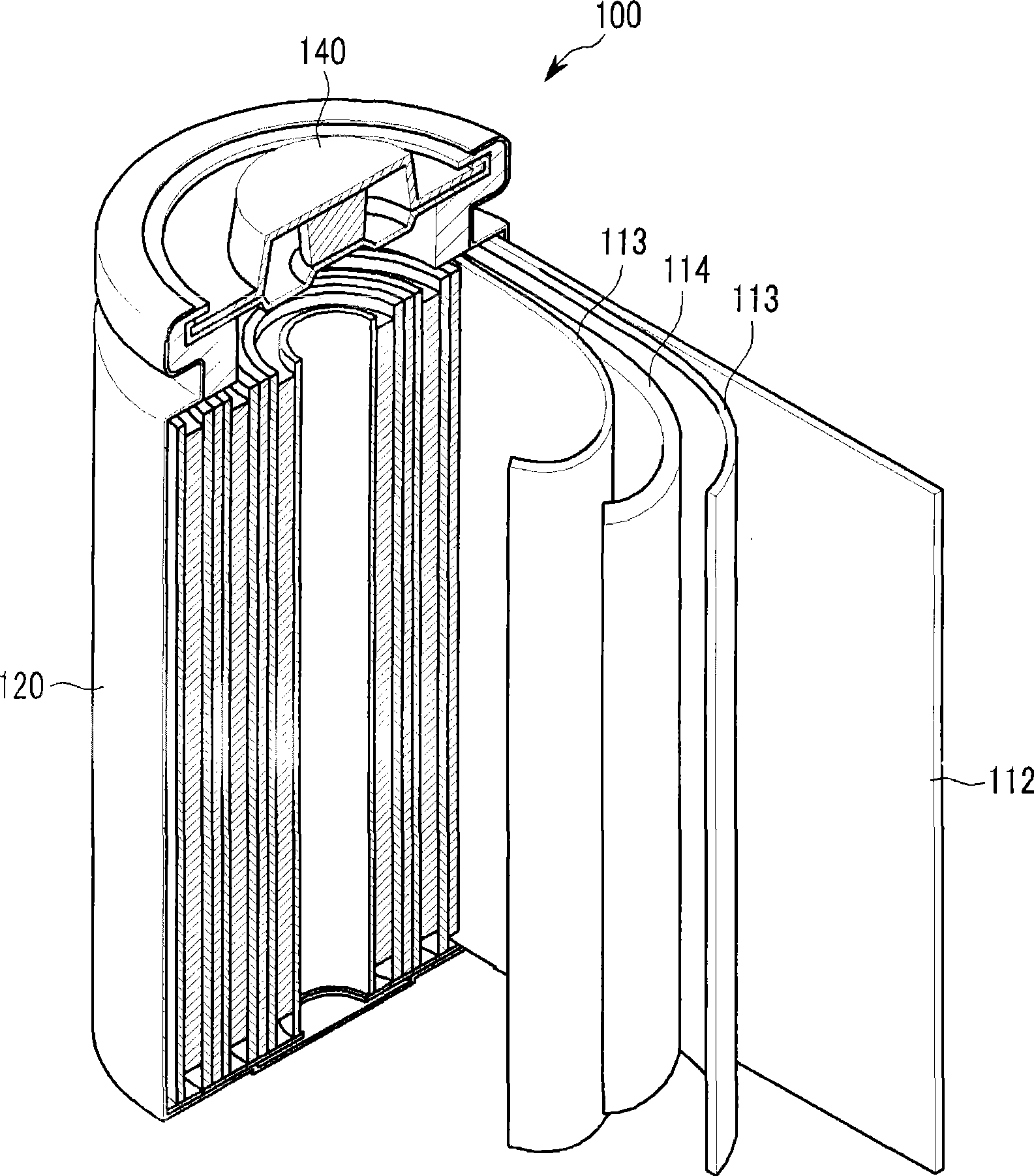
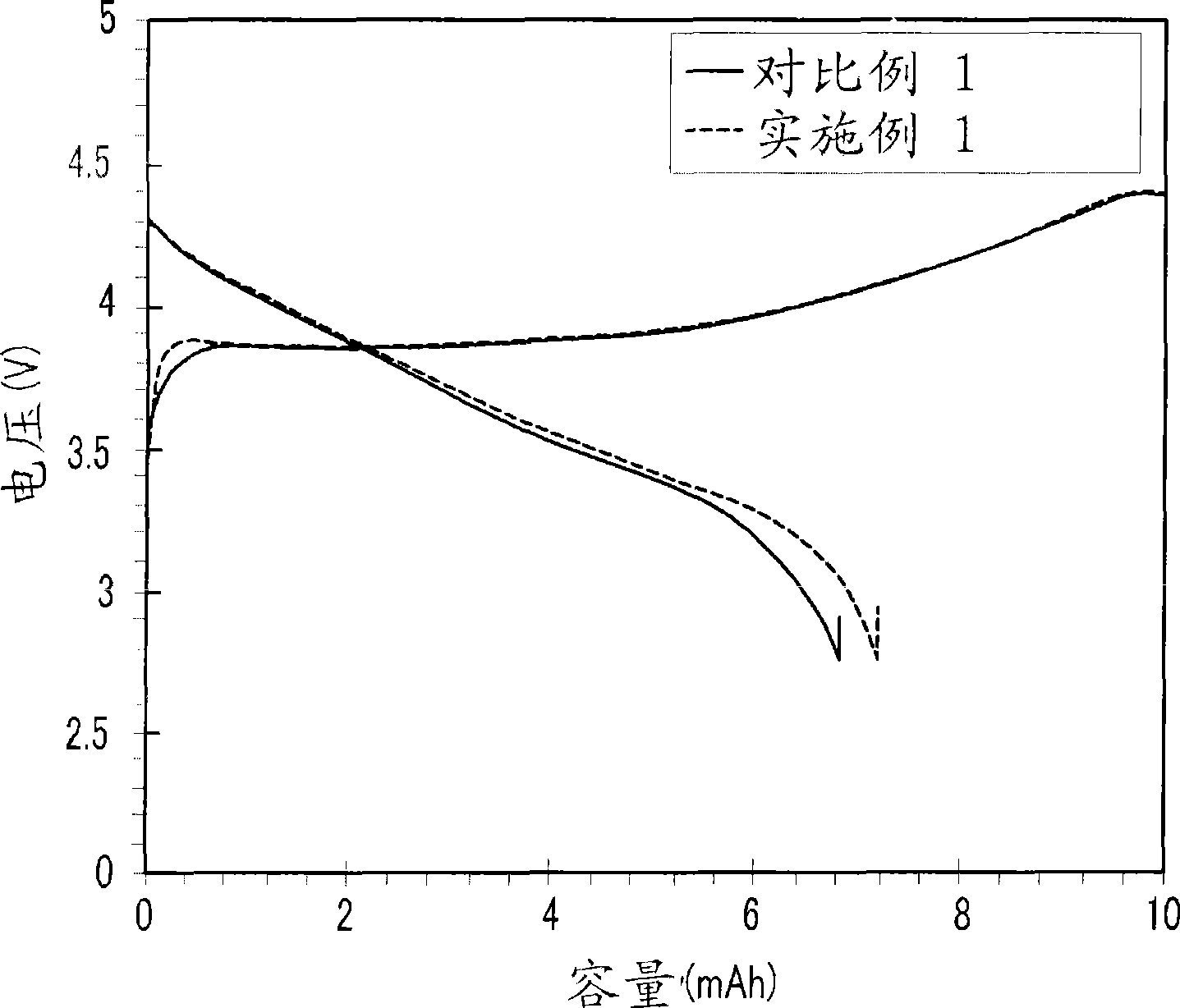
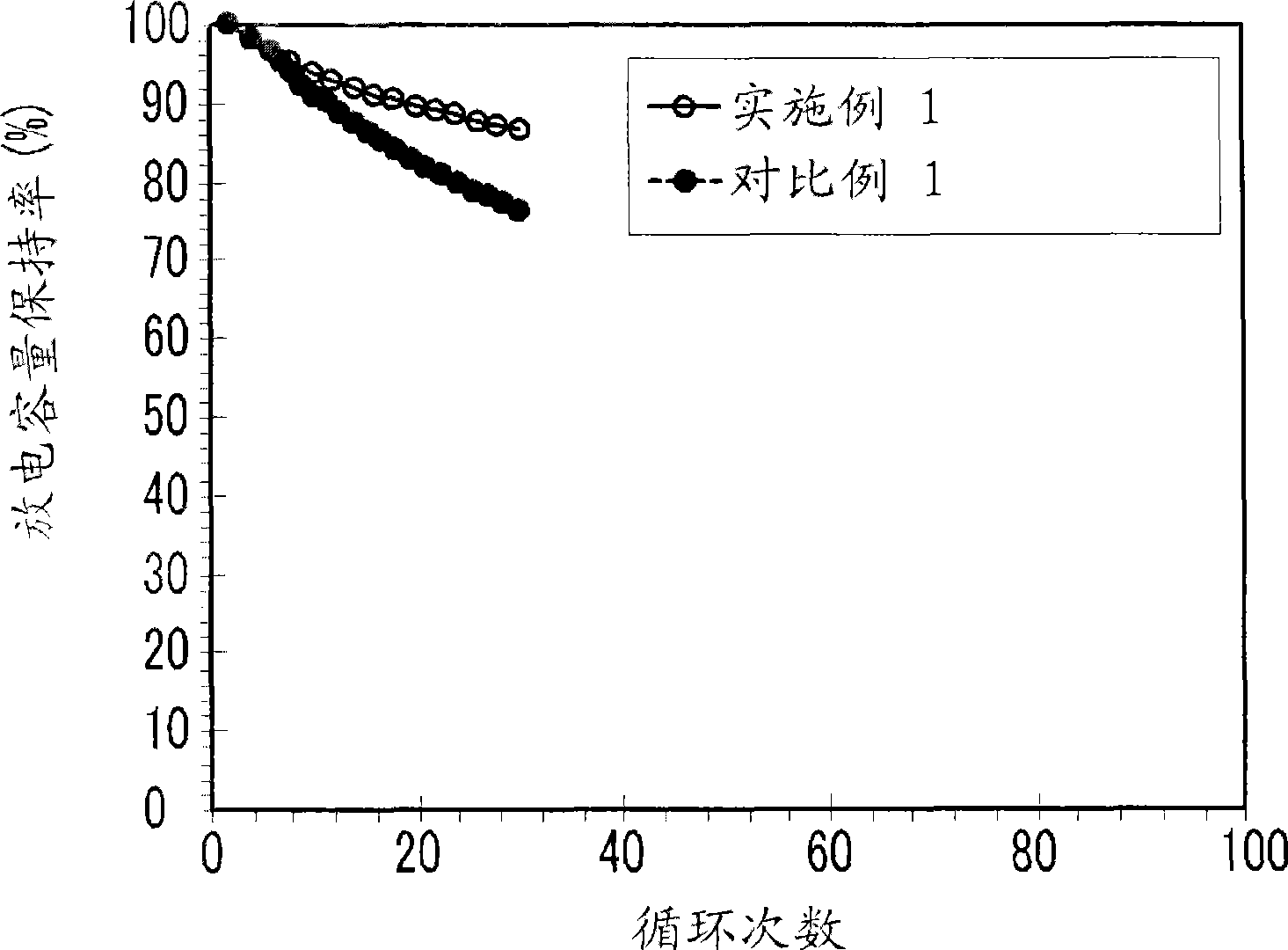
Negative electrode for rechargeable lithium battery, and rechargeable lithium battery including the same
A lithium battery and recharging technology, applied in the field of rechargeable lithium battery and negative electrode for rechargeable lithium battery, can solve the problem of not showing sufficient improvement in battery performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0200] Embodiment 1: the making of negative electrode
[0201] Silica negative electrode active material (SHR12, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.) was mixed with carboxymethylcellulose with a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 90,000 dissolved in water and polyacrylic acid with a Mw of 100,000 dissolved in water , to provide a composition for forming an active material layer. Carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylic acid are provided at a molar ratio of 73.5:26.5 according to dry state calculation, and the obtained mixture includes 93 wt% of silicon oxide negative electrode active material, 5 wt% of carboxymethyl cellulose and 2 wt% of polyacrylic acid.
