Method for characterizing metal organic double layer thin film mass transfer microcosmic mechanism
A metal-organic, thin-film technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis by electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, difficult to obtain, and inability to accurately determine the microscopic mechanism of diffusion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
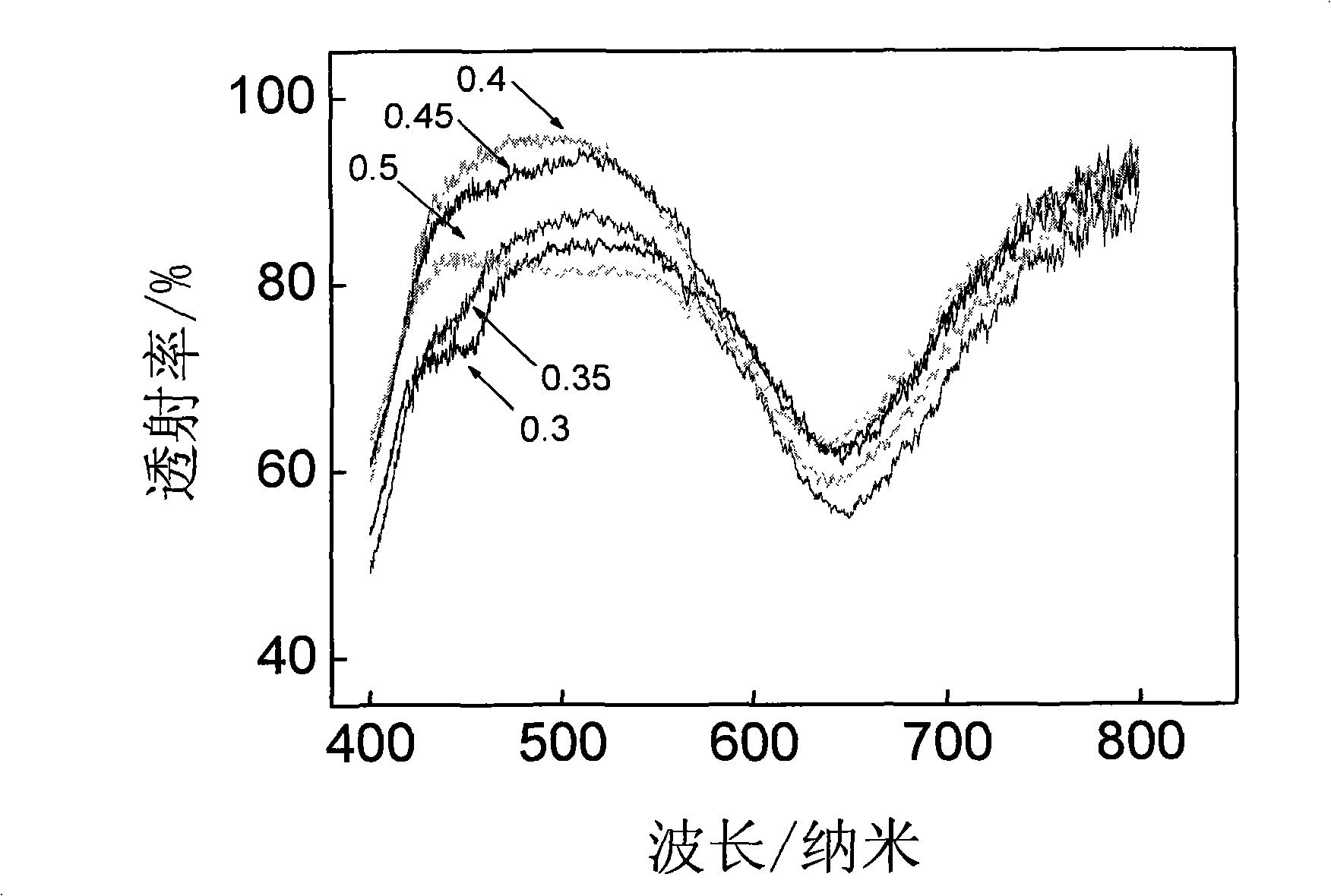
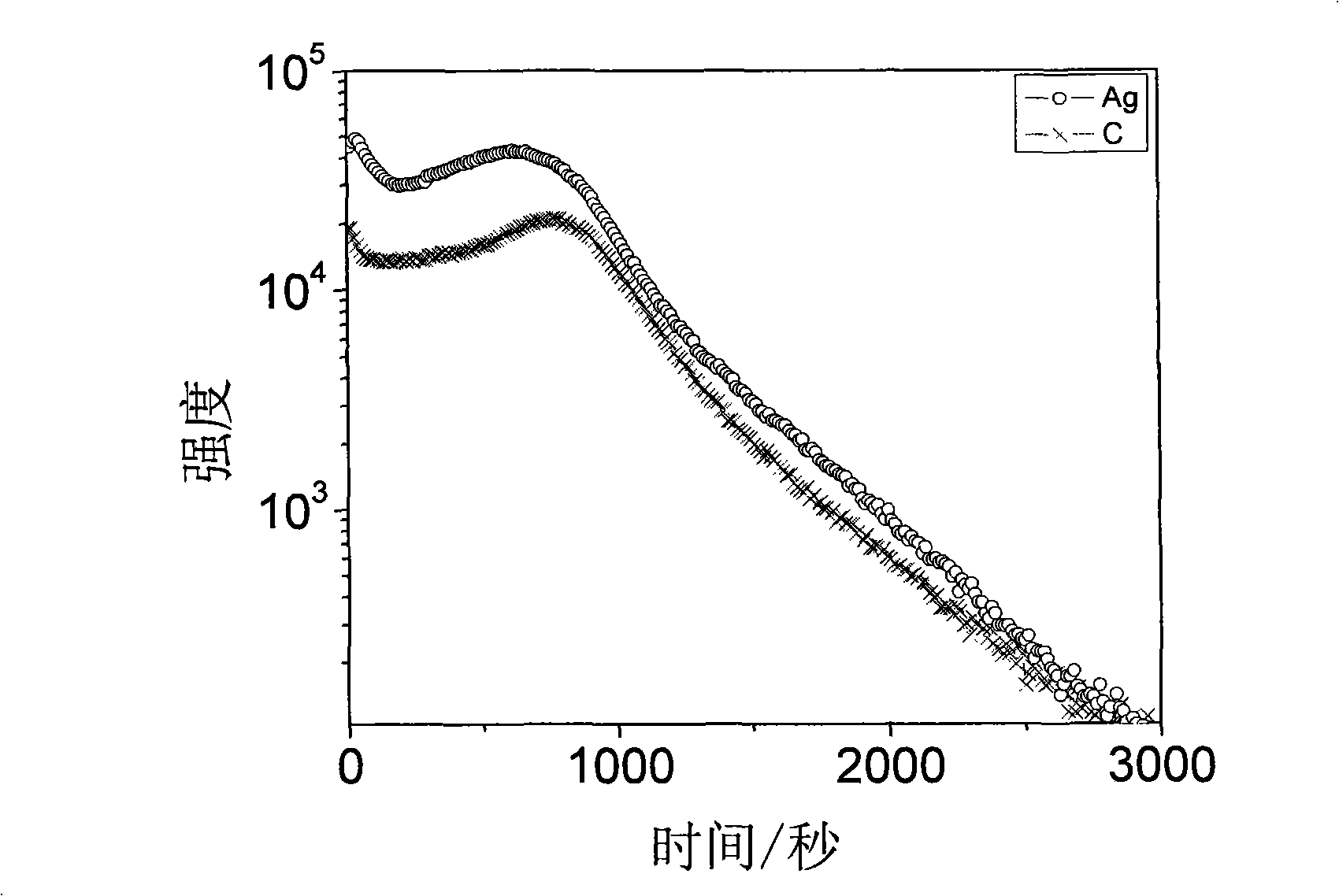
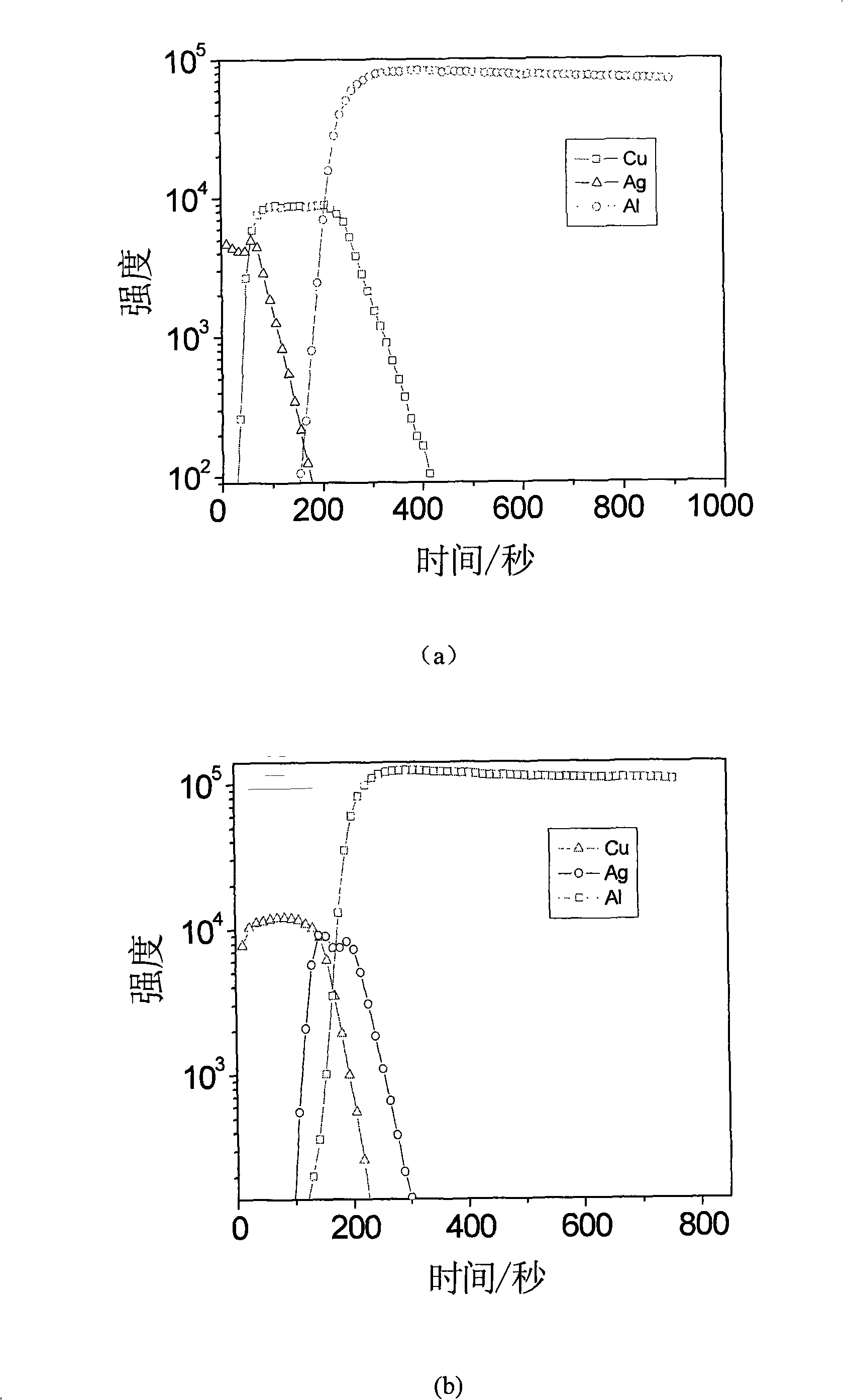
[0021] Firstly, the physical vapor deposition method is used at a vacuum degree of not less than 2×10 -3 Deposit a double-layer metal M on the substrate under the vacuum condition of Pa 1 , M 2 And use SIMS analysis to determine the metal layer M 1 There is no obvious interdiffusion phenomenon between M2 and M2; under the same conditions, metal / organic thin films with different thickness ratios are evaporated, and electrochemical reactions occur under certain conditions to form metal-organic complex thin films, which are determined by testing their transmission spectra. The optimal thickness ratio of the reaction; under the same vacuum condition, the metal M is sequentially evaporated on the substrate 1 (Heterogeneous Metal) Thin Film, Metal M 2 (Measurement metal) thin film, organic thin film, get M 1 ,M 2 , a three-layer film system of organic matter, wherein the ratio of the total thickness of the metal layer to the thickness of the organic matter is slightly greater t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com