Magnesium alloy microbial corrosion method based on solid medium
A technology of solid medium and microbial corrosion, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, weather resistance/light resistance/corrosion resistance, etc. Intuitive results, saving experimental drugs, and the effect of saving experimental drugs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
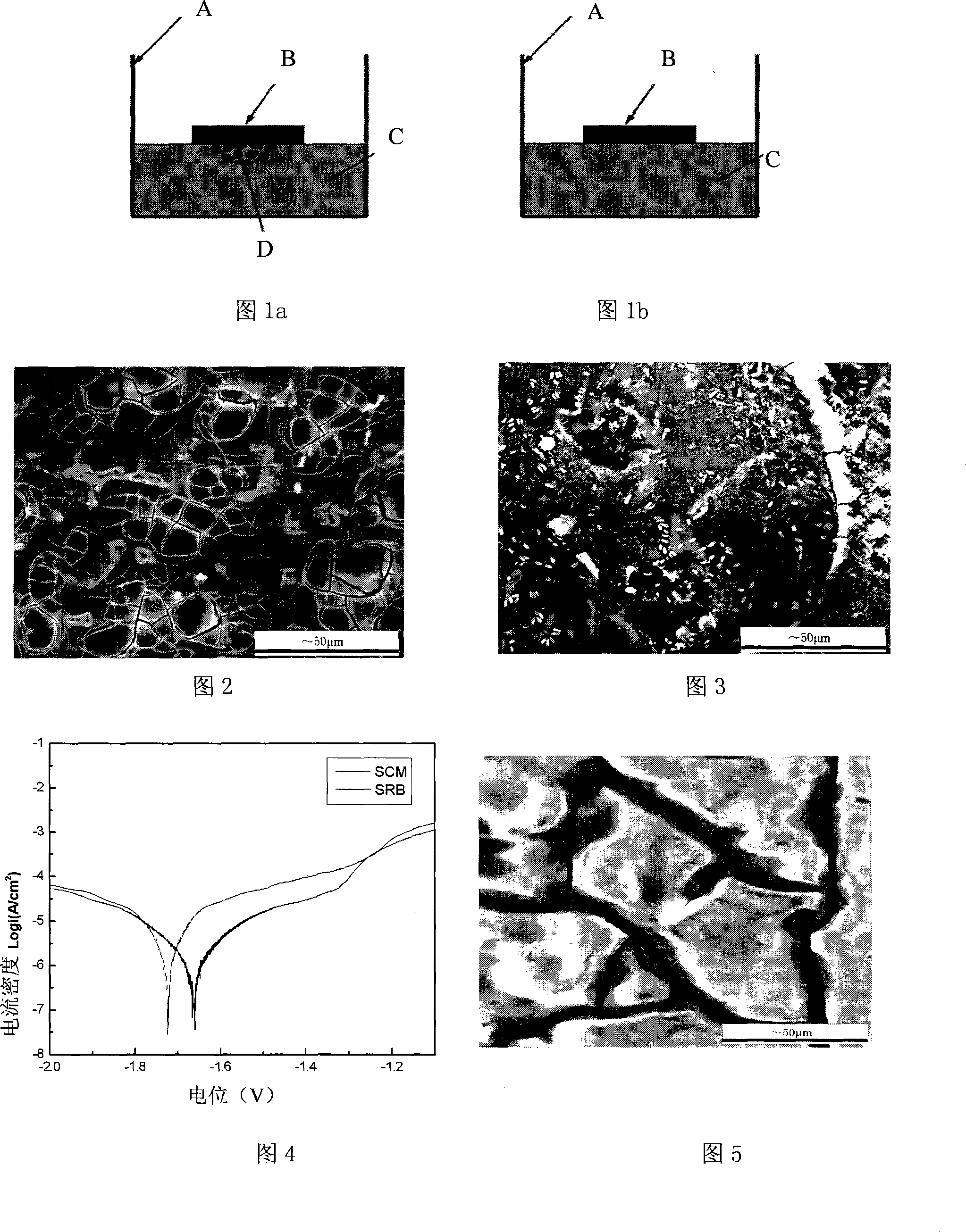
[0050] Using this method to study the microcorrosion of AZ91 magnesium alloy, it is found that the main feature of microbiological corrosion of AZ91 magnesium alloy is pitting corrosion (see Figure 3). By comparing the 24h corrosion morphology under sterile and sterile conditions (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Prove that bacteria can indeed cause pitting corrosion of AZ91 magnesium alloy. The morphology of pitting is similar to that of bacterial colonies. It can be seen from Figure 3 that the metabolism of bacterial colonies is particularly serious for the corrosion of magnesium alloys. Under the scanning electron microscope, the relationship between the position of the bacterial colony and the position of the corrosion pit in the corrosion morphology obtained by the patch corrosion method can be clearly observed. It can be deduced that the metabolism of the bacterial colony has an important influence on the corrosion pit. Fig. 4 is the polarization curve measured after the magne...
