Holmium-contained Nd-Fe-B rare earth permanent magnetic material and manufacturing method thereof
A rare earth permanent magnet and neodymium iron boron technology, applied in the field of magnetic materials, can solve problems such as unspecified Ho, and achieve the effect of reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
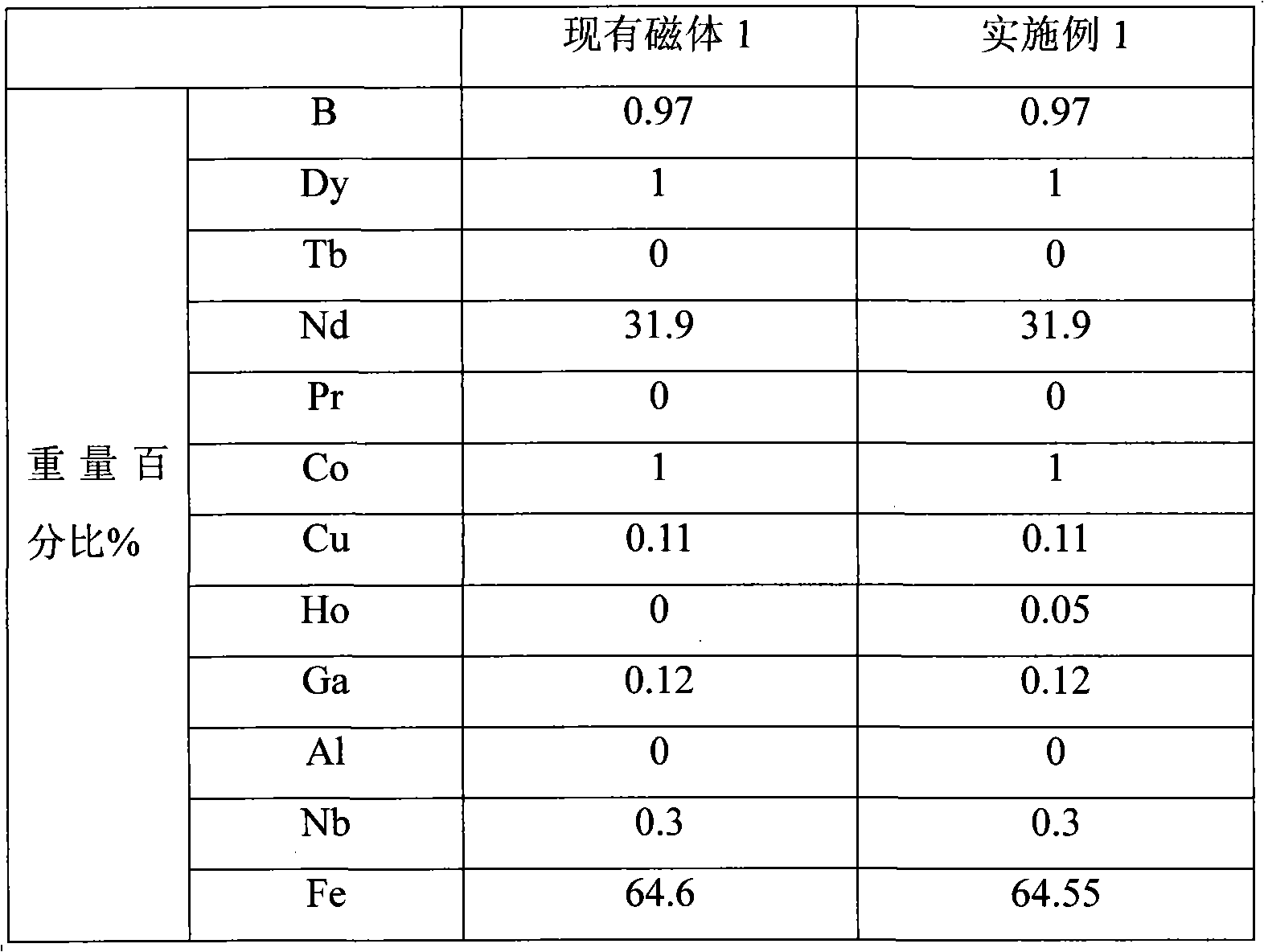
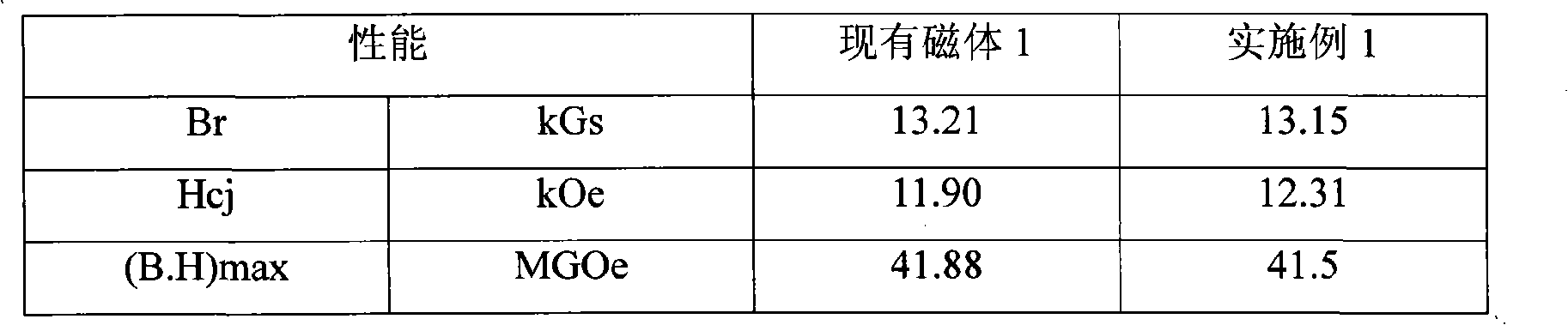
[0044]A kind of neodymium iron boron rare earth permanent magnet material containing holmium, according to the batching described in following table 1:
[0045] Table 1
[0046]
[0047] Then adopt following steps to prepare NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet material:
[0048] (1) Smelting-casting: the raw materials are formed into molten alloy liquid by vacuum melting method, and then the molten alloy liquid is cast and cooled into a book-shaped alloy ingot with a thickness of about 20 mm;
