Public key encryption and decryption method and digital signature method thereof
An encryption, decryption, and public key technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as inability to resist linearized equation attacks and differential attacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
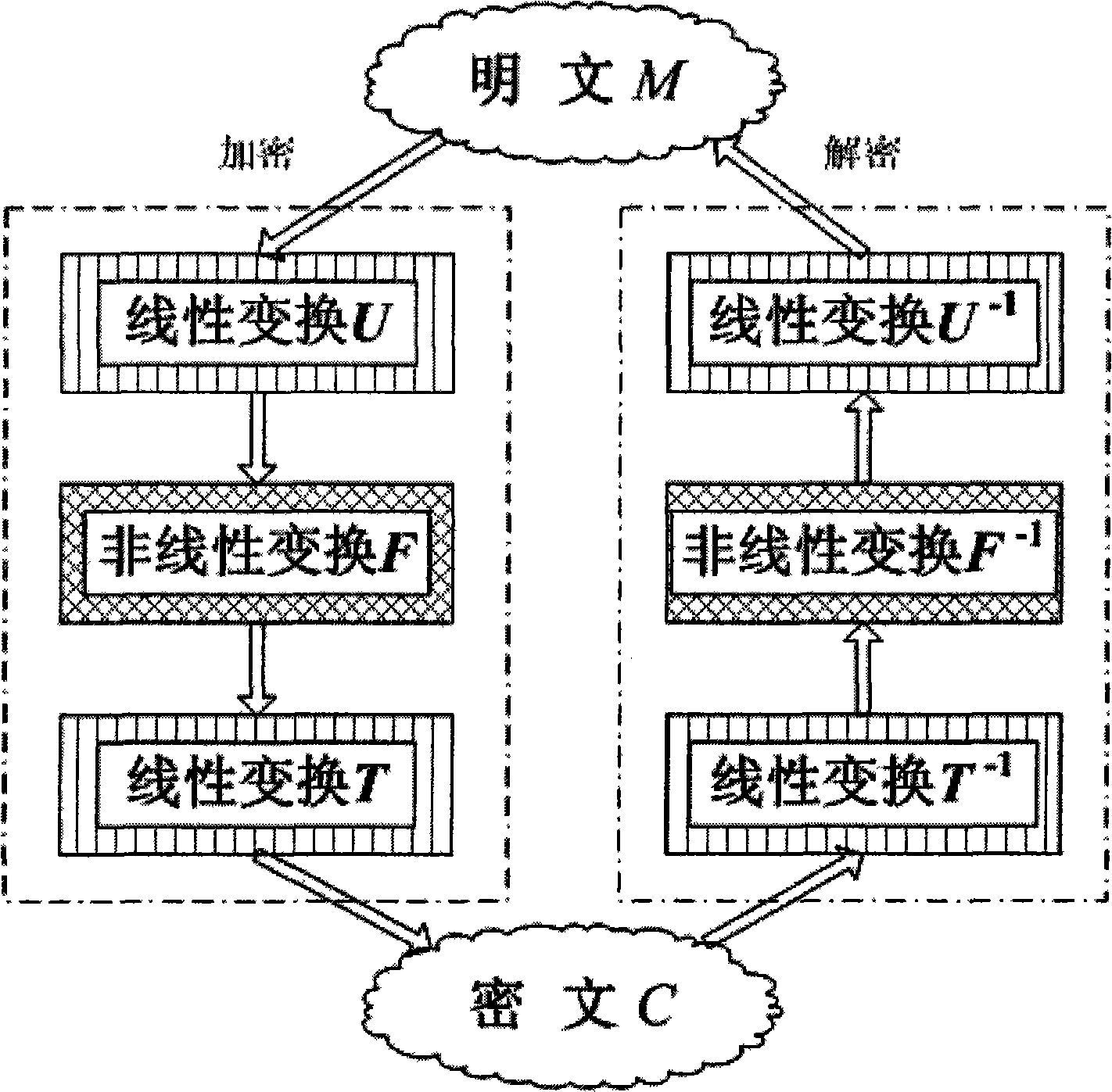
[0079] (I) Establish the system: first use the basic domain F 2 = {0, 1} to construct small and large fields: small field F 8 =F 2 [X] / (X 3 +X+1), big field F 8 3 = F 8 [ X ] / ( X 3 + X + 1 ) , Then define F 8 3 arrive a bijection of ∀ w = ( w 0 , w 1 , w 2 ) ∈ F 8 3 , So it is possible to pass the bijection small field F 8 He Dayu Element conversion between.
