High-heat direct reduction dezincing method for zinc-containing dust carbon-bearing briquette
A dust and agglomerate technology, applied in the field of coal-based high-temperature direct reduction, can solve the problems of increasing the consumption of the reduction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
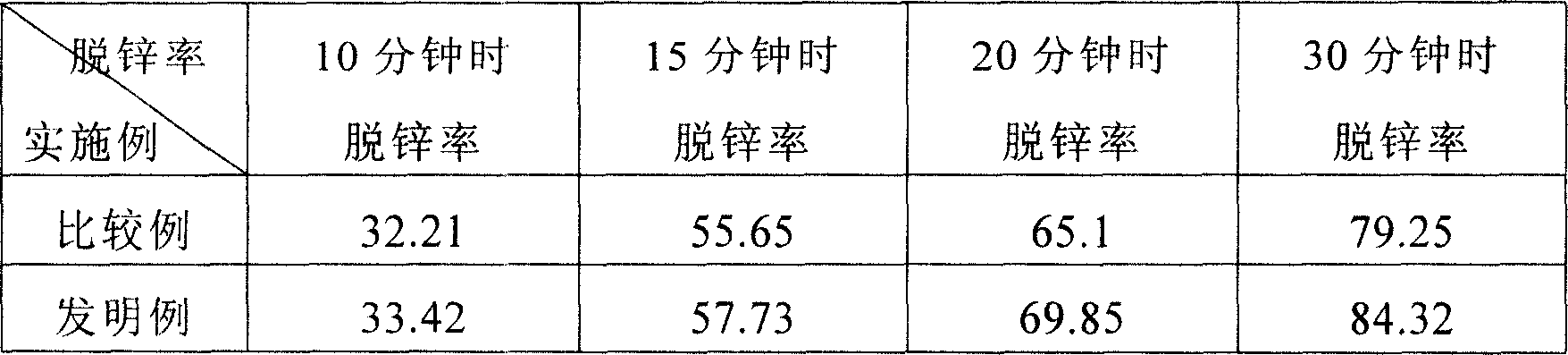
[0030] The original zinc-containing dust alkalinity is 1.1, and at 1250° C., the dezincification rates obtained after reduction respectively for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes are shown in the comparative example in the following table 1; meanwhile, according to the present invention, the alkalinity Add slaked lime to the original zinc-containing dust of 1.1 to increase the alkalinity. The amount of slaked lime added accounts for 3.13% of the agglomerate, and the alkalinity is increased to 1.3. Then, it is mixed with coal powder to make agglomerates. 3.82% of the block, followed by reduction at 1250°C for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes respectively for the dezincification rates obtained in the following table 1 of the invention example. It can be clearly seen from the following table 1 that after the invention example increases the alkalinity compared with the comparative example, its dezincification rate is also significantly improved co...
Embodiment 2
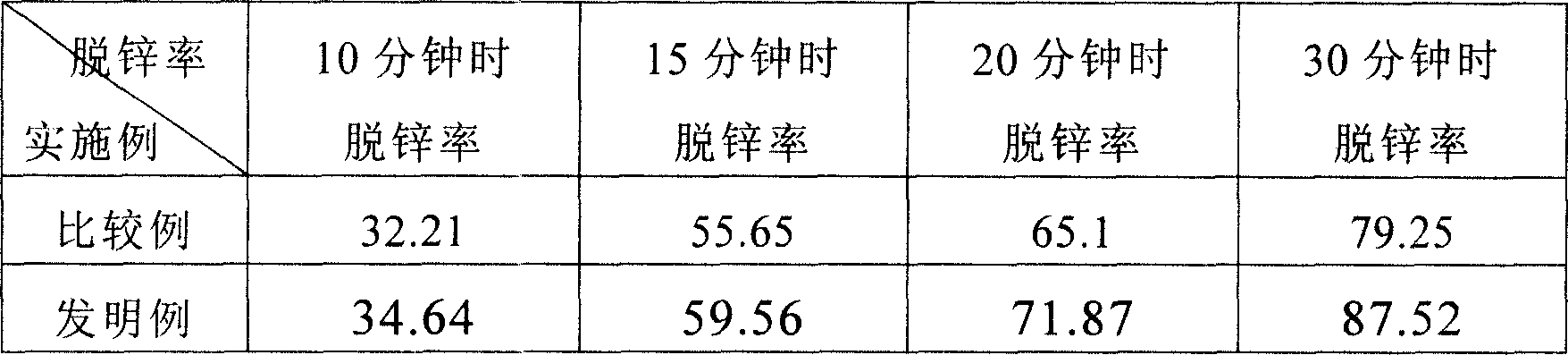
[0034] The alkalinity of the zinc-containing dust is 1.1, and at 1250° C., the dezincification rates obtained after reduction respectively for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes are shown in the comparative example in the following table 2; meanwhile, according to the present invention, the alkalinity Lime powder is added to the original zinc-containing dust of 1.1 to increase the alkalinity. The amount of lime powder added accounts for 5.03% of the agglomerate, and the alkalinity is increased to 1.8. Coal powder is then mixed in for agglomeration, and the amount of coking coal powder added accounts for 3.70% of the agglomerate. Then, the dezincification rates obtained after reduction at 1250° C. for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes are also shown in the invention examples in Table 2 below. It can be clearly seen from the following table 2 that after the inventive example increases the alkalinity compared with the comparative example, its dezi...
