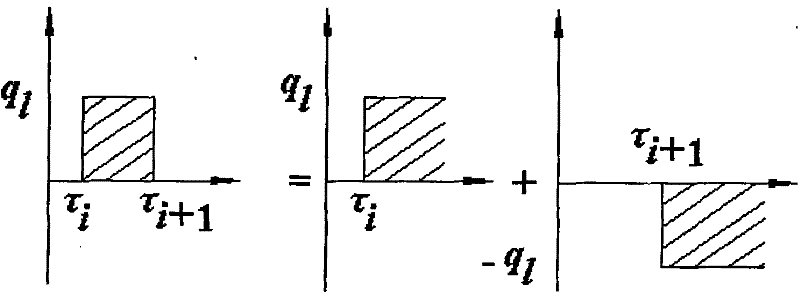Rock thermophysics on-site test method under non-constant power condition
A field test, non-constant technology, used in soil material testing, measuring devices, thermal analysis of materials, etc., can solve problems such as long test cycle, unstable power, test failure, etc., to reduce test costs and reduce stability requirements , the effect of shortening the test time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
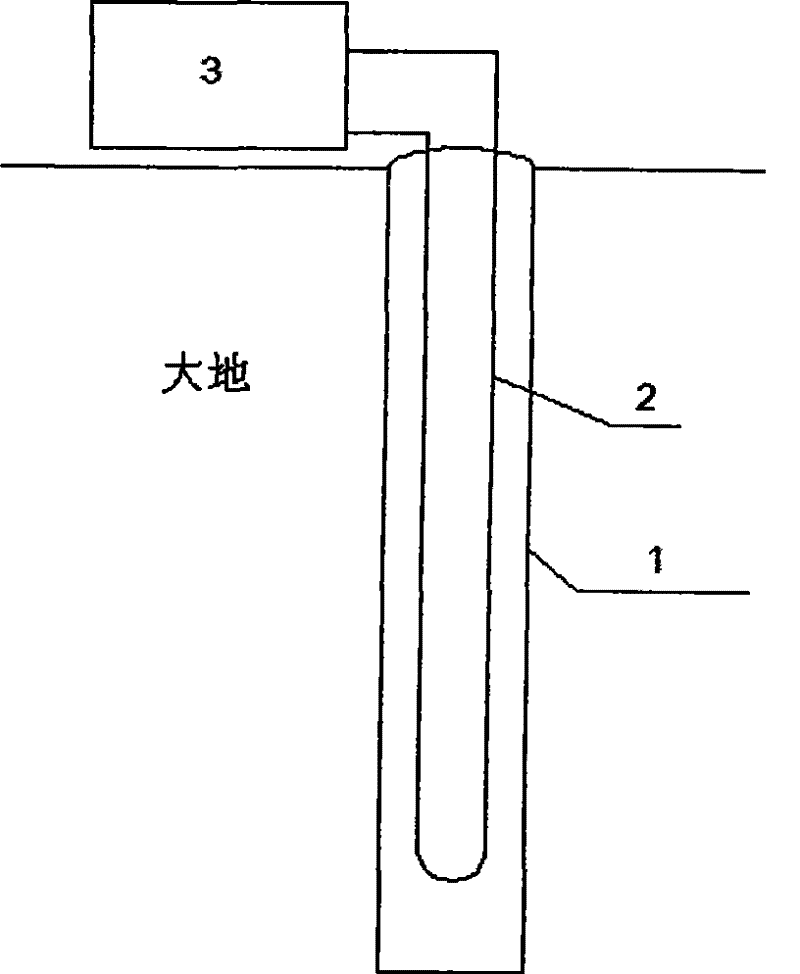
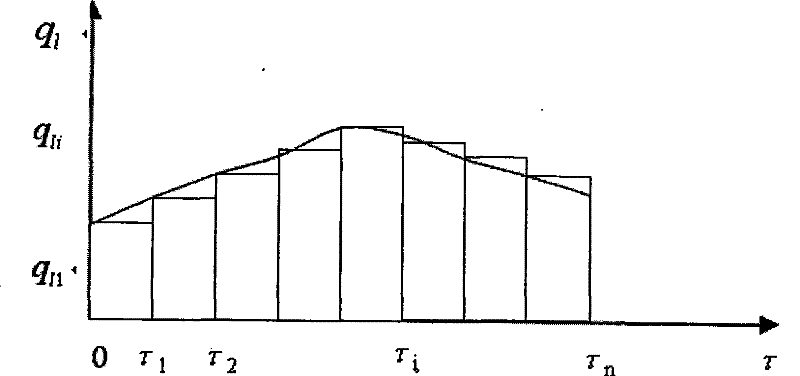
[0058] The method of the invention is used to test the thermal physical parameters of underground rock and soil in a construction site. In this test, the depth of the buried pipe is 100 meters, and the geological composition is: 1-3 meters is clay, and 3-100 meters is sandstone. About 24 hours after the start of the test, the heating of the tester was interrupted for about 40 minutes due to power supply. After restarting the heater, the test continued for about 4 hours, and the heating was interrupted again for about 14 hours due to power supply. Thereafter, restart the heater again, continue the test for about 6 hours, and then stop the test. The test results show that the average thermal conductivity of underground rock and soil is 3.18W / m℃, and the average volumetric specific heat is 2.59×10 6 J / m3 ℃. Figure 4 It is the comparison between the actual measurement of the change of the average temperature of the circulating water in the buried pipe with time and the average...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com