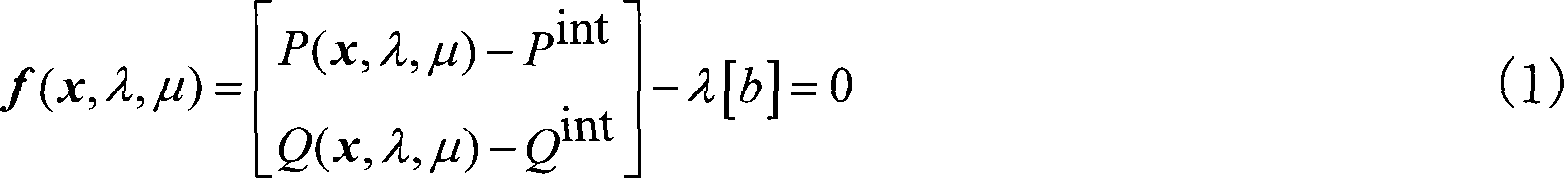Forecast accident power system voltage stabilization fast on-line analyzing and preventing control method
A voltage stability and accident prediction technology, applied in the field of fast online analysis and preventive control of power system voltage stability, can solve problems such as slow calculation speed, time-consuming branch fault analysis, and the need for initial values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
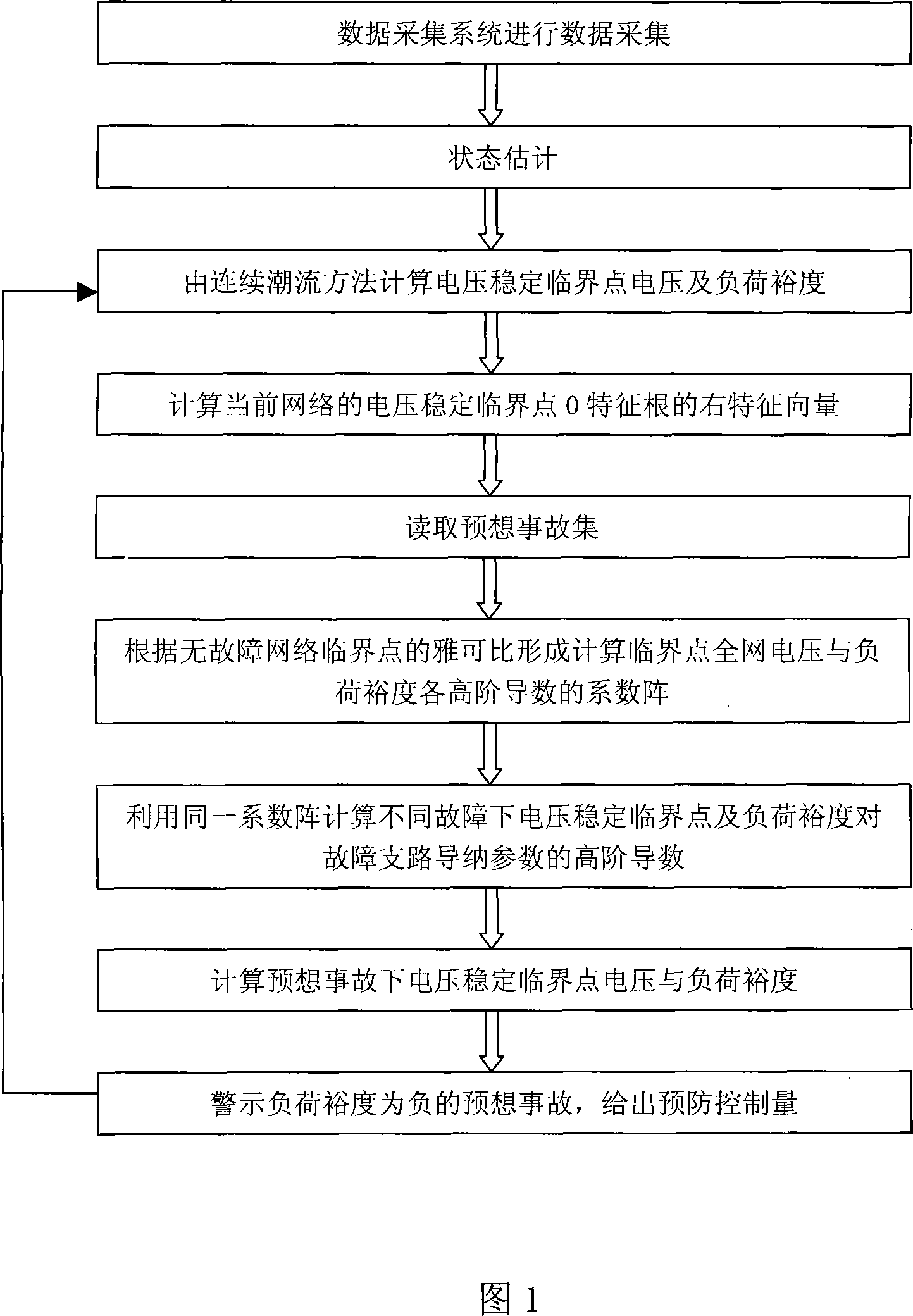
[0195] The original data of the IEEE 30 bus simple system can be found in the relevant information. Taking this system as an example, the active load and reactive load of all nodes increase proportionally, and the SNB of the base state network is obtained by using the continuous power flow method. Four branch faults including "5-7", "15-23", "22-24" and "4-12" were selected as the research objects. Figure 3 shows the trajectory curve of the load margin at the SNB point approaching from the fault forward to the fault when the three-phase open-circuit fault occurs in different lines, where n represents the number of Taylor series expansions. It can be seen from Figure 3 that it is difficult to obtain the load margin at the SNB point after the fault with the first-order approximation. The faults of some non-critical lines can be approximated by the 2nd to 3rd order derivatives. The load margin of the SNB point after the fault , for most faults including more serious faults; the ...
Embodiment 2
[0202] For the original data of the IEEE-118 node system, please refer to the related materials. Taking this system as an example, the active load and reactive load of all nodes increase proportionally, and the SNB of the base state network is obtained by using the continuous power flow method. Four branch faults including "15-19", "44-45", "30-38" and "45-46" were selected as the research objects. Figure 4 shows the approximation trajectory of the SNB point after the three-phase open-circuit fault occurs in these lines.
[0203] Table 2 shows the comparison between the load margin of the SNB point obtained by using the 7th derivative approximation when the above line fails and the accurate solution of the load margin of the SNB point after the fault calculated by the continuous power flow method.
[0204] Table 2: IEEE-118 node system results comparison between the method described in this patent and the continuous power flow method
[0205] fault branch
[0206] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com