Control of lattice spacing within crystals
A lattice and crystal technology, applied in the field of lattice spacing control, can solve the problems of uncertain reflection peak position, reduced intensity, increased width, etc., and achieve the effect of dynamic positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
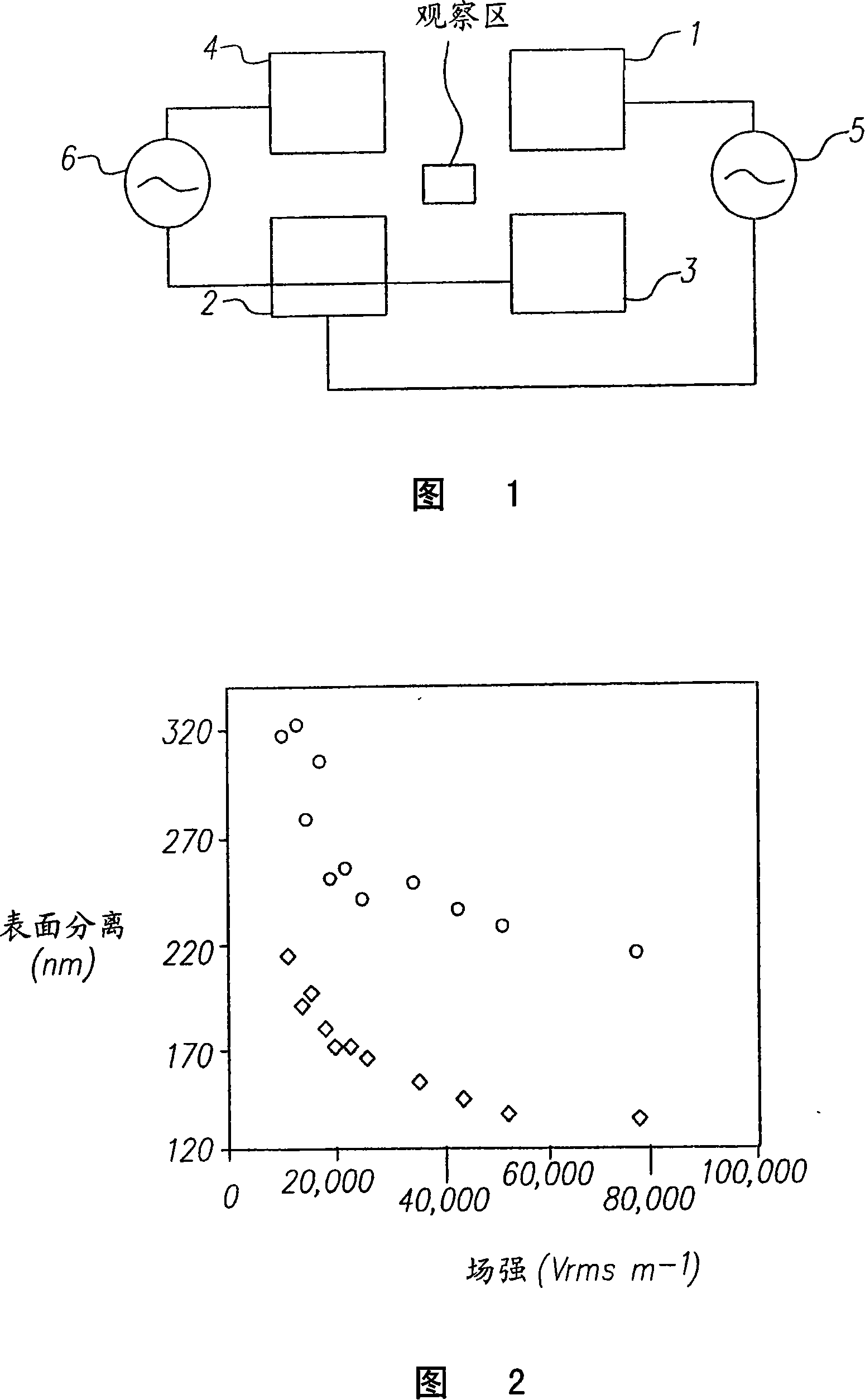
[0020] Figure 1 illustrates a layout of the electrodes used to demonstrate the method of the present invention.
