Composite material, light emitting element using the same, light emitting device, and electric apparatus
A technology of composite materials and light-emitting elements, which is applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of reducing the luminous efficiency of components and the inability to effectively extract light, and achieve the effects of high visible light transmittance, low excitation voltage, and good luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
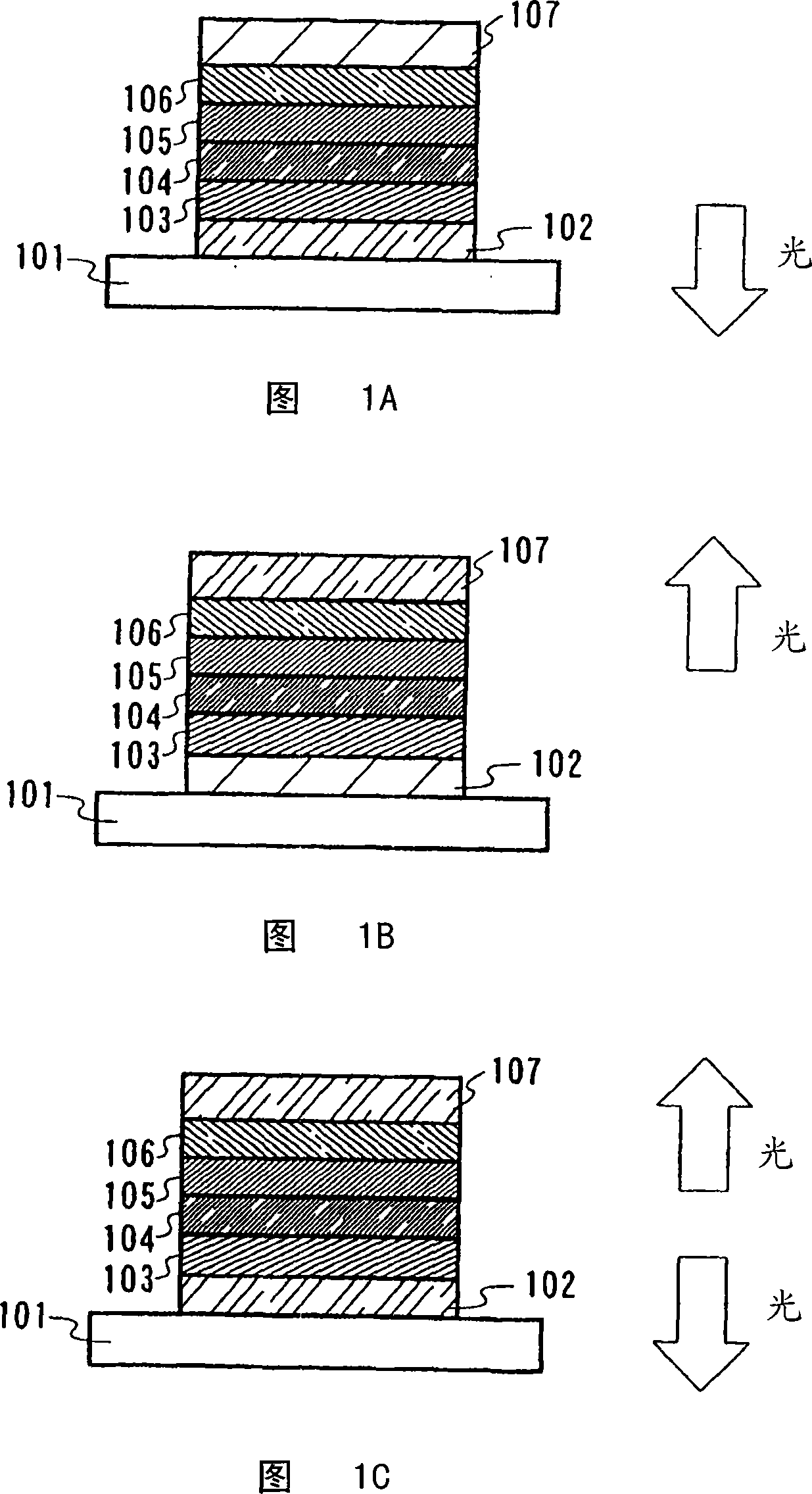
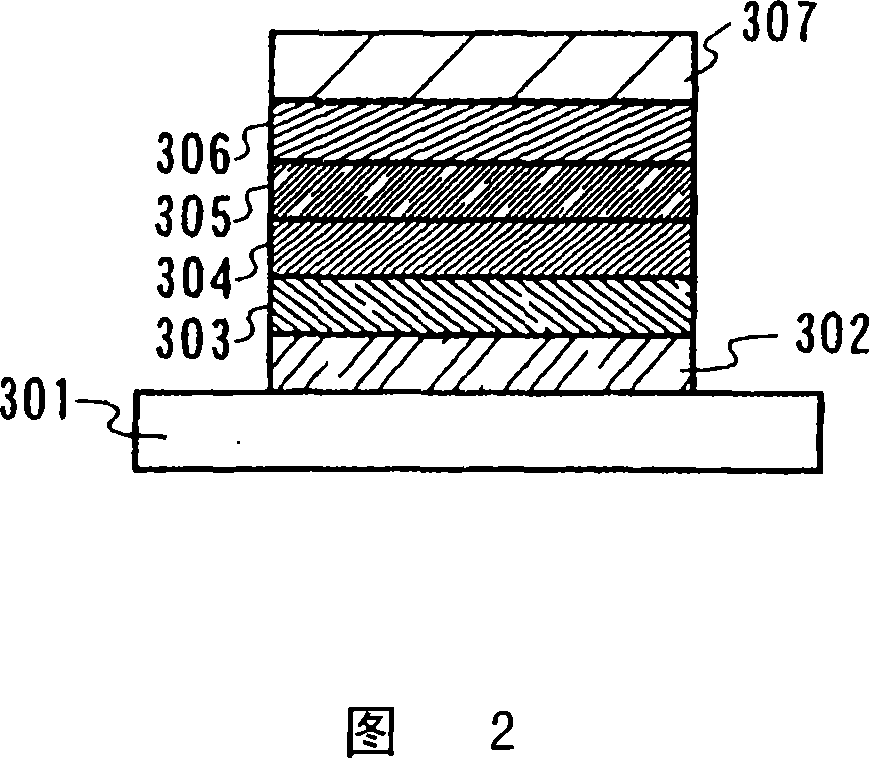
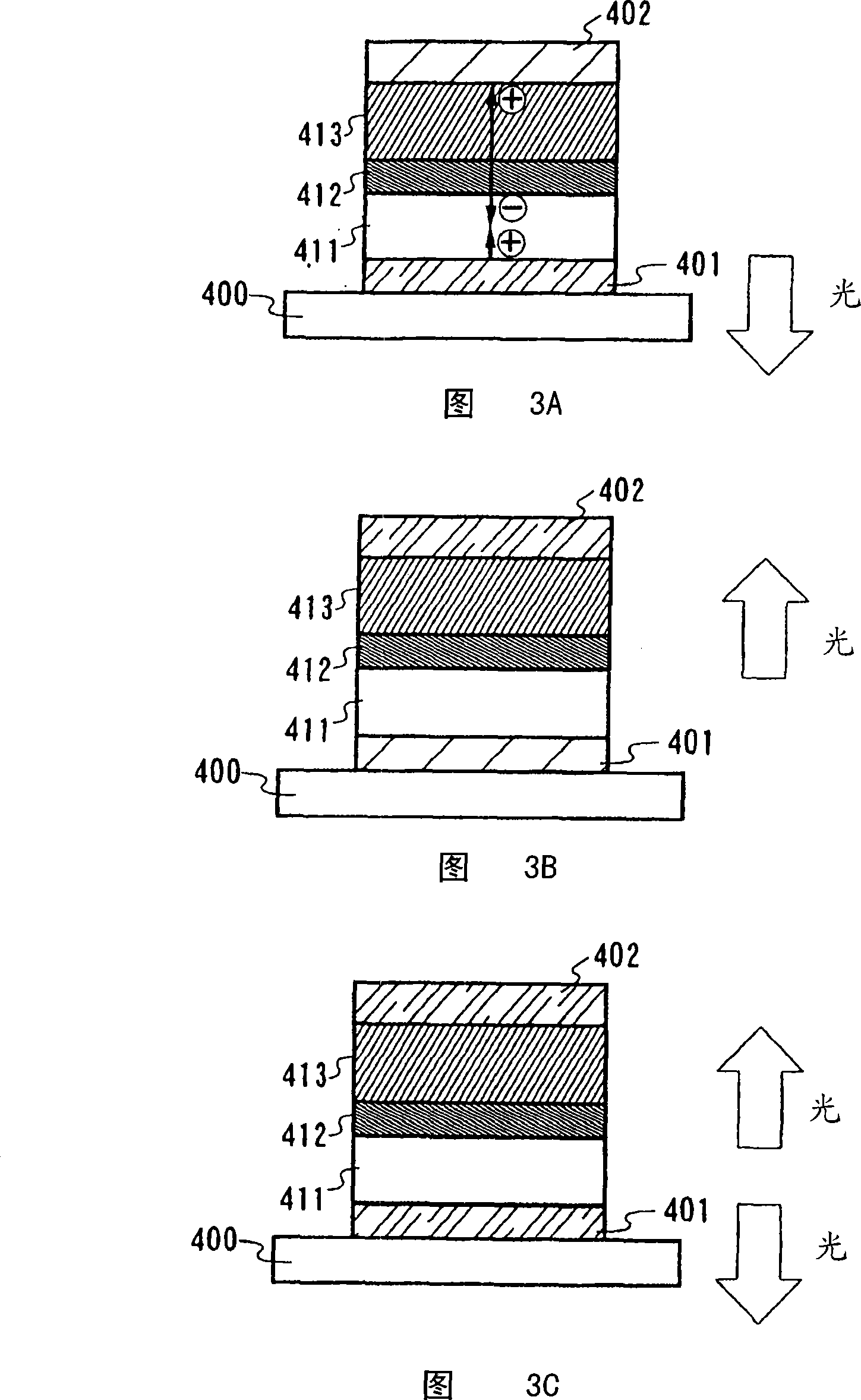
[0211] In Embodiment 1, a production example of the composite material of the present invention will be described. Further, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments, but the scope of the claims defines the present invention. The same is true for embodiment 2. In Embodiment 1, a manufacturing example of a composite material will be described in detail.
