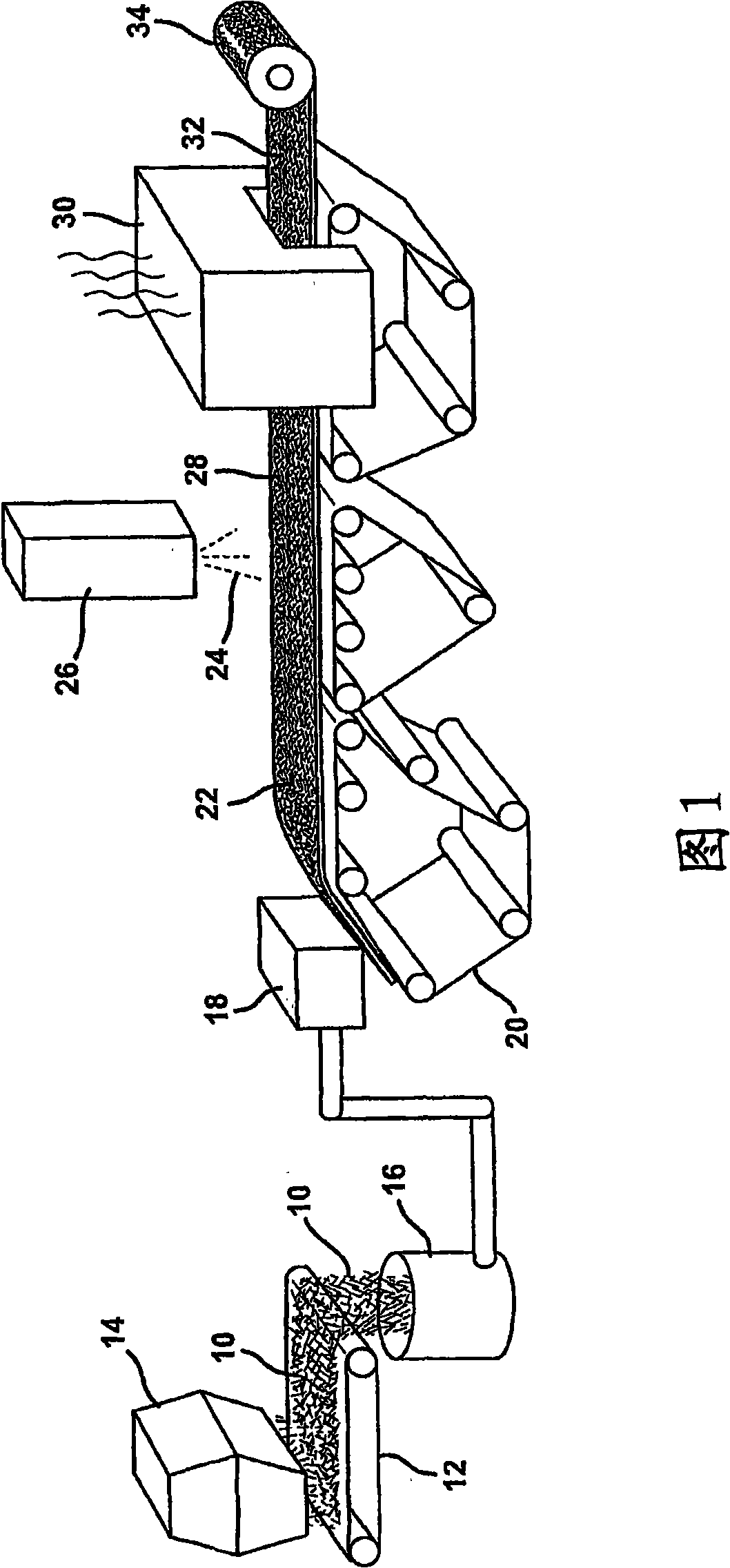
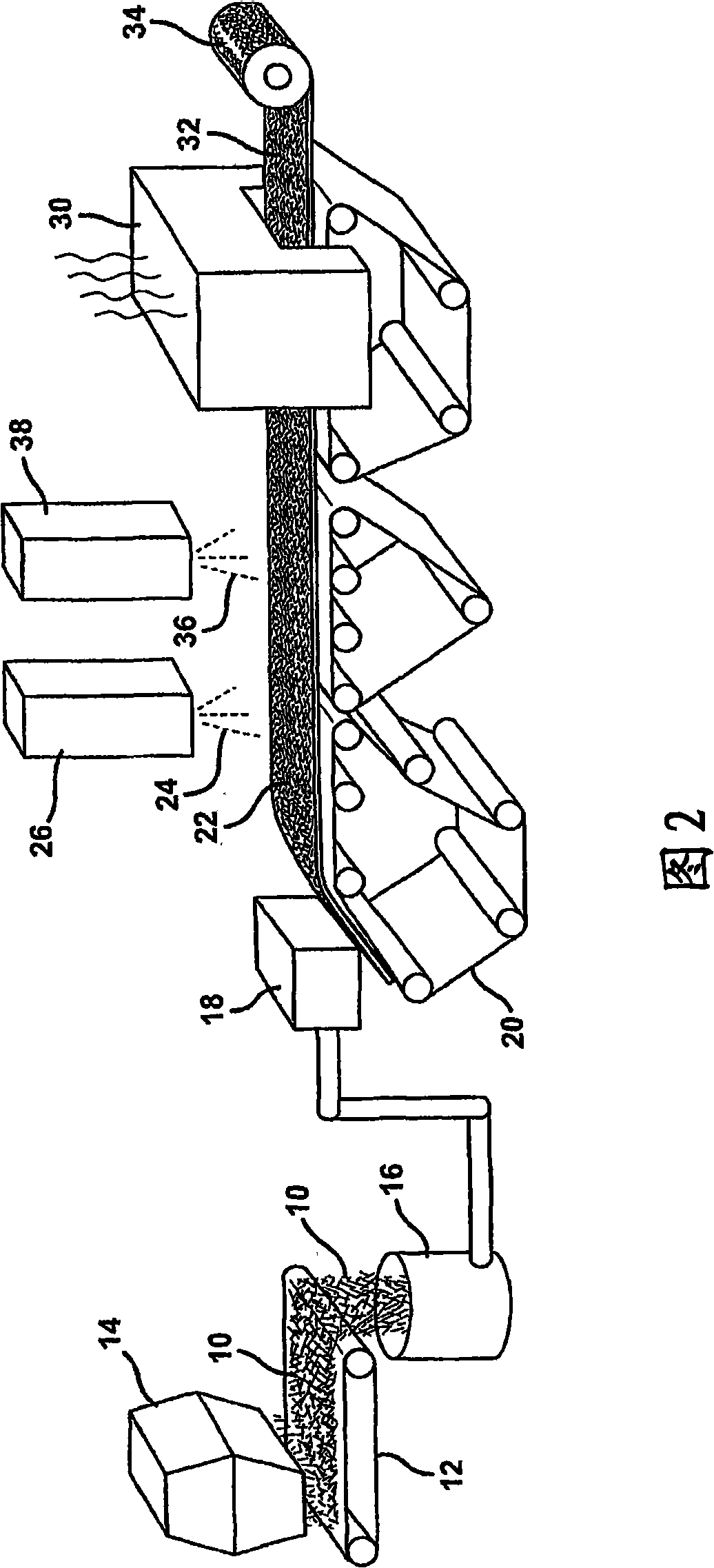
Wet formed mat having improved hot wet tensile strengths
A modified and original silk felt technology, which is applied in the direction of roofing using flexible materials, synthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paper, and non-fiber pulp addition, which can solve problems such as deterioration, increase productivity, and improve high temperature Effect of improving wet tensile strength and dry tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1: Chopped Glassogen Formed Using the Two-Part Adhesive Composition of the Invention High Temperature Tensile Strength Retention of Silk Mat
[0069] The adhesive compositions listed in Tables 2-6 were generally prepared in buckets as described below. Specifically, Comparative Adhesive Composition A (Table 2) was prepared by mixing a urea formaldehyde resin (Bordon FG 472 from Bordon Chemical Co.), a latex adhesive (DL 490NA from Dow Reichhold) and water.
[0070] Adhesive prepreparations for adhesive compositions B-E (Tables 3-6) of the present invention were prepared by mixing urea-formaldehyde resin (Bordon FG 472 from Bordon Chemical Co.), latex adhesive (DL 490NA from Dow Reichhold) and water. mixture. Mix acetic acid and water to form an acidic solution. Aminosilanes A-1100 and Y-9669 (GE Silicones) were added to the acidic solutions shown in Table 3-6 and stirred moderately for hydrolysis. The hydrolyzed aminosilane was then added to the adhesive p...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: Chopped Glassogen Formed Using the Two-Part Adhesive Composition of the Invention High Temperature Tensile Strength of Silk Mats and Panels