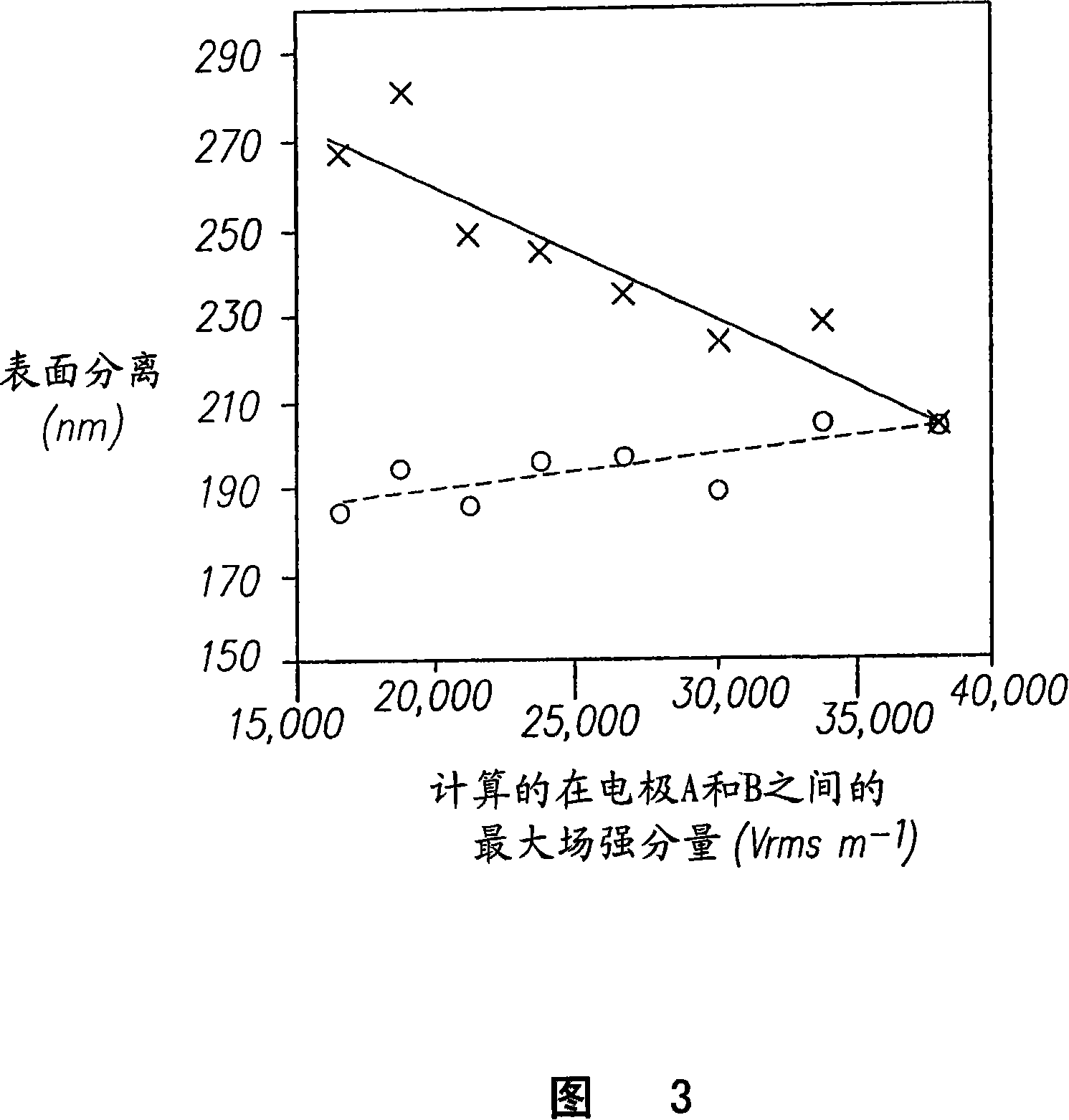
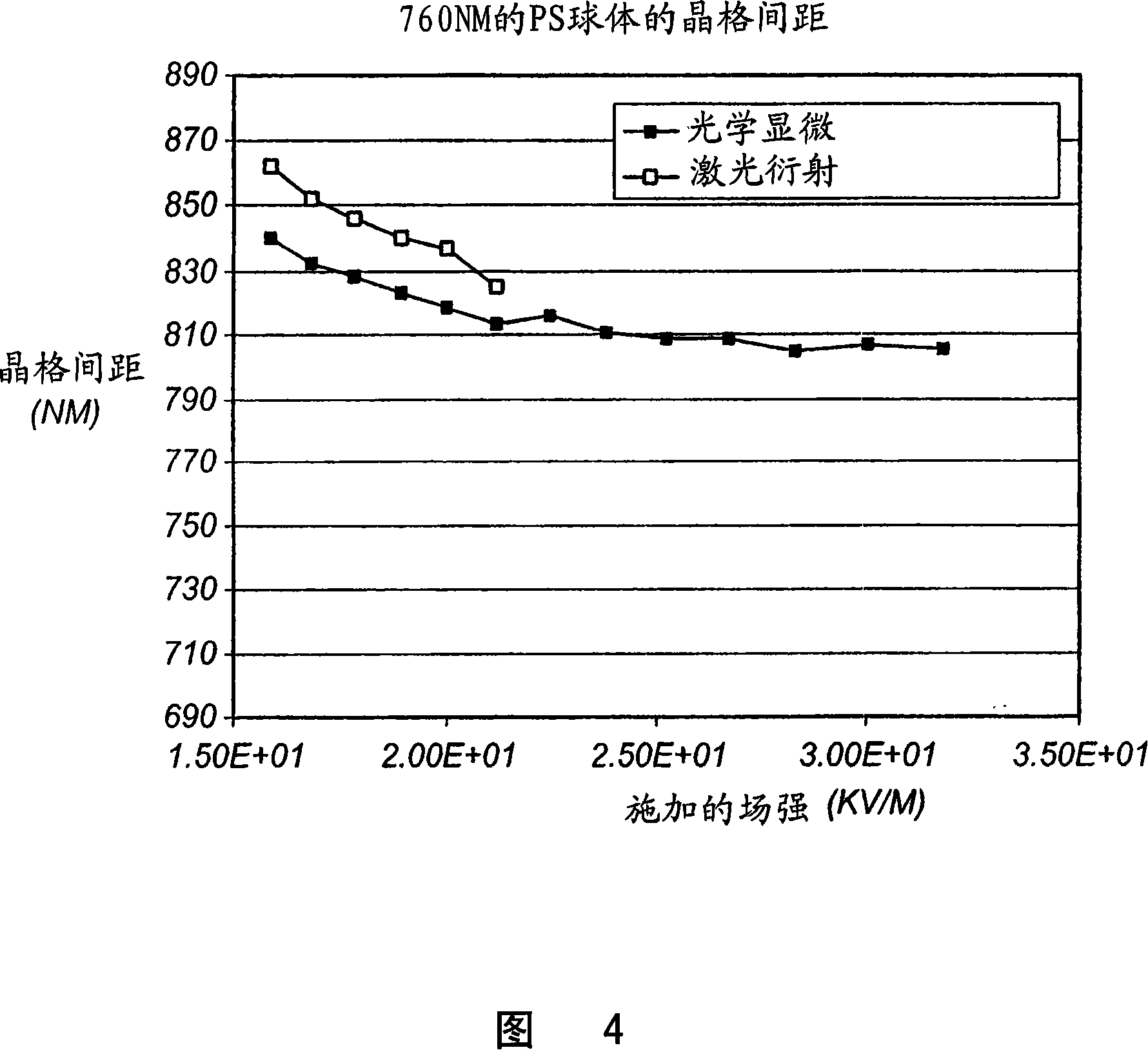
[0021] Four electrodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 are arranged around the observation area. Electrodes 1 and 2 are connected to a signal amplifier 5 . Electrodes 3 and 4 are connected to a signal amplifier 6 . These four electrodes are coplanar. In the experiments performed, the distance between electrodes 1, 4 and 2, 3 was 159 μm. The distance between electrodes 1,3 and 2,4 is 142 μm. However, the gap can be adjusted as desired. A smaller distance means a lower voltage to achieve the desired effect, i.e. about 30000Vm -1 Strength of.
[0022] The electrodes consisted of a 40 nm thick layer of platinum sputter coated on a glass microscope slide. Typically a 10 μL aliquot of the diluted suspension of anionic polystyrene latex particles is placed between the electrodes and covered with a microscope coverslip. In the presence of the suspension, the side-to-side resistance ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com