Six-beam structure acceleration sensor and method for making same
An acceleration sensor and beam structure technology, applied in the field of sensor structure, can solve the problems of electrical quantity output and mismatch at the detection end, and achieve the effect of flexible design, reducing interference and increasing the bonding area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
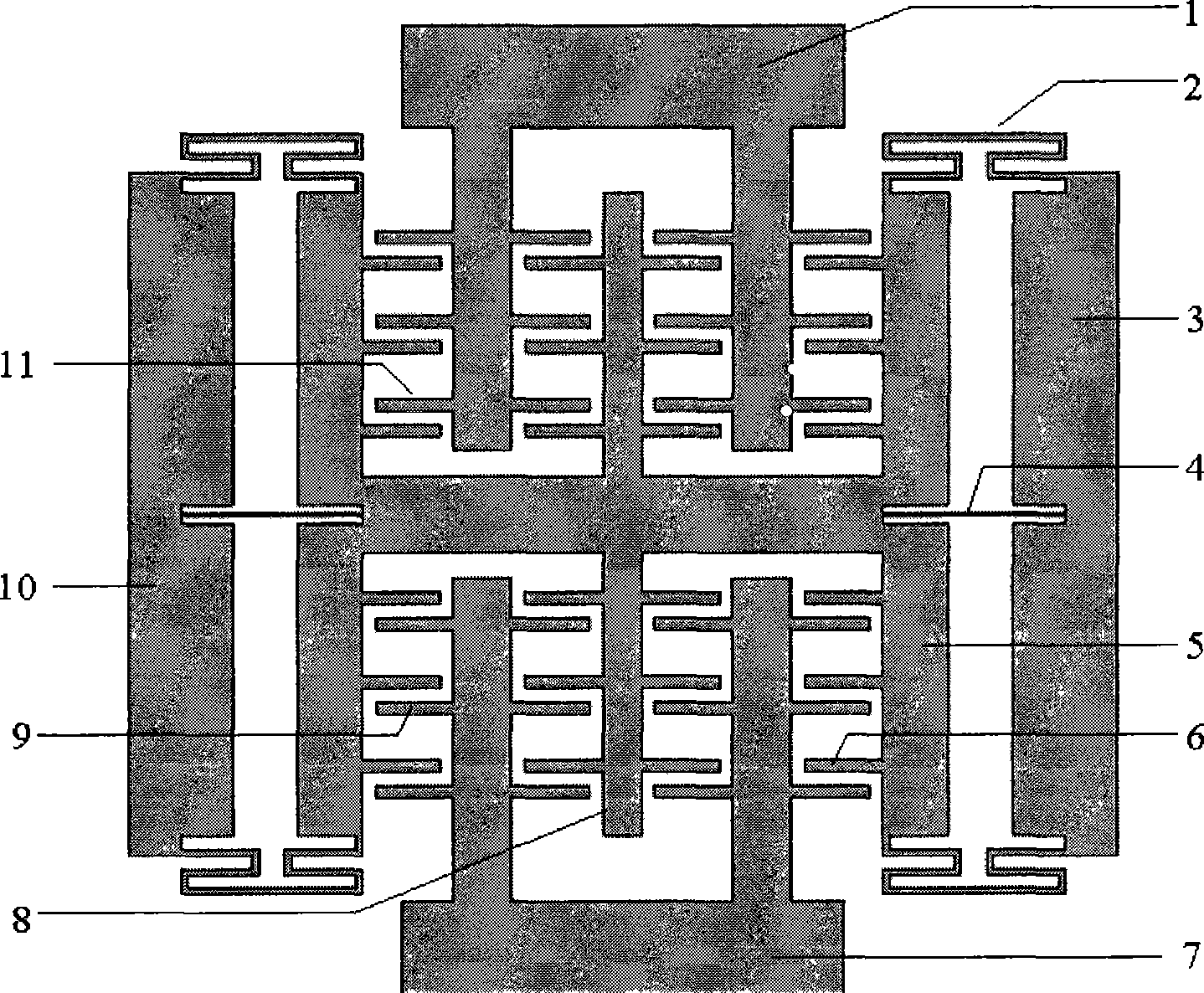
[0031] Embodiment 1: When there is an upward acceleration acting on the acceleration sensor, under the action of inertial force, the movable electrode 6 connected to the mass block will have a downward direction relative to the fixed electrode 11 and the fixed electrode 9 connected to the bonding block. At this time, the capacitance C1 formed between the movable electrode 6 and the upper fixed electrode 11 will become smaller, while the capacitance C2 formed between the movable electrode 6 and the lower fixed electrode 9 will become larger. The magnitude of the acceleration can be measured by differential detection of the variation of C2.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: When there is a leftward acceleration acting on the acceleration sensor, under the action of inertial force, the movable electrode 6 connected to the mass block will have a direction to the fixed electrode 11 and fixed electrode 9 connected to the bonding block. At this time, the capacitance C3 formed between the movable electrode 6 and the upper fixed electrode 11 will not change, and the capacitance C4 formed between the lower fixed electrode 9 will also remain unchanged, so that the movable electrode 6 and the upper and lower The total capacitance formed between the fixed electrode 11 and the fixed electrode 9 will also remain unchanged. In this way, lateral acceleration will not change the output of the sensor, that is, there will be no lateral sensitivity interference during operation.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: Due to the deviation of the process, the structure is mismatched, and the left and right comb teeth are asymmetrical. When a lateral acceleration acts on the acceleration sensor, as described in Embodiment 2, lateral sensitivity interference will occur. However, due to the effect of the anti-interference beam 4, the displacement of the mass block 5 and the movable electrode 6 connected thereto is greatly limited, and no transverse sensitivity interference will occur.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com