Random access method and system
A random access and random access sequence technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of long time domain, unavailable extended prefix sequence, and inability to flexibly support channels, etc., to achieve the goal of improving overall performance, speed, and utilization Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
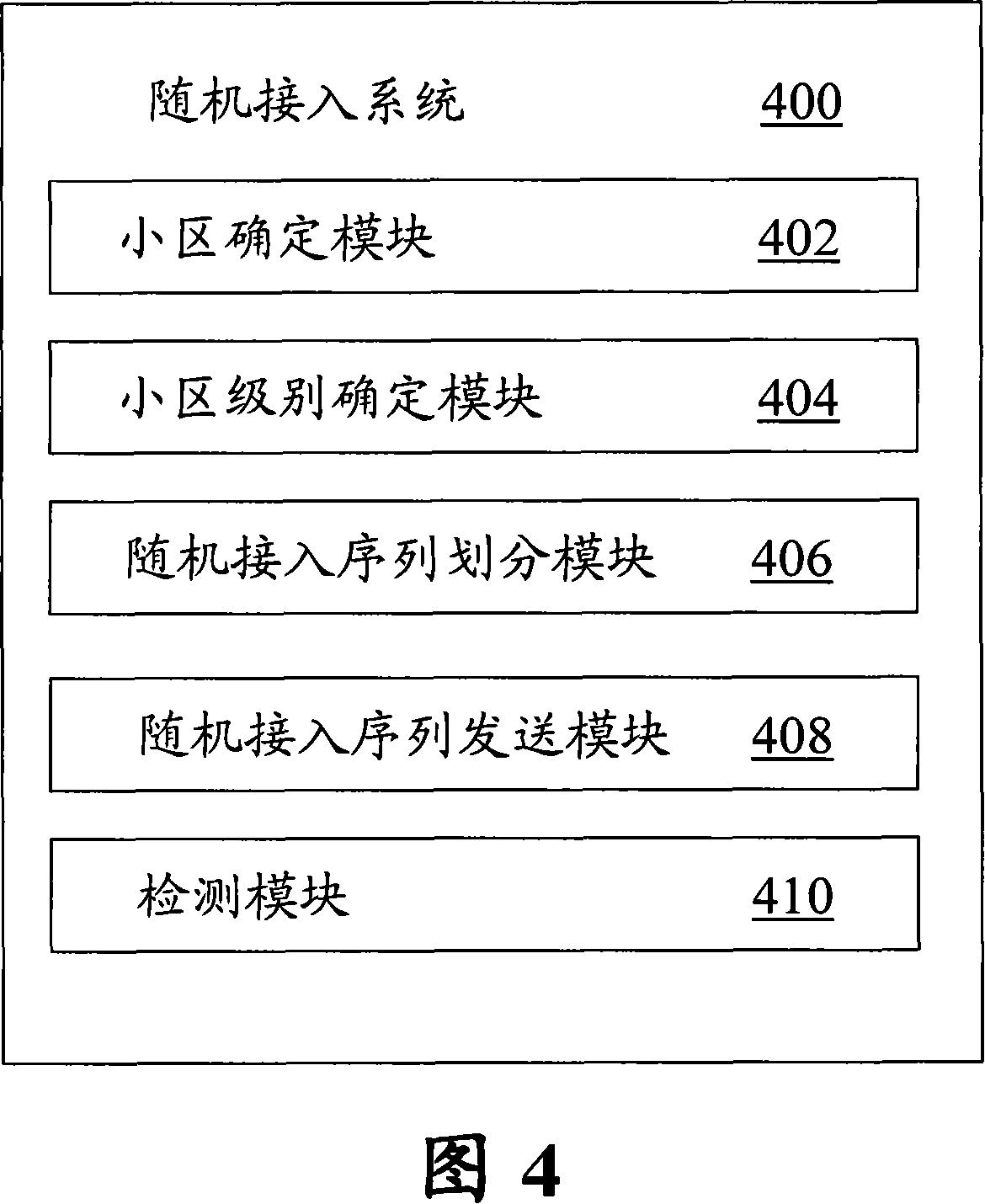
[0051] In the first embodiment of the present invention, a random access method is provided. The first embodiment will be described below with reference to FIG. 3, which is a flowchart showing a random access method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0052] As shown in Figure 3, the random access method according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps: Step S302: Determine the cell level for each of the multiple cells, and divide the multiple cells into first-level cells to second-level cells N-level cells, where N is an integer greater than 1; Step S304: When the user initiates an access request, determine the cell level of the cell to which the user belongs; Step S306: According to the determined cell level of the cell, send a message to the cell in the cell according to predetermined rules The user sends a random access sequence (which may be a Walsh code or other orthogonal codes), and in step S308, the base...
no. 2 example
[0067] In the second embodiment of the present invention, a random access method is provided, which differs from the first embodiment in that:
[0068] In step S306, for users in the second-level to Nth-level cells, the random access prefix is no longer divided into multiple parts, and the distance between the user and the base station is no longer considered, but the random access prefix is only continuously and repeatedly sent according to the cell level. The number of times the access sequence is different, wherein the higher the cell level of the cell, the more times the random access sequence is continuously and repeatedly sent.
[0069] Except for what is particularly pointed out above, the random access method according to the second embodiment of the present invention is substantially the same as the random access method according to the first embodiment of the present invention. In order to unnecessarily obscure the present invention, references to Repeated descri...
no. 3 example
[0071] In the third embodiment of the present invention, a random access method is provided, which differs from the random access methods according to the first and second embodiments of the present invention in that:
[0072] In step S306, for users in the second-level to Nth-level cells, the random access prefix is no longer divided into multiple parts, but the random access prefix is still determined according to the distance between the user and the base station and / or the moving speed of the user. The number of access sequences, wherein the farther the user is from the base station and / or the greater the moving speed of the user, the more times the random access sequence is continuously and repeatedly sent.
[0073] Except for the content specifically pointed out above, the random access method according to the third embodiment of the present invention is substantially the same as the random access method according to the first and second embodiments of the present inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com