[0080] The reversible linear transformation component adopts the sma...
Embodiment 2
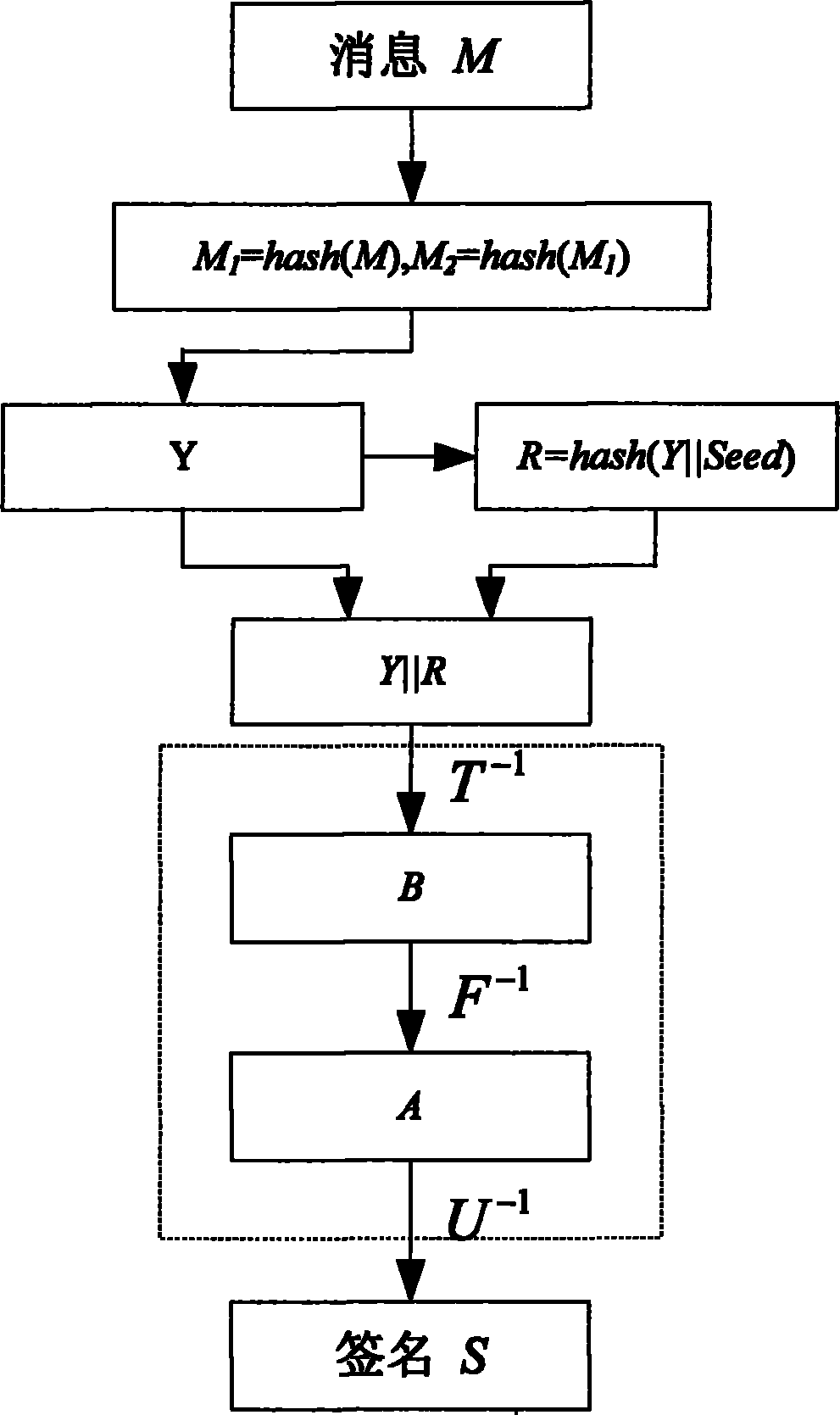
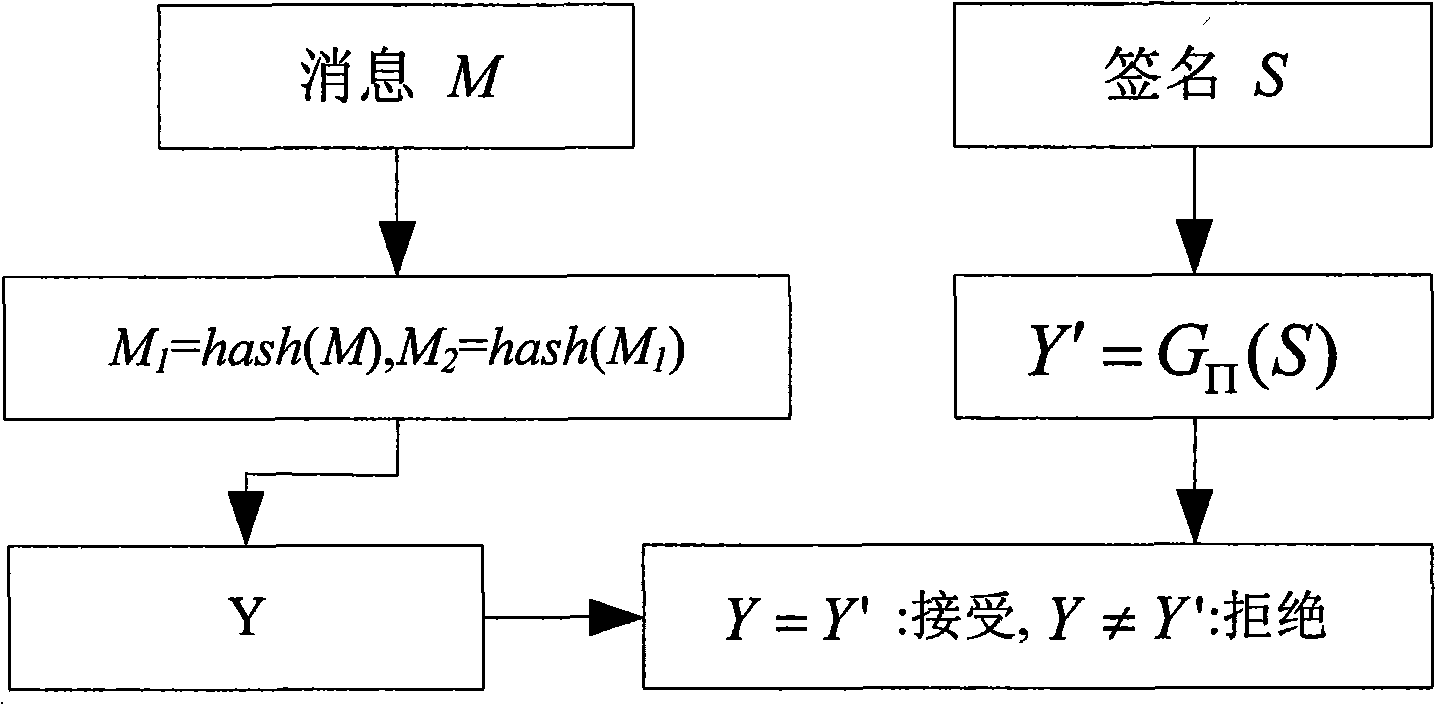
[0101] Example 2 gives a security of at least 2 80 An efficient signature scheme for :
[0102] System parameters: select parameters k=5, n=37, θ=7, r=16, select SHA-1 for the Hash function, and the output length of SHA-1 is 160 bits. So q=2 k = 32, construct the middle domain F 32 He Dayu f 32 =F 2 [x] / (x 5 +x 2 +1), F 32 37 = F 32 [ x ] / ( x 37 + x 12 + x 10 + x 2 + 1 ) . Then generate an 80-bit random seed Seed and in the middle field F 32 Randomly generate two affine bijective U, T, then the system private key is {T -1 , U -1 , Seed} requires 1.72Kbytes of storage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com