Method for reclaiming copper and aluminum form copper-clad aluminum wire waste material and anode device used for electrolysis equipment thereof
A technology of anode device and electrolysis equipment, which is applied to the improvement of process efficiency, photographic technology, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of no copper-clad aluminum scrap recycling, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple equipment and convenient operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The raw material of this embodiment is the original copper-clad aluminum wire scrap with a diameter of 2 mm and a mass of 25 g, wherein the weight percentage (mass fraction) of copper is 33.3%. The raw copper-clad aluminum wire waste is leached with waste electrolyte to remove part of soluble impurities to obtain copper-clad aluminum bare wire waste.
[0019] The method of this embodiment is as follows:
[0020] ①Cut the copper-clad aluminum bare wire waste into a certain length (suitable for placing in the anode frame, 10cm in this embodiment).
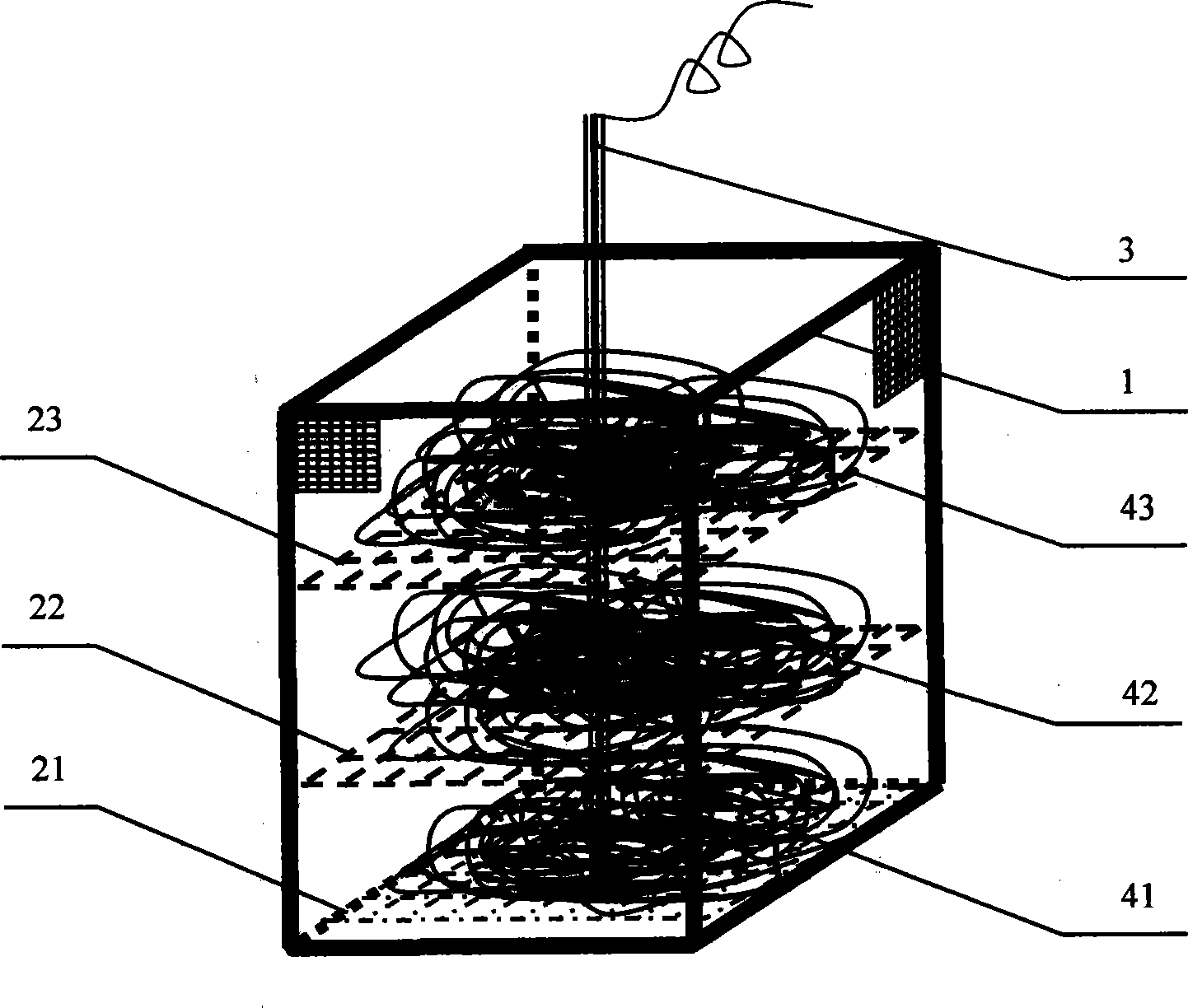
[0021] see figure 1 , the first titanium mesh 21 is placed in the porous plastic anode frame 1 with a porosity of 40%, and the copper-clad aluminum bare wire scrap is placed on the first titanium mesh 21 to form a first stack of copper-clad aluminum bare wires 41. The first The adjacent copper-clad aluminum bare