Hot-rolled steel sheet, method for production thereof and molded article formed from hot-rolled steel sheet
A technology of hot-rolled steel plate and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, heat treatment furnaces, heat treatment equipment, etc., and can solve problems such as non-existent stable manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
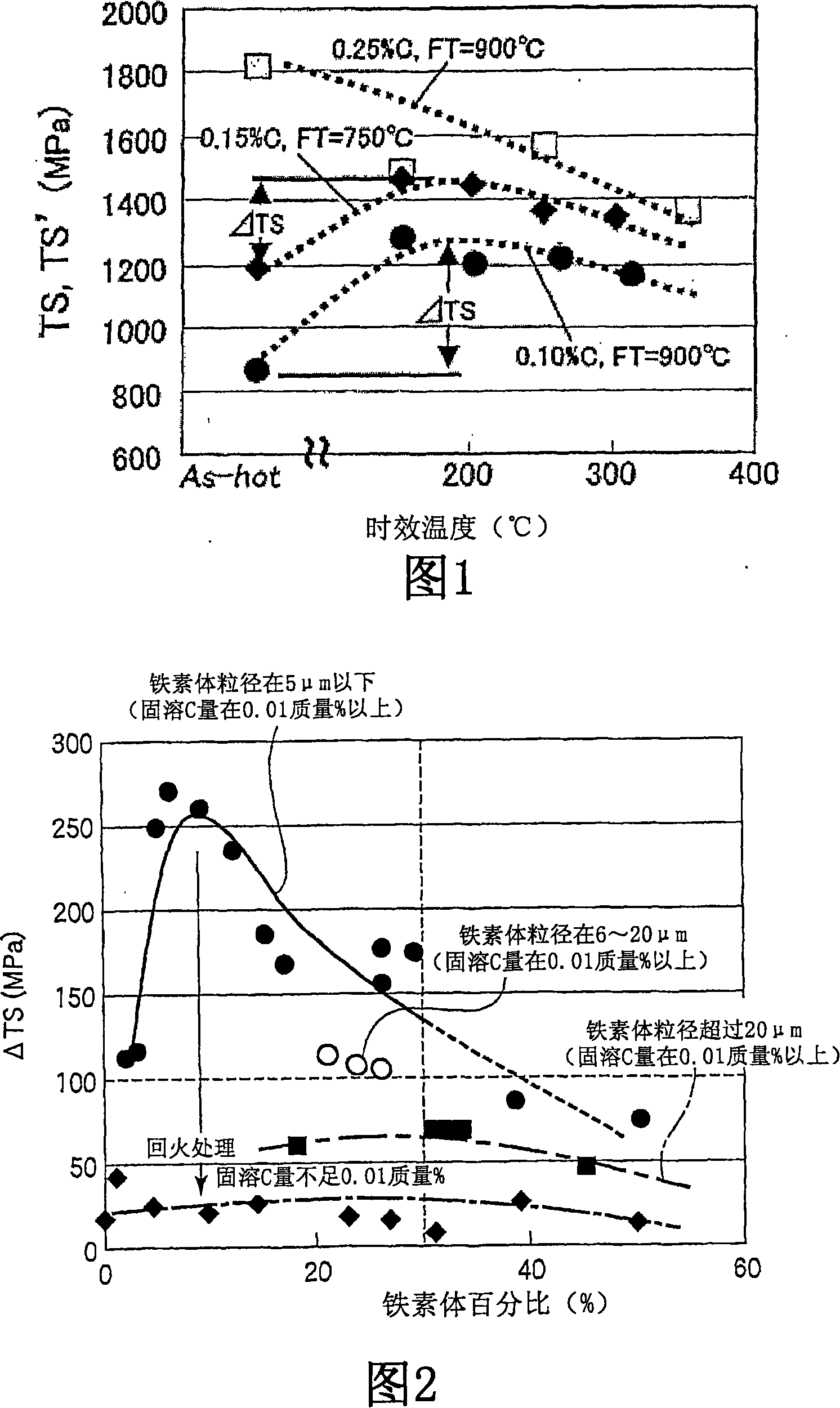
[0155] First, a first example in which strain age hardening characteristics are studied will be described.
[0156] After smelting molten steel with the composition shown in Table 1 (the balance is Fe and impurities) and making a steel slab, the steel slab was heated to 1250°C and hot rolled under the conditions shown in Table 2 to produce A hot-rolled steel strip (hot-rolled sheet) with a plate thickness of 3.0 mm. Except for the sample designation J, the quenching final temperature is the same as CT. For the obtained hot-rolled steel strip (hot-rolled sheet), the microstructure, solid solution C content, tensile properties, and strain-age hardening properties were determined by the following procedures.
