside the weld seam, and the weld seam is well formed. The tensile strength of the welded joint r...
Embodiment 3
[0029] The connection method of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0030] The materials of this embodiment are T2 copper and Q235 carbon steel, each with a thickness of 8mm. The plate processing is shown in Figure 2: the T2 copper side end surface is processed to 100°, and the Q235 steel side end surface is processed to 80°, that is, α=80° , using CO 2 The laser has an output power of 9.5Kw, the focus is adjusted to 4mm below the surface of the workpiece, and the welding speed is 1m / min. The two materials are butted, the laser beam is biased on the steel side, the distance from the carbon steel plate side is d=2.0mm from the center line of the butt joint, and the size of the test piece is 100×30×8mm.
[0031] The results of this example show that: the macroscopic view of the weld seam shows no macroscopic defects, there are no defects such as pores and cracks inside the weld seam, and the weld seam is well formed. The tensile strength of welded joints rea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com