wire scraps in the stacked copper-clad aluminum bare wires 41 are in contact with each other, and the copper-clad ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The method of the present embodiment is the same as the embodiment 1, and the difference is:
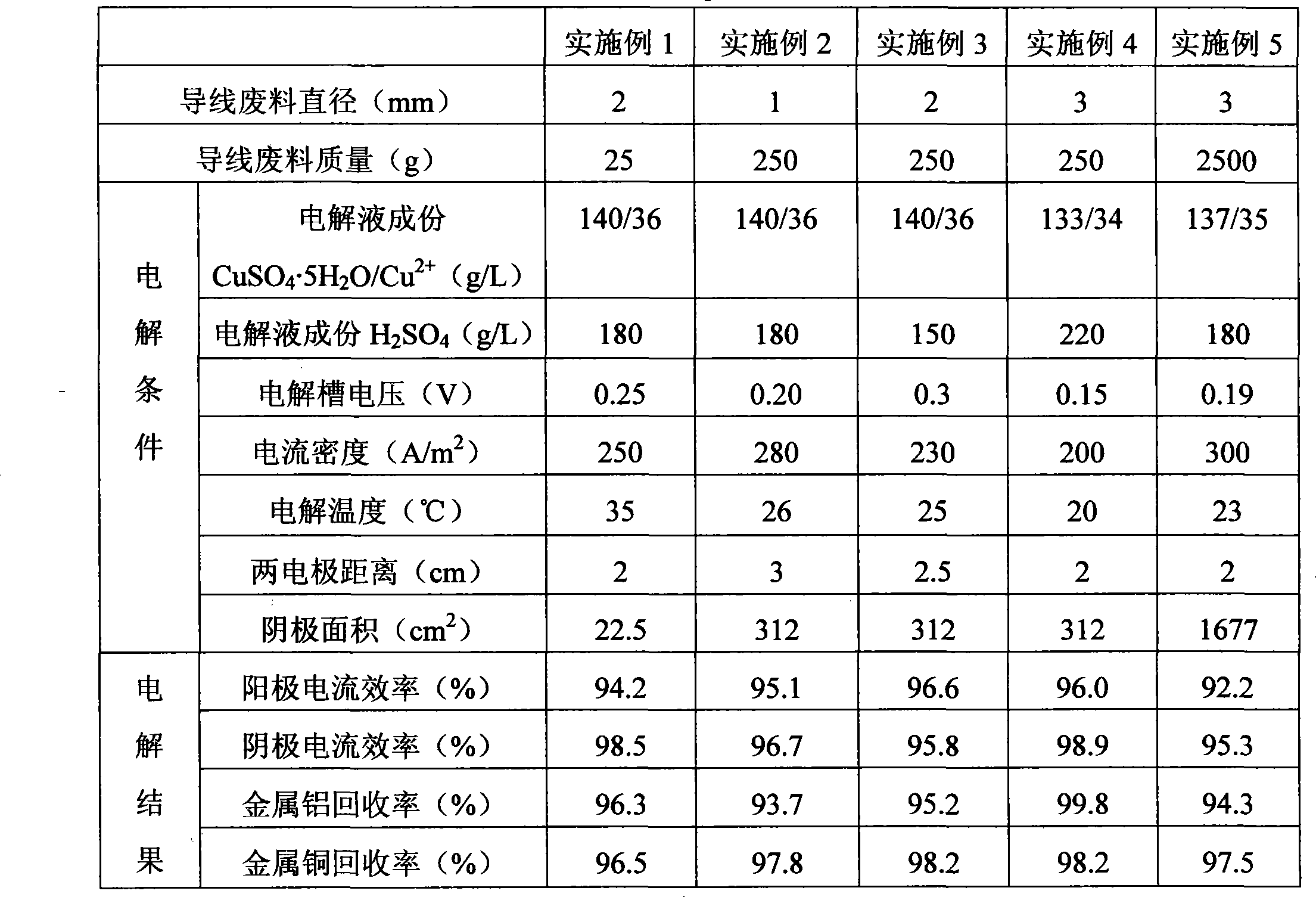
[0027] The diameter of the original copper-clad aluminum wire scrap is 1 mm and the mass is 250 g, and the plastic coating on the original copper-clad aluminum wire scrap is removed to obtain the copper-clad aluminum bare wire scrap. The electrolysis conditions and electrolysis results are shown in Table 1.
[0028] The anode device in step ① in this embodiment also has a second titanium mesh 22 and a copper-clad aluminum bare wire scrap placed on the second titanium mesh 22, and the copper-clad aluminum bare wire scrap placed on the second titanium mesh 22 is formed The second stack of copper-clad aluminum bare wires 42; the second titanium mesh 22 is placed on the top of the first stack of copper-clad aluminum bare wires 41, the bottom of which is in contact with the first stack of copper-clad aluminum bare wires 41, and the upper part is in contact with the second stack of ba...
Embodiment 3
[0031] The method of this embodiment is the same as that of embodiment 2, and the difference is: electrolysis conditions and electrolysis results (see Table 1).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com