[0157] (1) Microstructure
[0158] A test piece was selected from the obtained steel strip, and the microstructure was photographed using an optical microscope or a scanning electron microscope for a cross section (L cross section) parallel to the rolling direction. Then...
no. 2 example
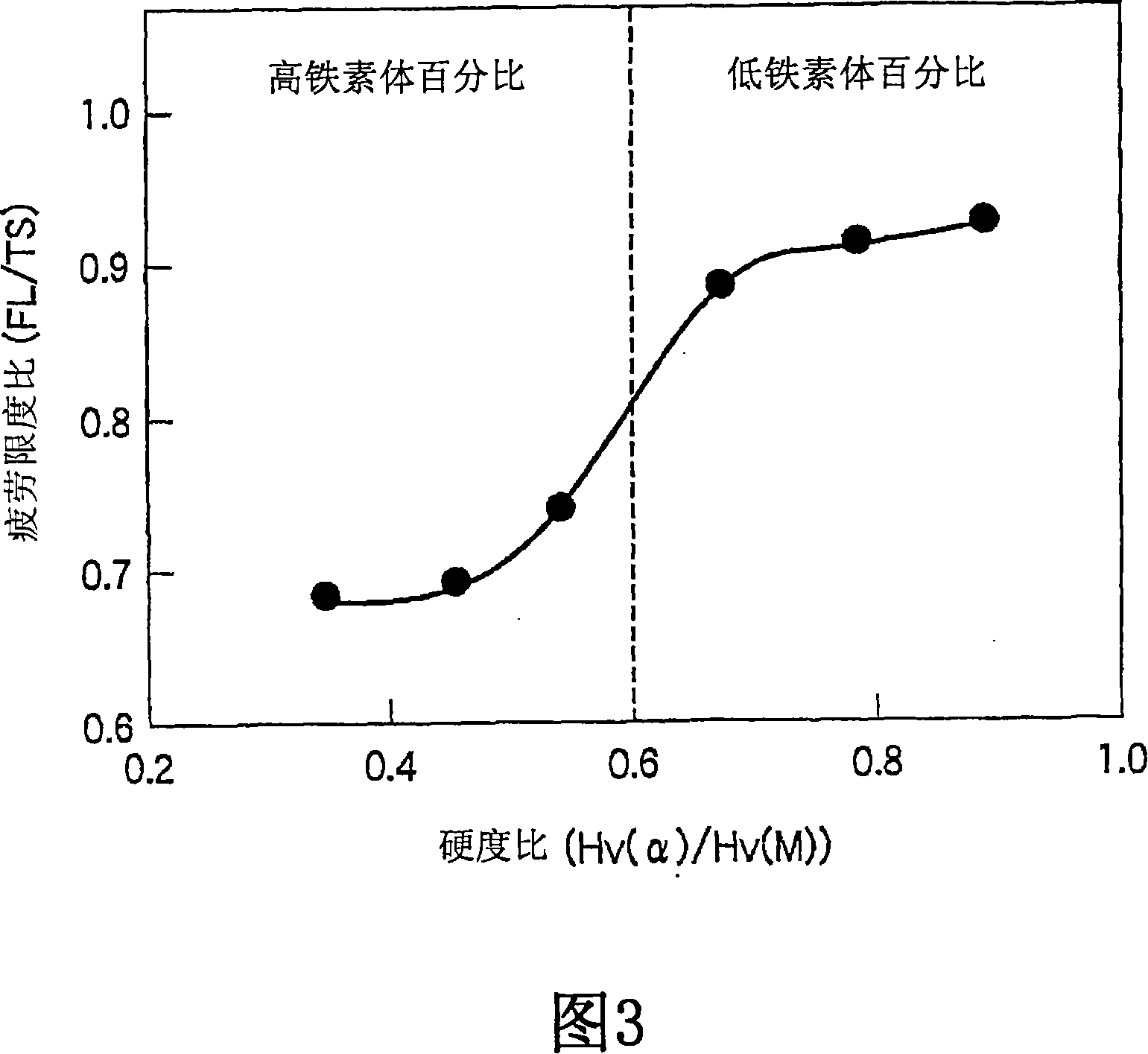
[0181] Next, a second embodiment will be described. Here, attention is also paid to fatigue properties in addition to strain age hardening properties.
[0182] After smelting molten steel with the composition shown in Table 4 (the balance is Fe and impurities), and making a steel slab, the steel slab was heated to 1200°C, and hot rolled under the conditions shown in Table 5, thereby producing A hot-rolled steel strip (hot-rolled sheet) with a plate thickness of 3.0 mm. For the obtained hot-rolled steel strip (hot-rolled sheet), the microstructure, solid solution C content, tensile properties, strain age hardening properties, main phase ferrite phase hardness after strain aging, and fatigue properties were determined. (1) microstructure, (2) solid solution C content, (3) tensile properties, and (4) strain age hardening properties were solved in the same manner as in the first example. Each hardness and fatigue properties were obtained as follows.
[0183] (5) Hardness
[01...
no. 3 example
[0204] The smelted composition contains C: 0.1%, Si: 0.01%, Mn: 2.2%, P: 0.012%, S: 0.005%, Al: 0.045%, N: 0.003%, and the balance is composed of Fe and impurities After forming the molten steel and making it into a steel slab, the steel slab was heated to 1250° C. and hot-rolled under the conditions shown in Table 7 to make a hot-rolled steel strip (hot-rolled plate) with a thickness of 2.0 mm. . Ar of the steel 3 The phase transition point is 701°C. FT is 800°C (ie Ar 3 Phase transition point + about 100°C), quench stop temperature and CT are 180°C (Ms point is 429°C).
[0205] In addition, sample symbol 3P was subjected to a low-temperature tempering treatment under the conditions in Table 7 after coil winding. And sample No. 3I is intentionally slow-cooled for a short time in the bainite nose region (about 500°C) to generate a small amount of bainite.
[0206] The results are shown in Table 8.
[0207] Table 7
[0208] try
Sample
remember
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com