Building board combining magnesium compounds and plant fibre and preparation method thereof
A technology of plant fibers and building boards, applied in the direction of solid waste management, sustainable waste treatment, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as ecological environment damage, achieve high mechanical performance, high economic and social benefits, and smooth surface Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] The main steps of building panels using magnesium compounds mixed with plant fibers are as follows:
[0079] A. Weigh each component as shown in Table 1, fully mix the aggregate, modified modifier, and thickening and toughening agent, grind after mixing, carbonize at 68°C, and homogenize at 20°C;
[0080] B, processing powder: the powder after above-mentioned homogenization is added water and stirred according to the ratio of 1: 1, obtains pasty mixture;
[0081] C. Making boards: add fillers to the pasty mixture, stir evenly, and then spread it on the glass cloth, the cloth size is 13×5×5, and then stack the multi-layer glass cloth, and the twisted cloth used for the surface layer is 13 ×6 mesh, formed by rolling with rollers; width 122×length 244×thickness 1.2-1.5.
[0082] D. Curing: The temperature is 55 ℃, drying and curing for 7 days.
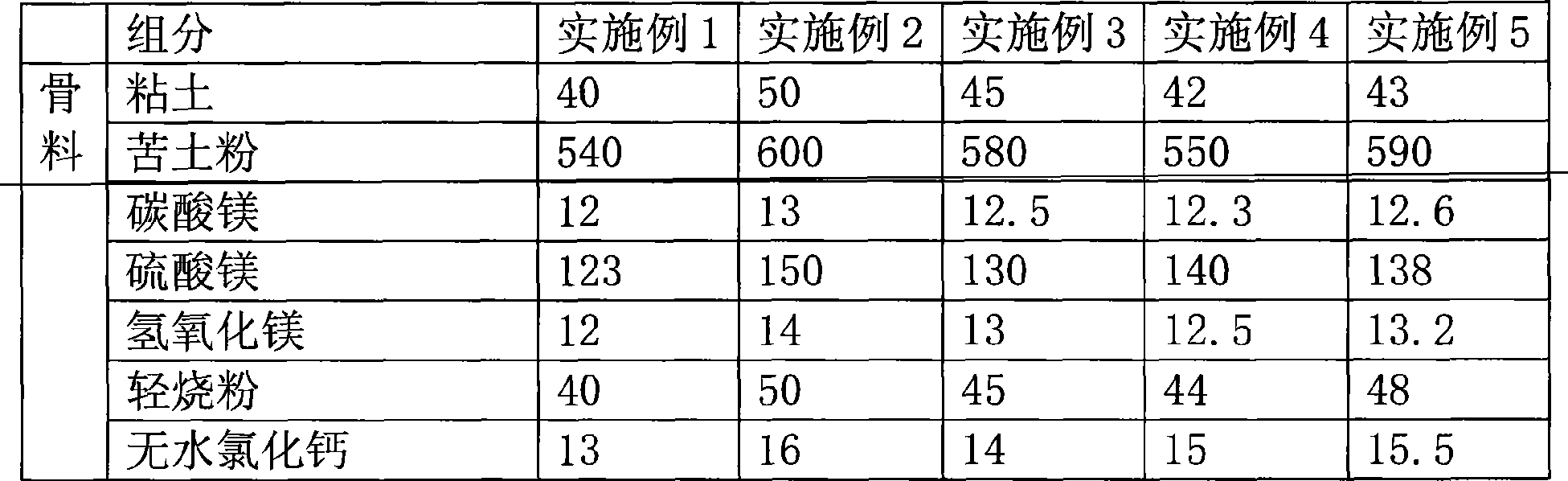
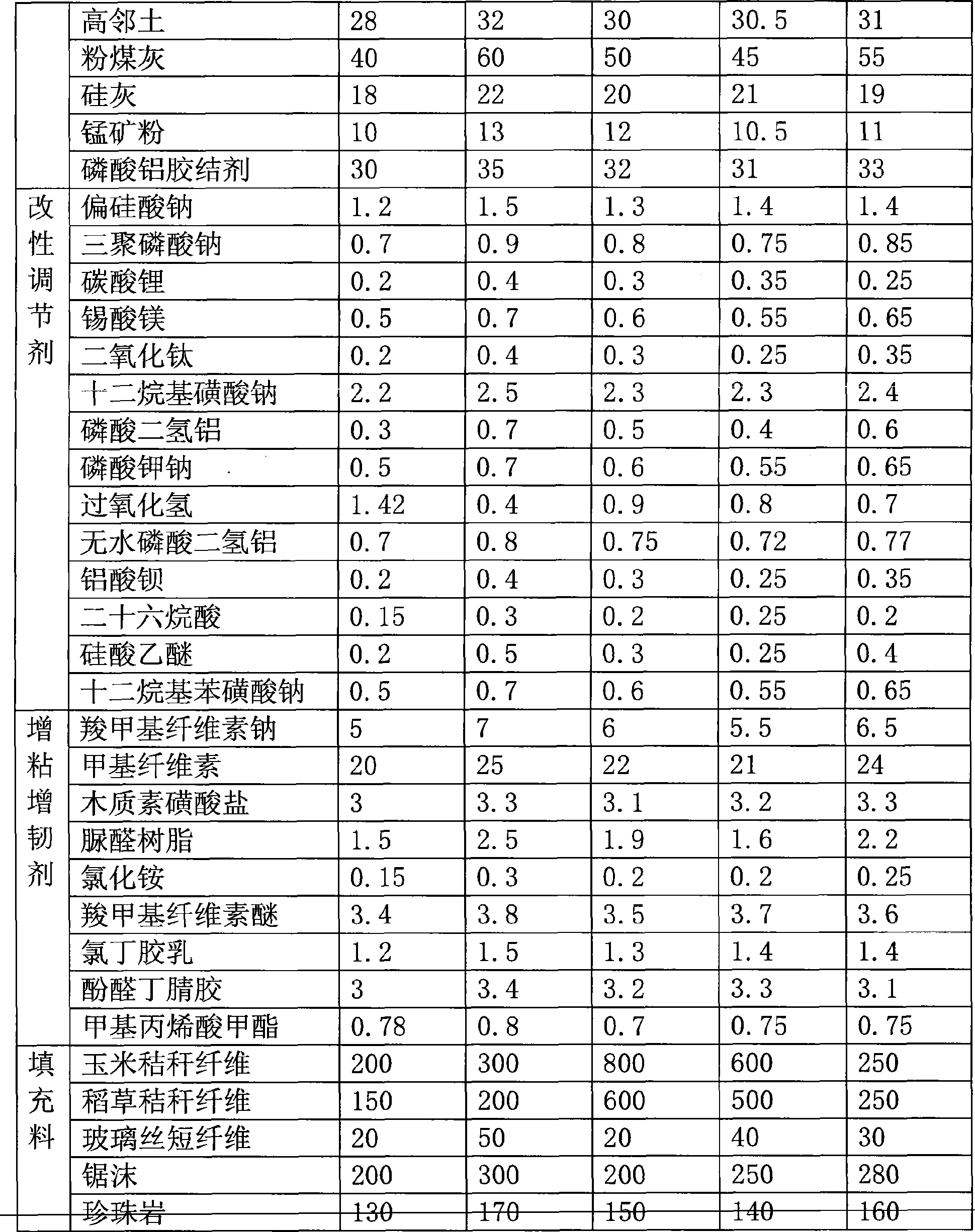
[0083] Table 1 Distribution ratio of each group (unit: kilogram)
[0084]
[0085]
Embodiment 2
[0087] The main steps of building panels using magnesium compounds mixed with plant fibers are as follows:
