Method for producing insect parasitic bacteria fruit body
A production method and technology of parasitic bacteria, applied in the direction of fungi, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining ascospores, difficulty in producing ascospores, and difficulty in stable production, so as to improve the utilization value, decrease the inhibitory activity, and increase the infection rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
[0057] Reference Example 1, Comparison of Insect Generations
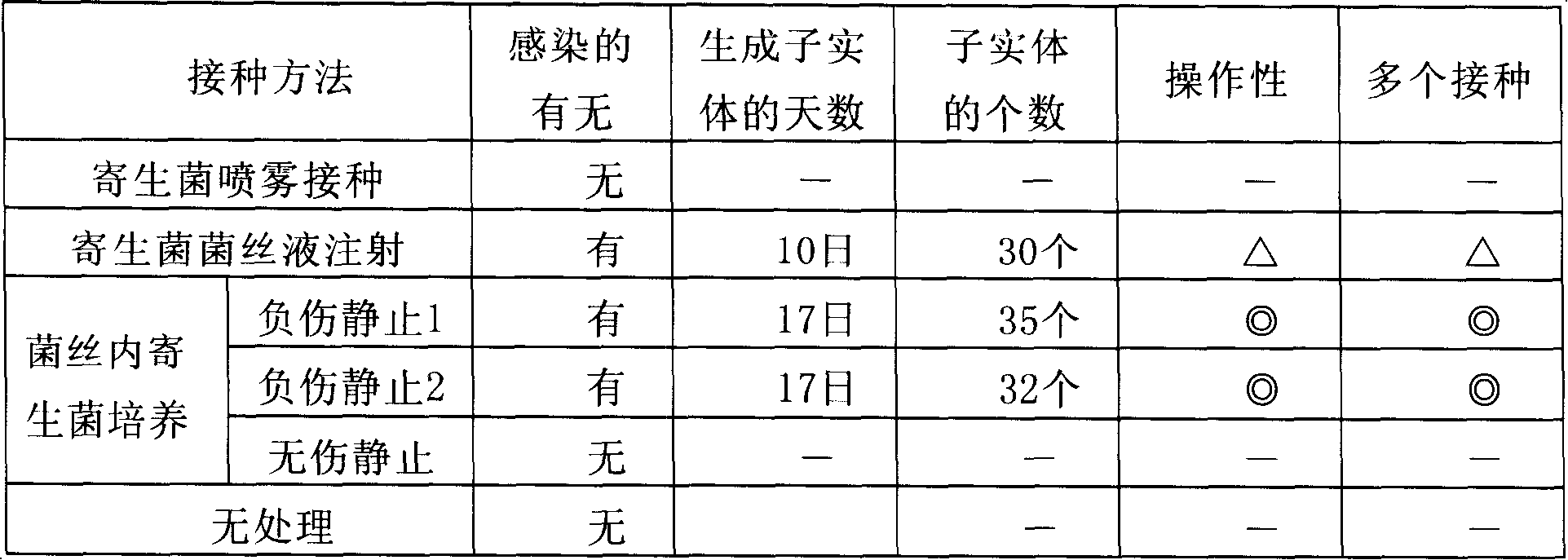
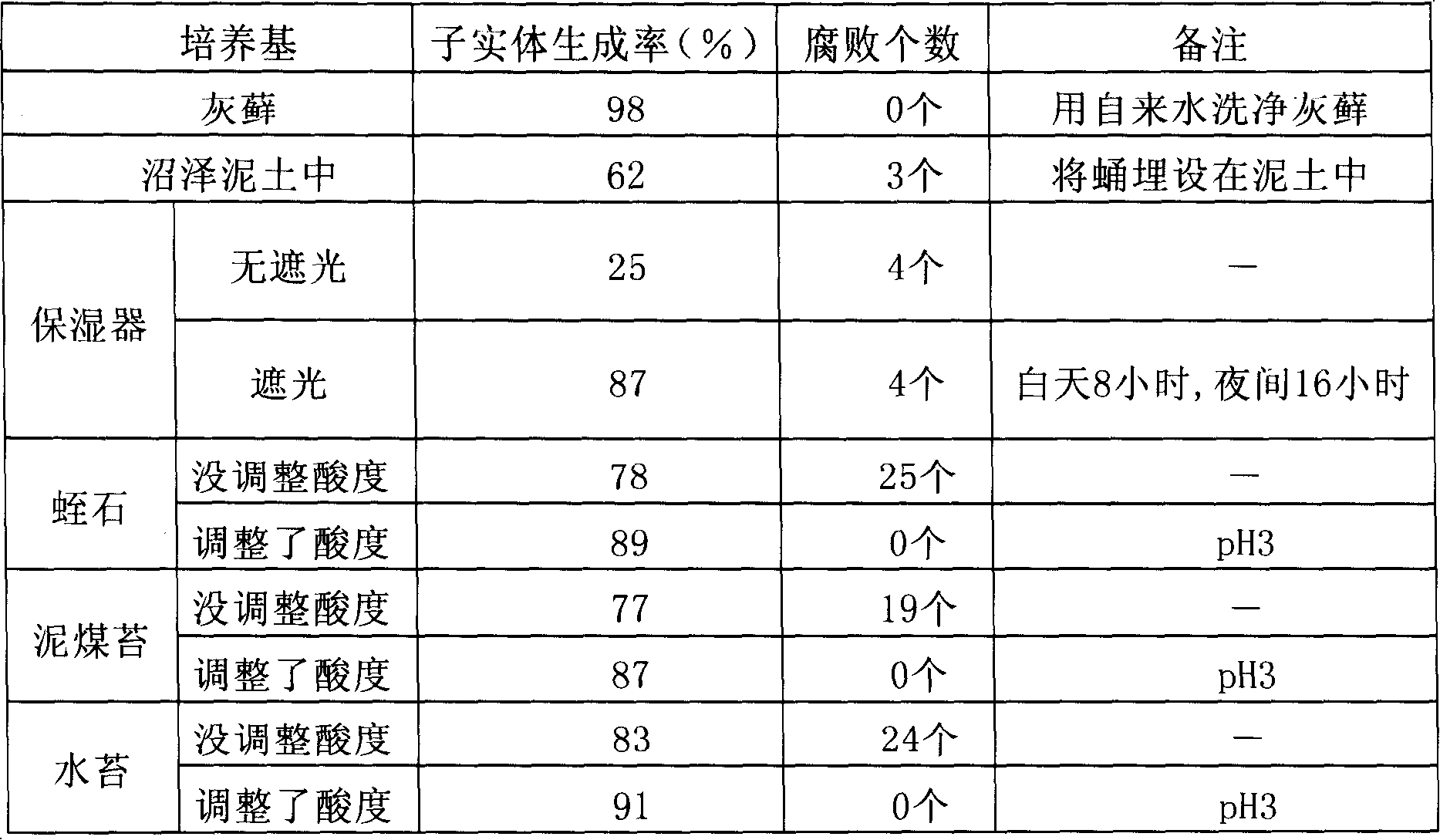
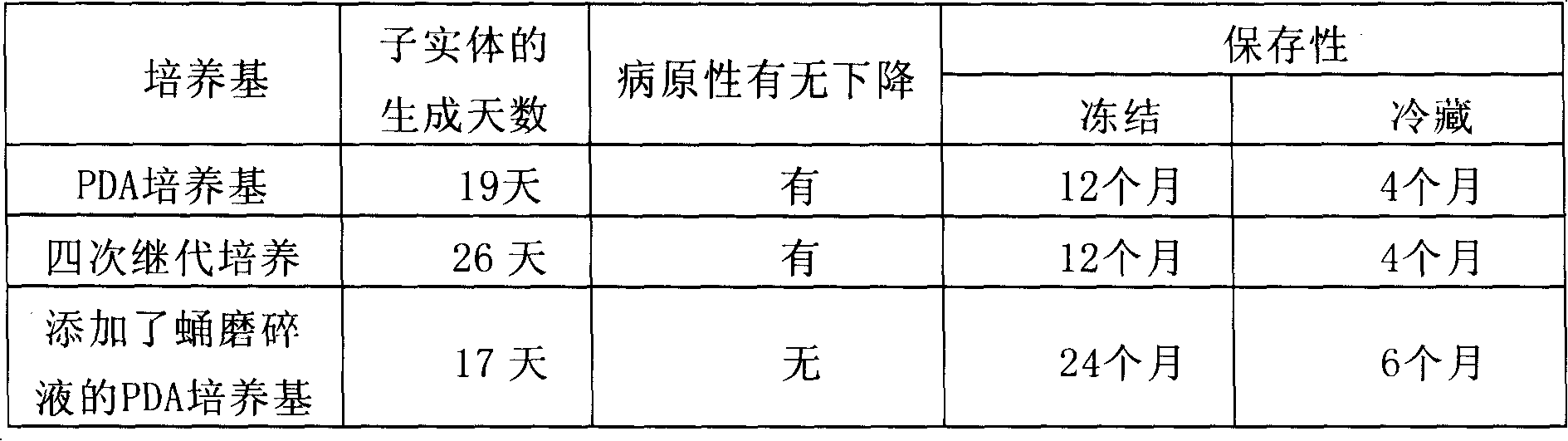
[0058] Place the insect parasites in PDA medium, propagate at 25°C for 10 days, and spread them. The 3rd (age), 4th, and 5th instars, 10 prepupae and 10 pupae of Spodoptera litura larvae were placed in the Let it stand there for 2 days and inoculate Cordyceps militaris. 35 days after inoculation, feeding and management were performed to investigate whether Cordyceps militaris was infected, the number of dead insects, and whether fruiting bodies were produced. A test was also carried out in the case where the above treatment was not performed (no treatment). The results are listed in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1
[0060] generations
[0061] From the results shown in Table 1, it can be seen that 9 of the prepupa were infected, 2 of the 3rd instar larvae, and 1 of the 4th instar larvae were infected. Although it can be determined that there are infected in the prepupa and some larvae like this, in other ge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com