Polymyxin derivatives and uses thereof
A technology of polymyxin and derivatives, applied in the direction of polymyxin, antibacterial drugs, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem of undisclosed bacteria's ability to sensitize antibiotics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
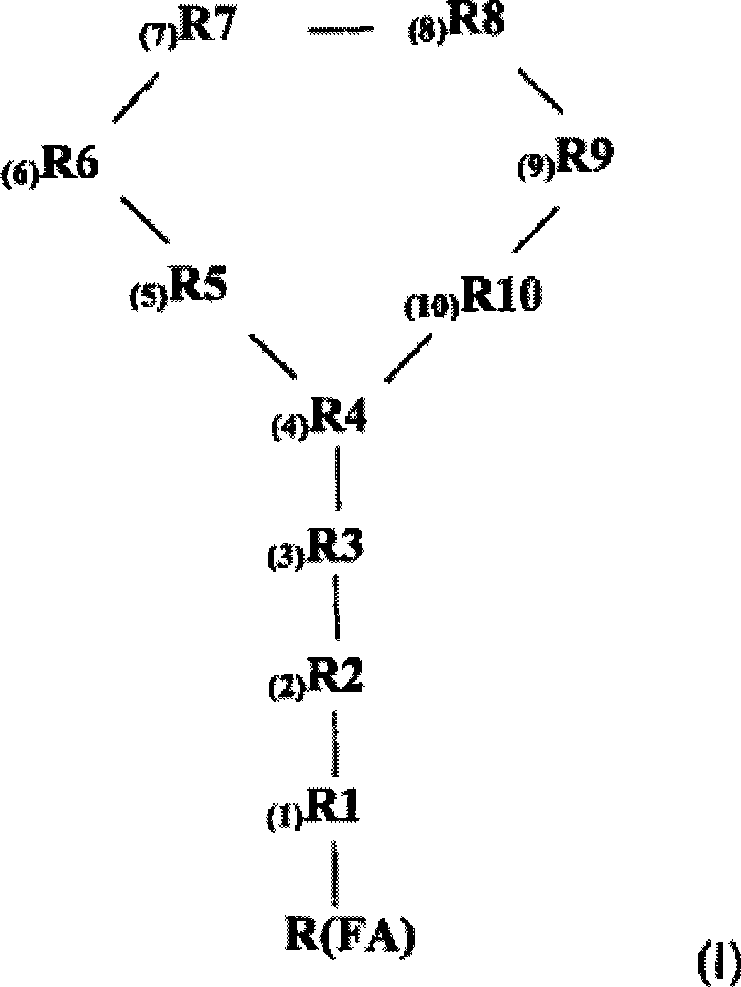
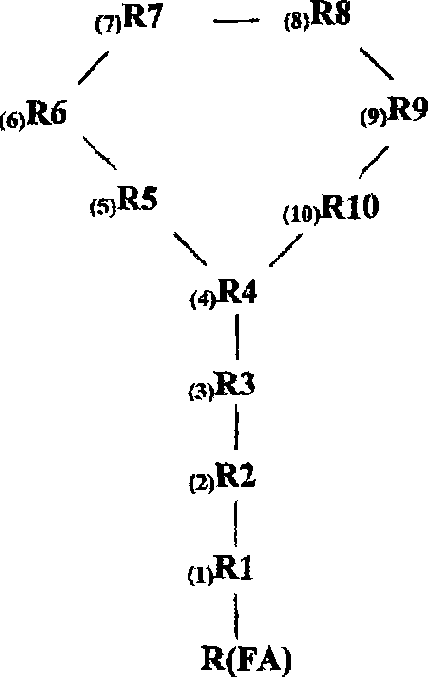
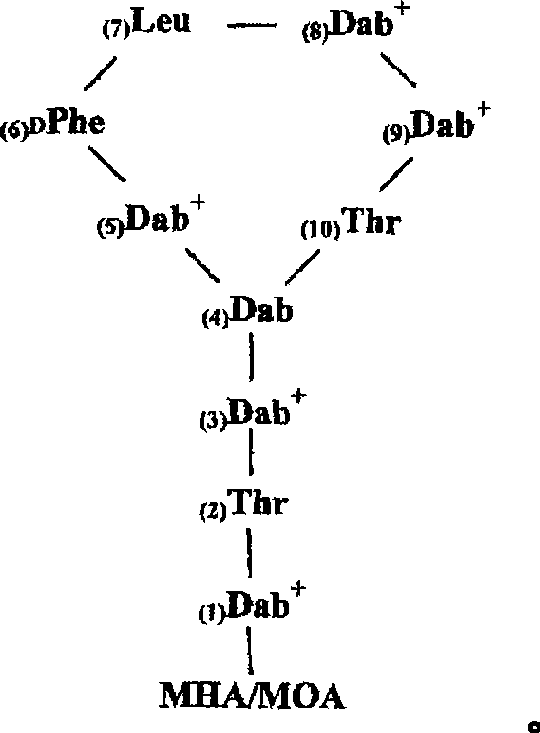
[0195] peptide synthesis
[0196] Polymyxin derivatives ("NAB peptides" or "NAB compounds") were synthesized by conventional solid phase chemistry using standard Fmoc protection strategies. The C-terminal amino acid is commercially available pre-attached to the solid phase, which when cleaved from the resin with acid yields the C-terminal carboxylic acid.
[0197] The protection strategy is to use three levels of independent protection—temporary Fmoc protection of the α-amino function, which is removed during the acid cleavage stage; and semi-permanent Fmoc protection covering the reactive side chain function while the cyclization reaction occurs. sexual protection. After the peptide is cleaved from the resin, the C-terminal carboxylic acid reacts with the amino function on the side chain of one of the amino acids to form a cyclic peptide. After the cyclization step, removal of the semi-permanent protecting group yields the NAB peptide.
[0198] Thus, the alpha amino functi...
Embodiment 2
[0209] The compound has direct antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli
[0210] The peptides synthesized in Example 1, each having at least 2 but not more than 3 positive charges, were investigated for their ability to inhibit the growth of E. coli. The assay was performed using LB agar (LB Agar Lennox, Difco, BD, Sparks, MD, USA) plates. The indicator organism E. coli IH3080 (K1:018) is an encapsulated strain originally isolated from a neonate with meningitis (Vaara et al., 1984) and obtained from the National Institute of Public Health (Helsinki, Finland).
[0211] From an overnight grown culture of IH3080 on LB agar made approximately 10 8 cells / ml suspension. An aliquot of this suspension was then pipetted onto the agar plate and the plate was shaken gently to spread the suspension evenly over the entire surface of the plate. Afterwards, the unabsorbed portion of the suspension was removed by using a Pasteur pipette. After the surface had dried, small holes (2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0223] Direct antibacterial activity of selected NAB compounds against Acinetobacter Baumea and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
[0224] The direct antibacterial activity of 12 NAB compounds against Acinetobacter boumee ATCC 19606 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 was determined by using the susceptibility assay described in Example 2. The results are shown in Table 3. Five compounds (NAB7062, NAB734, NAB737, NAB739, and NAB740) had significant activity against Acinetobacter permea. In Example 2, the same compound was shown to be very effective against E. coli. The antibacterial activity of NAB739 and NAB740 was comparable or even stronger than polymyxin B.
[0225] Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the most active NAB compounds were NAB739, NAB740 and NAB736 with little activity against Escherichia coli and A. NAB740 was the most active compound, as active as polymyxin B. All three NAB compounds lacked positive charges in the side chains and were still resistant to Pseudomonas a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com