Embodiment 3
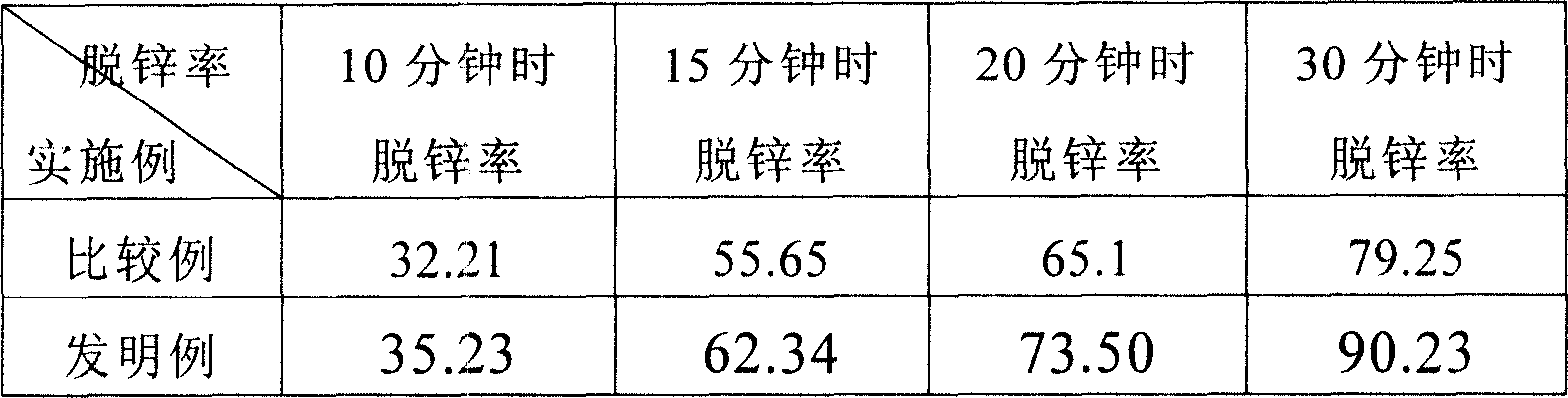
[0038] The alkalinity of the zinc-containing dust is 1.1, and at 1250° C., the dezincification rates obtained after reduction for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes are shown in the comparative example in the following table 3; meanwhile, according to the present invention, the alkalinity Adding limestone and dolomite mixed mud cake to the original zinc dust of 1.1 accounted for 14.2% of the agglomerate, increasing the alkalinity to 2.0. Then add petroleum coke powder to make agglomerates, and the amount of added petroleum coke powder accounts for 2.31% of the agglomerate. Then, the dezincification rates obtained after reduction at 1250° C. for 10 minutes, 15 minutes, 20 minutes, and 30 minutes are also shown in the invention examples in Table 3 below. It can be clearly seen from the following table 3 that after the alkalinity of the inventive example is increased compared with the comparative example, the dezincification rate is also significantly improved com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com