manufacture Embodiment 1
[0212] "Manufacturing Example 1" (DTDPPA+MoOx)
[0213] First, a glass substrate is fixed to a substrate holder in a vacuum evaporation apparatus. Then, pour DTDPPA (N, N'-two (p-tolyl)-N, N'-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine) independently in different resistance heating type evaporation sources (it is represented by the general structure ( 14) represents) and molybdenum oxide (valence of molybdenum: VI). in which the pressure is reduced to about 10 -4 Thin films were formed by using the composite material of the present invention by co-evaporation of DTDPPA and molybdenum oxide under vacuum conditions of Pa. In this case, the evaporation rate of DTDPPA was 0.4 nm / s, however molybdenum oxide was evaporated in an amount 1 / 4 of the amount of DTDPPA. The thickness of the film containing DTDPPA and molybdenum oxide was set to 50 nm.
[0214] The measurement results of the absorption spectrum of the composite material of DTDPPA and molybdenum oxide are shown in FIG. 11A . As shown ...
manufacture Embodiment 2
[0215] "Manufacturing Example 2" (DPAB+MoOx)
[0216] Manufacture the composite material containing DPAB and molybdenum oxide in the same manner as Manufacturing Example 1, the difference is to use DPAB (4,4'-bis[N-(4-diphenylaminobenzene) represented by structural formula (93) base)-N-phenylamino]biphenyl) to replace the DTDPPA of Manufacturing Example 1. The measurement results of the absorption spectrum of the composite material containing DPAB and molybdenum oxide are shown in FIG. 11B . As shown in Figure 1 IB, no significant absorption was observed in the visible region (400-700 nm). Further, absorption which was not observed in a single film containing only DPAB or a single film containing only molybdenum oxide was formed near 900 nm. This indicates the formation of voids.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com