Method for rapid quantitatively evaluating interaction of medicament nucleic acids
A quantitative evaluation and drug technology, applied in the fields of chemistry and physical sciences, can solve the problems of time-consuming, high equipment, etc., and achieve the effects of simple operation, less sample consumption, huge scientific value and economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
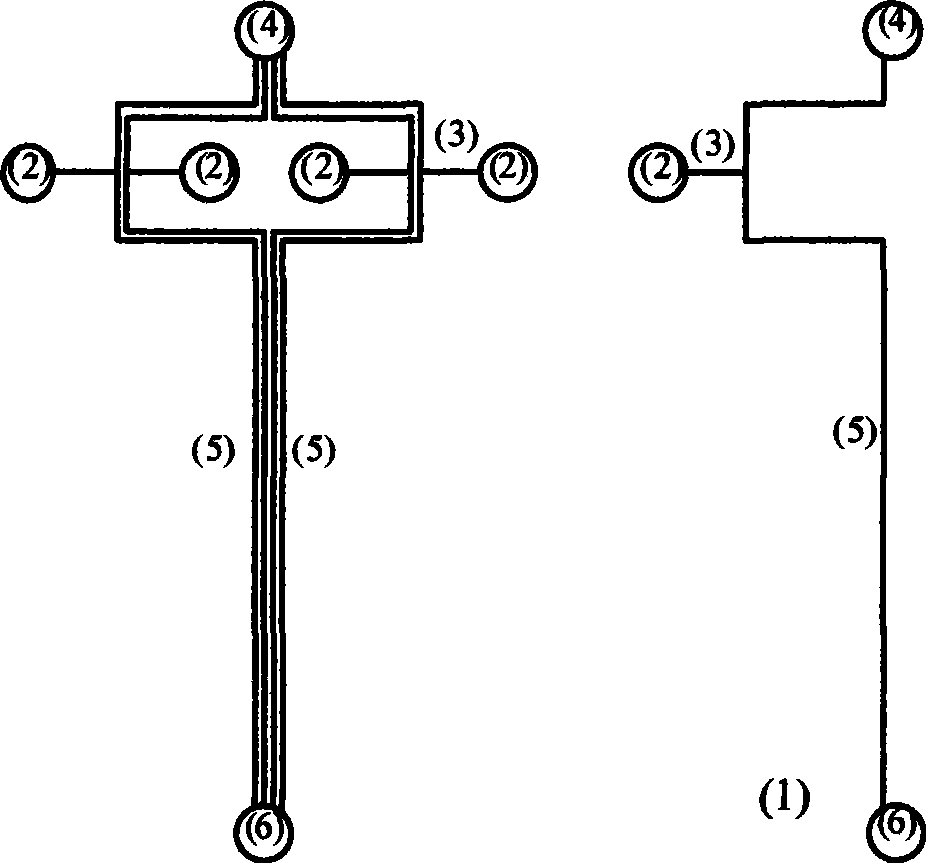
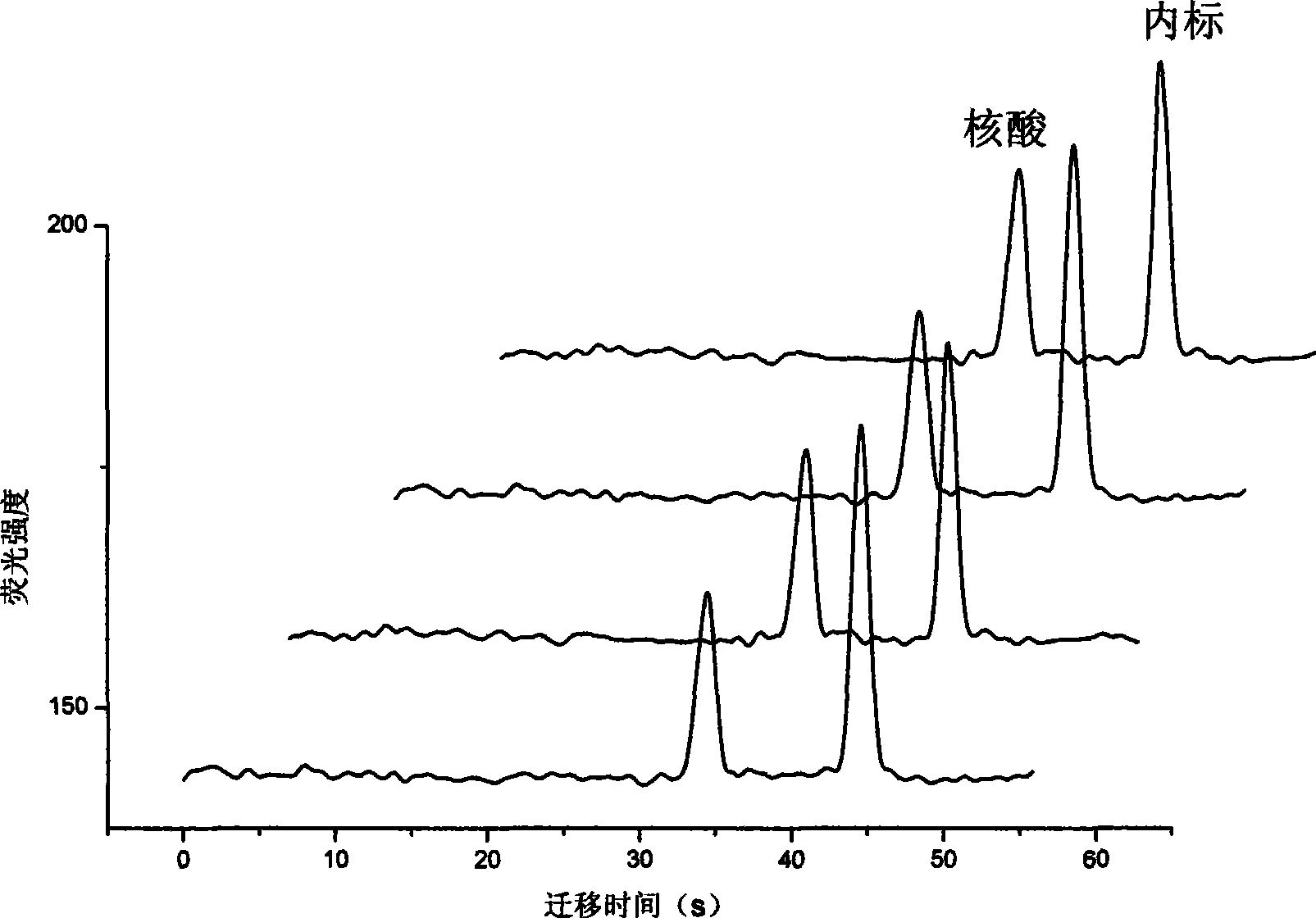
[0026] Assay for fluorescently labeled nucleic acids. The chips used in this experiment are figure 1 Shown is a glass chip containing four electrophoretic cells with channels 50 μm wide and 15 μm deep. Put the buffer into the buffer reservoir (4), and apply negative pressure to fill the buffer with the separation channel (5) and the waste liquid pool (6), mix 10 μM fluorescently labeled nucleic acid with 10 μM internal standard fluorescein, and mix the four Parts of the sample are added to the sample cell (2). Apply a voltage (field strength 400V) between the sample cell (2) and the waste liquid cell (6) for 6 seconds, then switch the voltage to between the buffer solution reservoir (4) and the waste liquid cell (6) (field strength 400V) strong 400V), the sample cell (2) applies a suppression voltage to prevent sample leakage, and is detected at a distance of 3cm from the injection point (results see figure 2 ). It can be seen from the figure that the peak area ratios of ...