[0202] The composition for forming the active material layer was screen-printed on the Cu current collector, and then heat-treated at 90°C. Next, at 200°C and a vacuum pressure of 1×10 -6 It was heat-treated again under the support to provide a negative electrode.
Embodiment 2
[0203] Embodiment 2: the making of negative electrode
[0204] Mix 93wt% of silica negative electrode active material (SHR12, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.), 4wt% of carboxymethyl cellulose, 2wt% of polyacrylic acid and 1wt% of conductive agent Super-P in water to provide Composition for forming an active material layer (mixture of carboxymethylcellulose and polyacrylic acid having a molar ratio of 69:31).
[0205] The composition for forming the active material layer was screen-printed on the Cu current collector, and then heat-treated at 90°C. Next, at 200°C and a vacuum pressure of 1×10 -6 It was heat-treated again under the support to provide a negative electrode.
Embodiment 3
[0264] Embodiment 3: the making of negative electrode
[0265] A composition for forming an active material layer was prepared by uniformly mixing 93 wt% of a silicon oxide negative electrode active material (available from Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.) and 7 wt% of a binder composition. The adhesive composition is prepared by mixing carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) with a Mw of 90,000 dissolved in water, polyacrylic acid (PAA) with a Mw of 100,000 dissolved in water, and polyvinyl chloride in a weight ratio of 1:1:1. Vinyl fluoride (PVdF) (available from Solvay Company, Hylar Latex 932).
[0266] The composition for forming the active material layer was screen-printed on the Cu current collector, and then heat-treated at 90°C. Next, at 200°C and a vacuum pressure of 1×10 -6 It was heat-treated again under the support to provide a negative electrode.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bond strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bond strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com