[0112] Using the adhesive compositions A, B and D listed in Tables 2, 3 and 5, respectively, the conventional sizing composition containing one or more film formers, at least one lubricant and a coupling agent The sized Type E chopped strand glass fibers were formed into a chopped glass strand mat on a flat plate former. Chopped strand glass fibers have a length of 1 1 / 4 inches, with a moisture content of 13.22%. The chopped strand mat using Binder Composition A (comparative) was replicated to demonstrate the reproducibility of the forming process and the average data from the two experiments was used as the Binder Composition A data in Tables 9 and 10. The wet tensile strength of 2 inch wide chopped strand mat test samples containing Adhesive Compositions A, B and D was then measured on an Instron tensile test...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Example 3: Chopped Glassogen Formed Using the Two-Part Adhesive Composition of the Invention High Temperature Tensile Strength of Silk Mats and Panels
[0122] The use of adhesive compositions A, B, and D listed in Tables 2, 3, and 5, respectively, facilitates the use of conventional sizing combinations containing one or more film formers, at least one lubricant, and at least one coupling agent The sized E-type chopped strand glass fibers were formed into a chopped glass strand mat on a flat plate former. Chopped glass fibers have a length of 1 1 / 4inches, with a moisture content of 13.69%. The chopped strand mat using Binder Composition A (comparative) was replicated to demonstrate the reproducibility of the forming process and the average data from the two experiments was used as the data for Binder Composition A in Tables 11 and 12. The wet tensile strength of chopped strand mats was determined according to the procedure outlined in Example 2. The experiment...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com