Embodiment 2
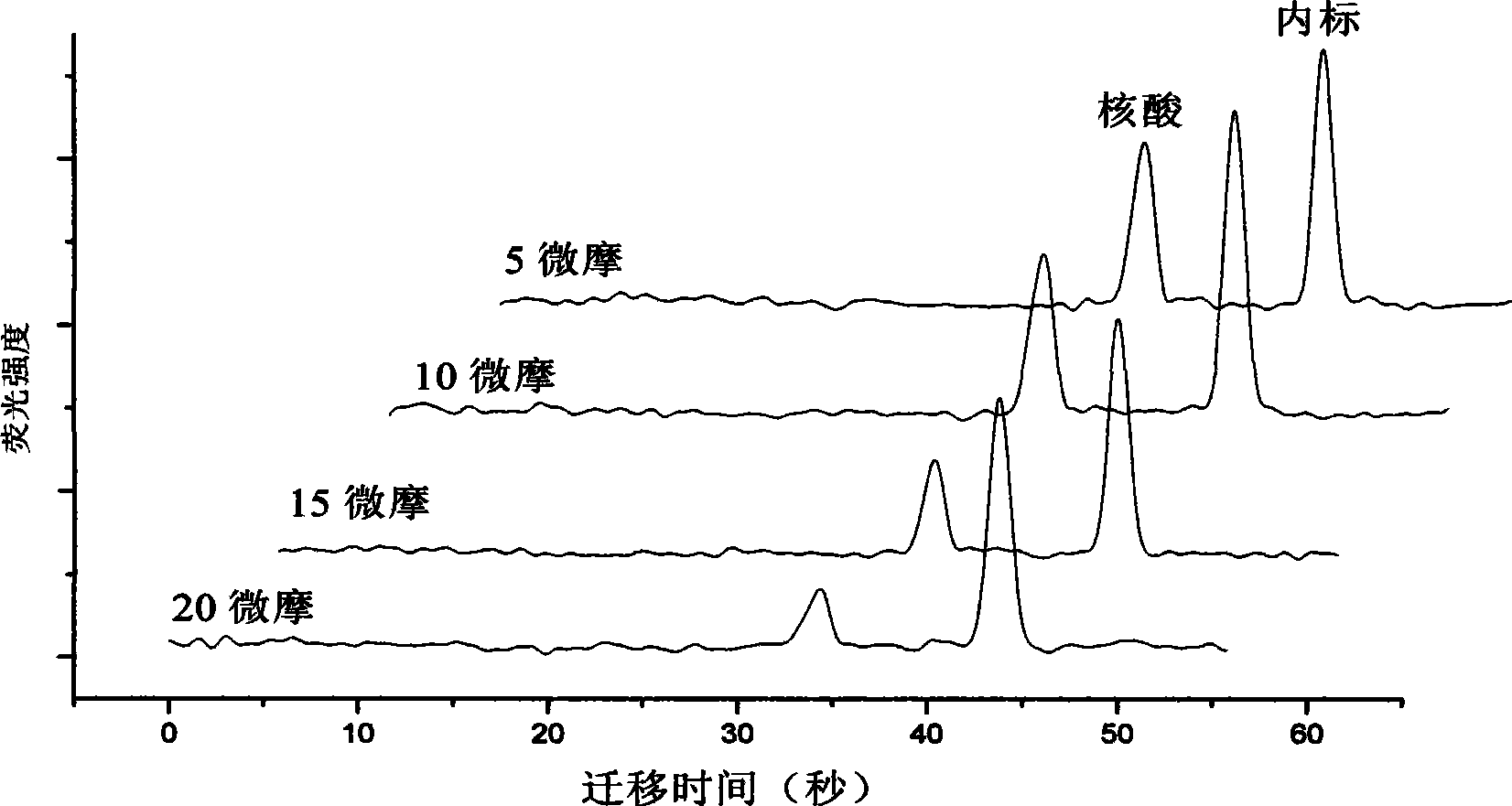
[0028] Determination of the binding constant of netropsin and nucleic acid. The chips used in this experiment are figure 1 Shown is a glass chip containing four electrophoretic cells with channels 50 μm wide and 15 μm deep. Put the buffer into the buffer reservoir (4), and apply negative pressure to fill the buffer with the separation channel (5) and the waste liquid pool (6), and mix the netlastin and the fluorescently labeled nucleic acid at a ratio of 0.5:1-2: 1 Concentration ratio mixing (10 μM internal standard fluorescein is added), and four mixed solutions with different concentration ratios are added to the sample pool (2). Apply a voltage (field strength 400V) between the sample cell (2) and the waste liquid cell (6) for 6 seconds, then switch the voltage to between the buffer solution reservoir (4) and the waste liquid cell (6) (field strength 400V) strong 400V), the sample cell (2) applies a suppression voltage to prevent sample leakage, and is detected at a dista...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com