[0088] A. Weigh each component as shown in Table 1, fully mix the aggregate, modified modifier, and thickening and toughening agent, grind after mixing, carbonize at 72°C, and homogenize at 22°C;
[0089] B, processing powder: the powder after above-mentioned homogenization is added water and stirred according to the ratio of 1: 1.2, obtains pasty mixture;
[0090] C. Making boards: add fillers to the pasty mixture, stir evenly, and then spread it on the glass cloth, the cloth size is 13×5×5, and then stack the multi-layer glass cloth, and the twisted cloth used for the surface layer is 13 ×6 mesh, formed by rolling with rollers; width 122×length 244×thickness 1.2-1.5.
[0091] D. Curing: temperature 65 ℃, drying and curing for 6 days.
Embodiment 3
[0093] The main steps of building panels using magnesium compounds mixed with plant fibers are as follows:
[0094] A. Weigh each component as shown in Table 1, fully mix the aggregate, modified modifier, and thickening and toughening agent, grind after mixing, carbonize at 65°C, and homogenize at 18°C;
[0095] B, processing powder: the powder after above-mentioned homogenization is added water and stirred according to the ratio of 1: 1.5, obtains pasty mixture;
[0096] C. Making boards: add fillers to the pasty mixture, stir evenly, and then spread it on the glass cloth, the cloth size is 13×5×5, and then stack the multi-layer glass cloth, and the twisted cloth used for the surface layer is 13 ×6 mesh, formed by rolling with rollers; width 122×length 244×thickness 1.2-1.5.
[0097] D. Curing: The temperature is 45 ℃, drying and curing for 8 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com