example 2
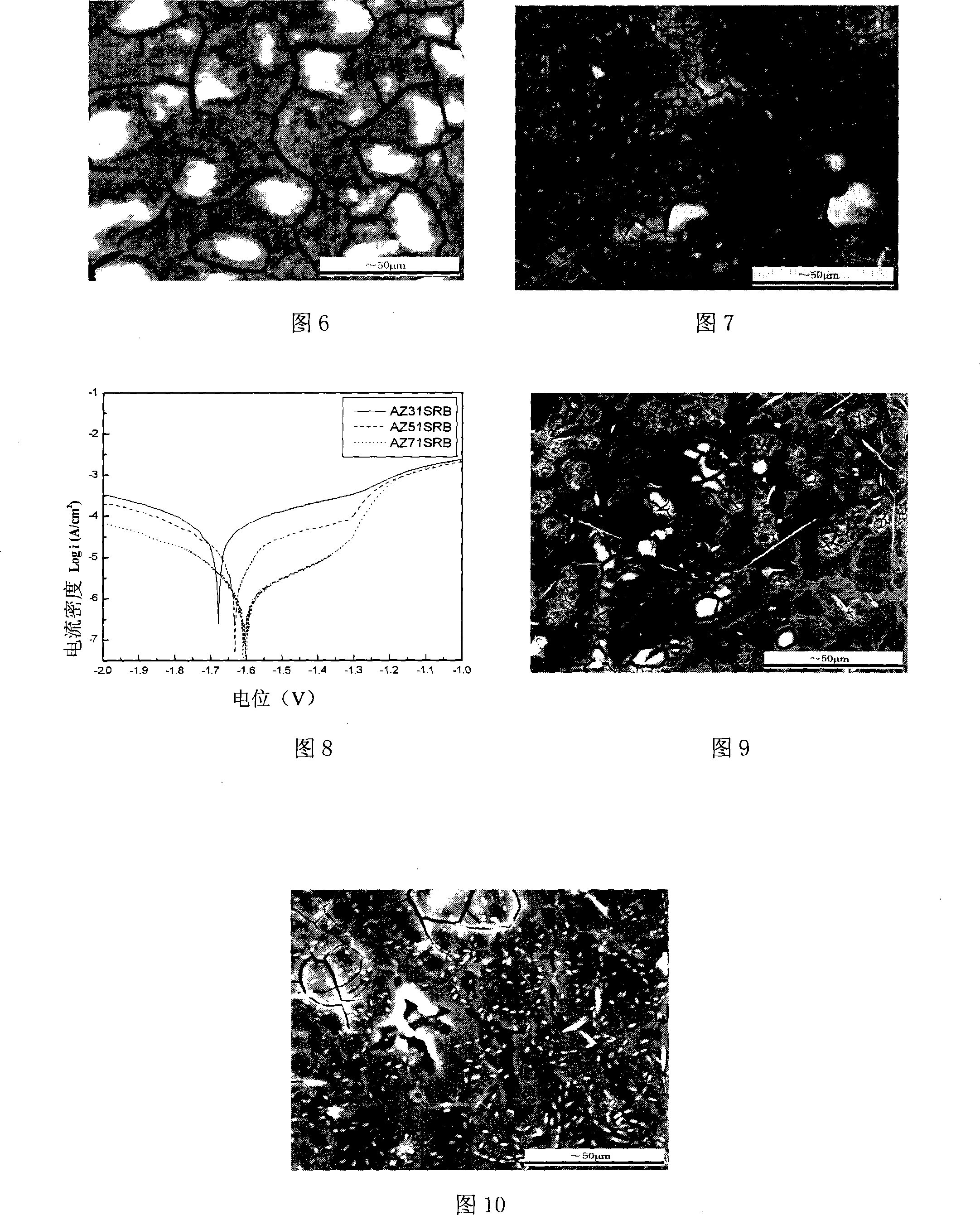
[0052] The effect of β phase content on the microbial corrosion of Mg-Al-Zn alloys was studied through the microbiological corrosion of AZ31, AZ51 and AZ71 magnesium alloys by chip corrosion method. Figure 5 shows the corrosion morphology of AZ31 magnesium alloy in the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria for 24 hours. It can be seen from Figure 5 that the surface of the AZ31 magnesium alloy electrode has been severely corroded, especially the α phase, and the corrosion product film has cracked and formed larger plates. It can be concluded from the morphology that a thick corrosion product film has formed on the surface of the electrode. At the same time, a white substance is attached to the surface of the alpha phase, and the existence of bacterial cells can be clearly seen in the white substance. The white film layer is the reaction product of bacterial metabolites and magnesium alloy electrodes. Figure 6 shows the corrosion morphology of AZ51 magnesium alloy electrode in...
example 3
[0055] Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the morphology micrographs of the microbial corrosion of the Ce-modified AZ91 magnesium alloy. The picture shows the corrosion morphology of the Ce-modified AZ91 magnesium alloy at 24 h when sterile. Figure 10 shows the microbiological corrosion morphology of Ce-modified AZ91 magnesium alloy at 24h. As can be seen from Figure 10, the distribution of bacteria and the way they divide. Through the comparison of Figure 9 and Figure 10, the influence of the existence of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their metabolism on the corrosion process of the Ce-modified AZ91 magnesium alloy can be obtained.
[0056] Therefore, it can be seen from the above examples that the patch corrosion method is an effective research method for the study of microbial corrosion of magnesium alloys.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com