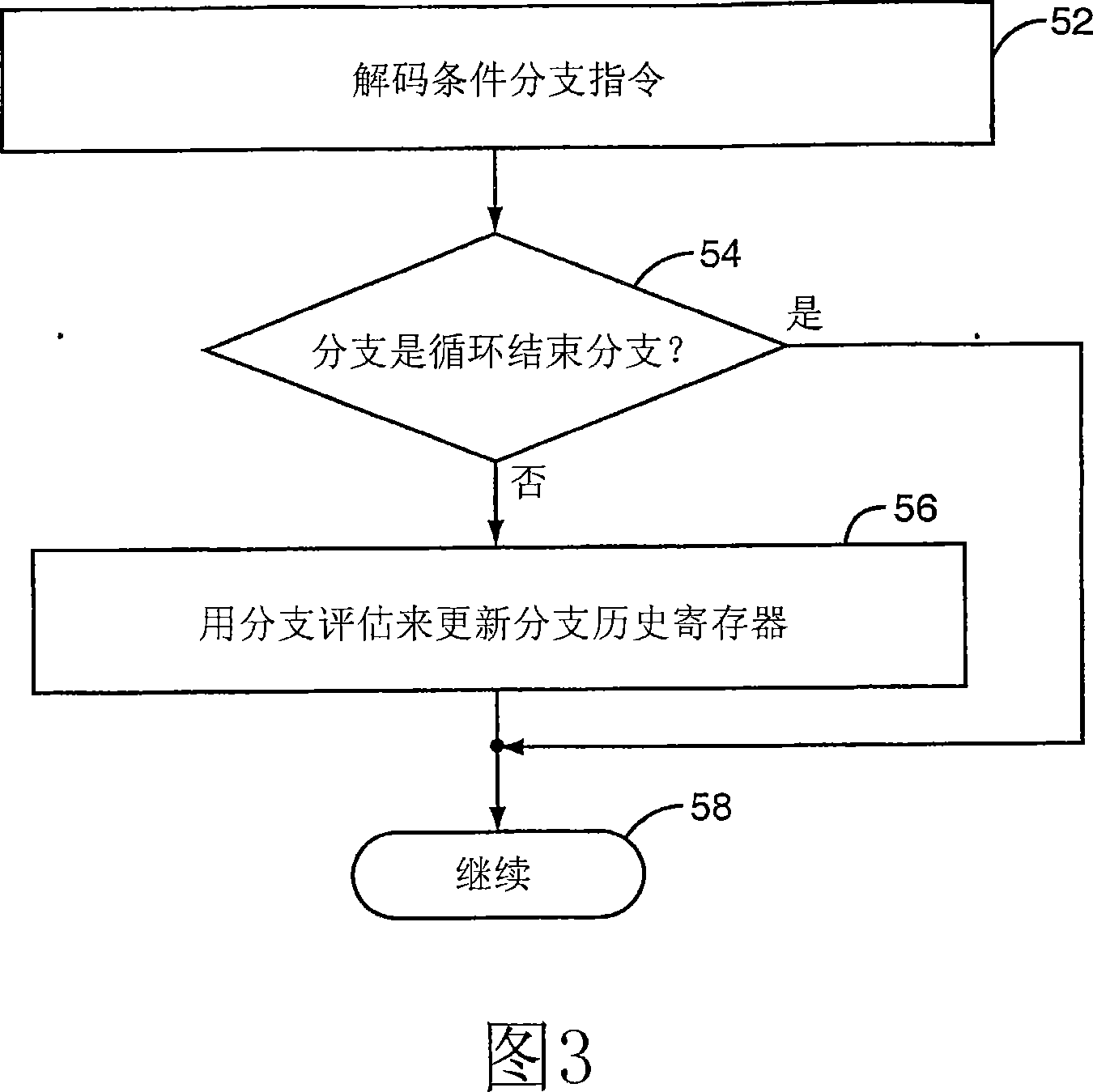
Suppressing update of a branch history register by loop-ending branches
A technology of branch history and loop end, applied in memory systems, instruments, machine execution devices, etc., can solve the problems of wasting BPT102 space, increasing code size, and increasing branch prediction training time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
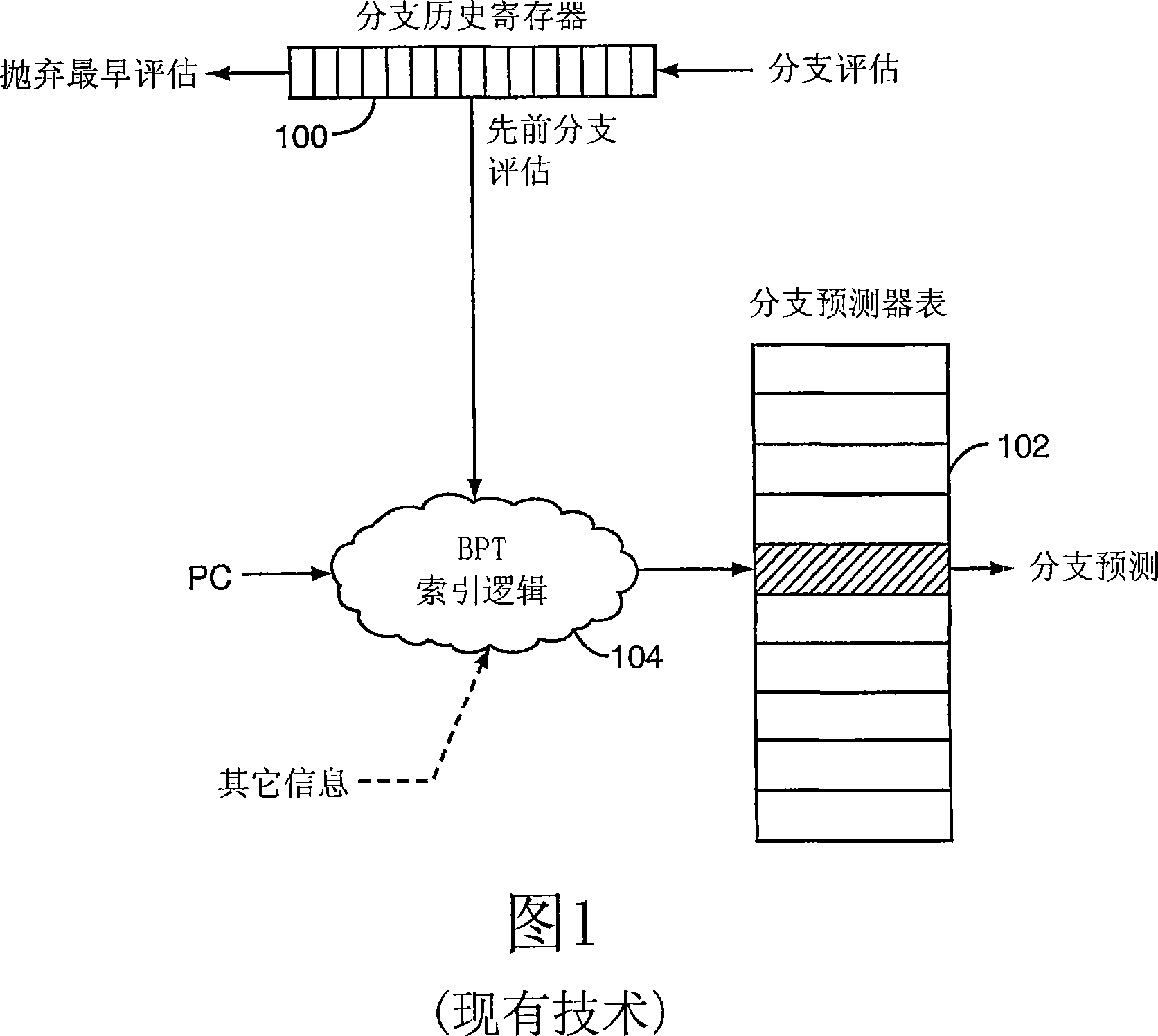
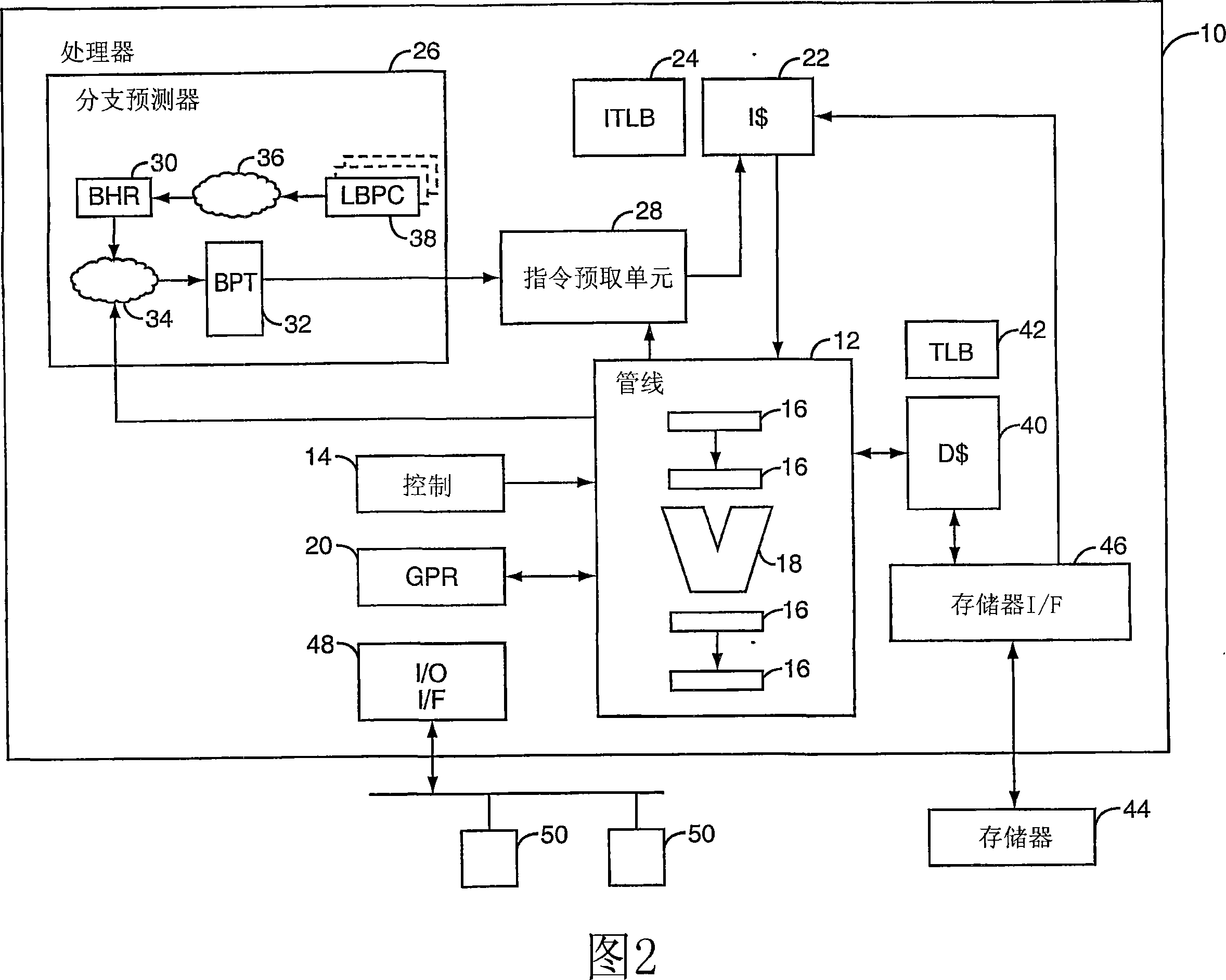
[0034] FIG. 1 depicts a functional block diagram of a processor 10 . Processor 10 executes instructions in instruction execution pipeline 12 according to control logic 14 . In some embodiments, pipeline 12 may be of a superscalar design, having multiple parallel pipelines. Pipeline 12 includes various registers or latches 16 organized into stages, and one or more arithmetic logic units (ALUs) 18 . A general purpose register (GPR) file 20 provides registers comprising the top of the memory hierarchy.
[0035] The pipeline 12 fetches instructions from an instruction cache (I-cache) 22 , where memory address translation and grants are managed by an instruction-side translation lookaside buffer (ITLB) 24 . When conditional branch instructions are decoded early in pipeline 12 , branch predictor 26 predicts branch behavior and provides the prediction to instruction prefetch unit 28 . Instruction prefetch unit 28 speculatively fetches instructions from instruction cache 22 at the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com