[0049] (2) Pulverization: the ingot is pulverized into powder by the hydrogen crushing method, the average particle size is <1 mm, and pulverization: the powder with the average particle size of 3-5 μm is made by the jet mill method;
[0050] (3) Forming: the powder is pressed into a compact by molding;
[0051] (4) Sintering: sintering the compact in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1080°C for 4 hours;
[0052] (5) Tempering: Tempering the sintered compact in a vacuum sintering furnac...
Embodiment 2
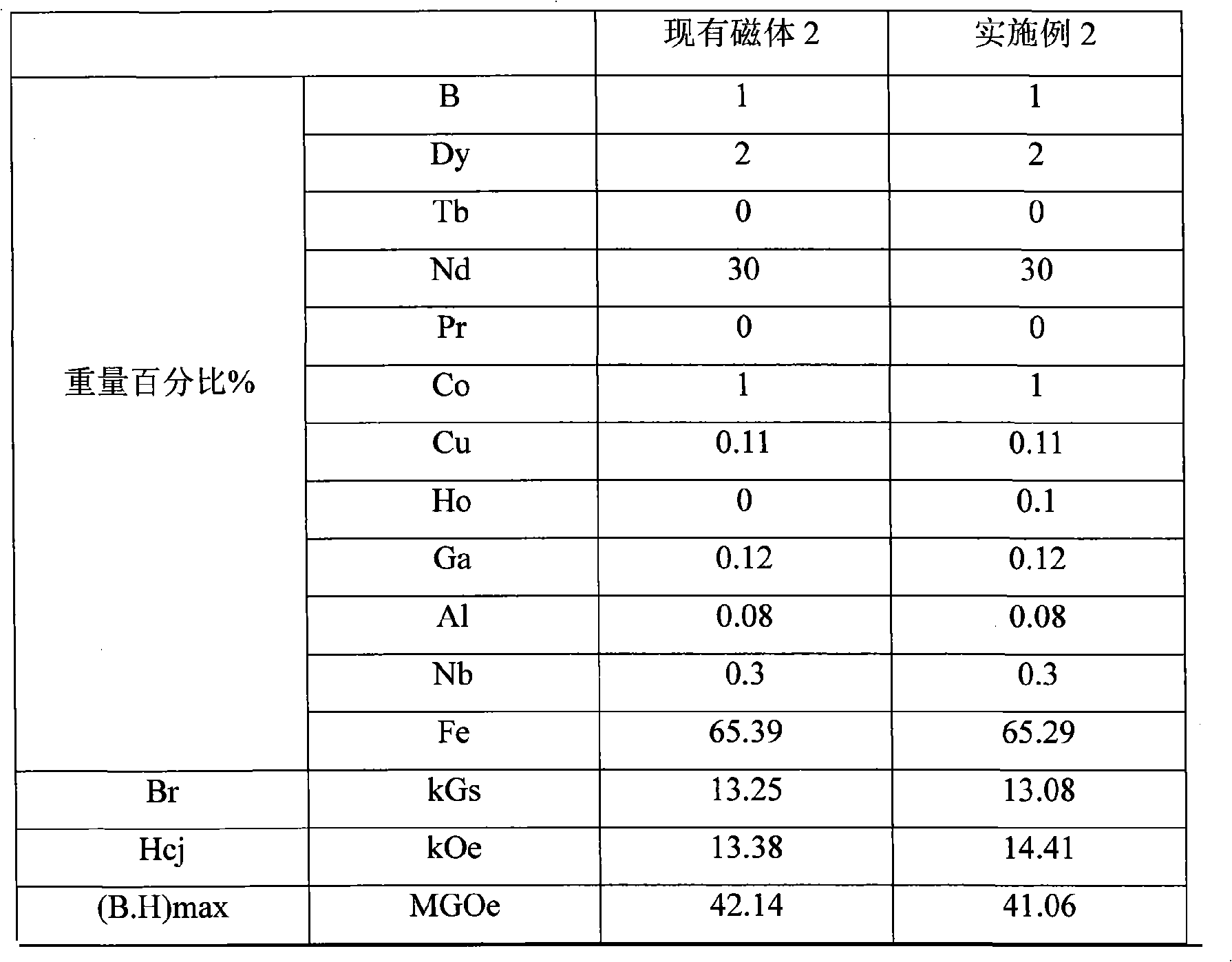
[0059] The smelting step adopts vacuum smelting; the thickness of the alloy ingot is about 10mm; the ingot is crushed into powder by the mechanical coarse crushing method, and the average particle size is <1mm; forming: forming by molding and cooling isostatic pressing; sintering: the blank after forming Carry out sintering at 1085° C. for 1 hour in a vacuum sintering furnace; finally temper at 500° C. for 1 hour, and the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet materials. See Table 3 for the results.
[0060] table 3
[0061]
[0062] By comparison, it can be found that the Hcj of the magnet of Example 2 added with Ho is 1.03 kOe higher than that of the existing magnet 2 without Gd added.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The smelting process adopts vacuum smelting, and the alloy ingot with a thickness of about 0.3mm is used; the solution heat treatment process (1090°C) is used between the casting and crushing processes; the ingot is crushed into powder by hydrogen crushing method, and the average particle size is <1mm; forming : Formed by rubber molding method; vacuum sintering furnace temperature is 1085°C, tempering temperature is 480°C, and the remaining steps are the same as implementation 1 to obtain NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet materials. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0065] Table 4
[0066]
[0067] By comparison, it can be found that the Hcj of the magnet of Example 3 added with Gd is 0.983 kOe higher than that of the existing magnet 3 without Ho added.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com