Excess polymer ring removal during ophthalmic lens manufacture
A technology for ophthalmic lenses and polymers, which can be used in applications, home appliances, and other home appliances, and can solve problems such as supplying monomers or reaction mixtures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
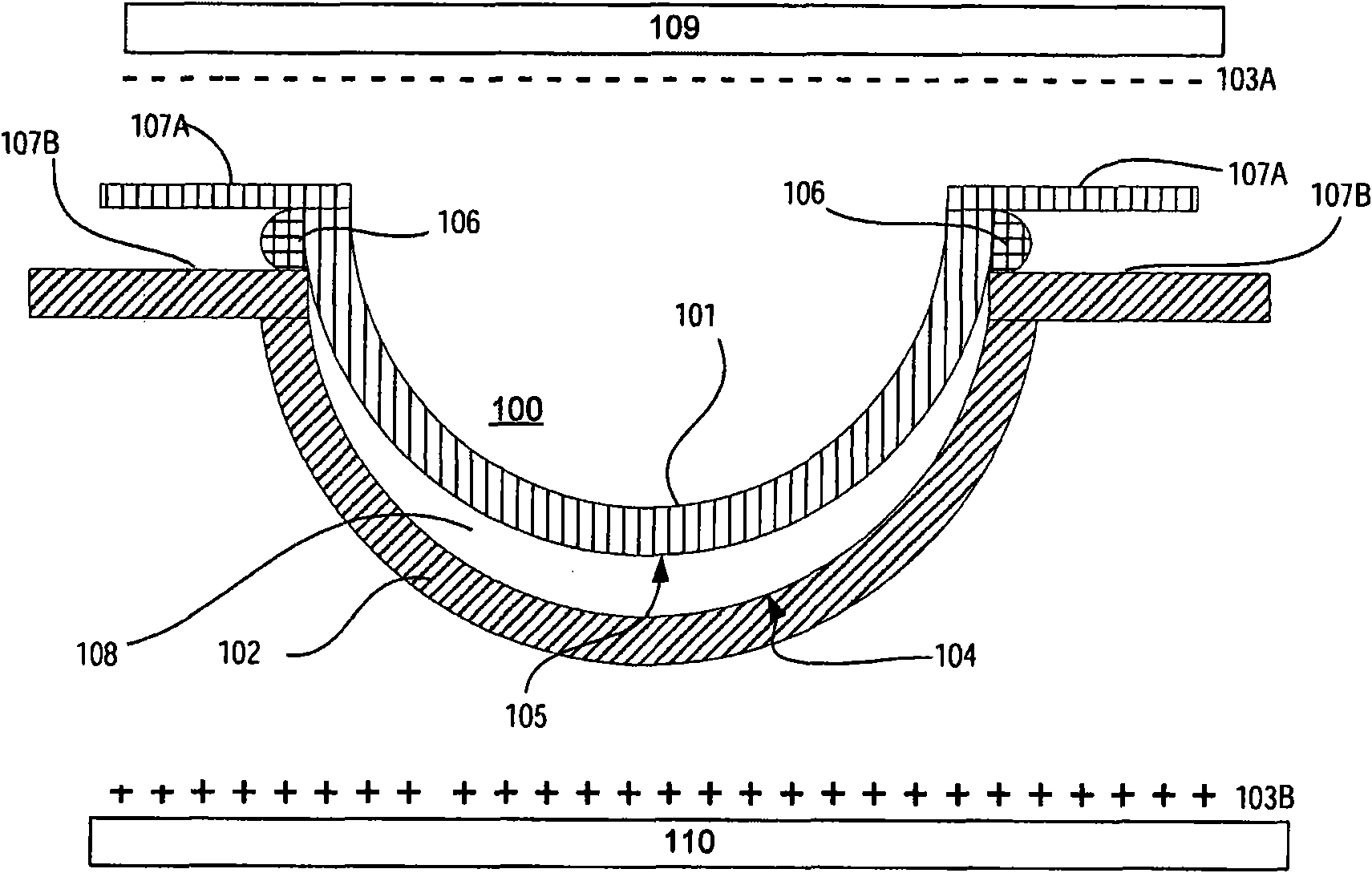
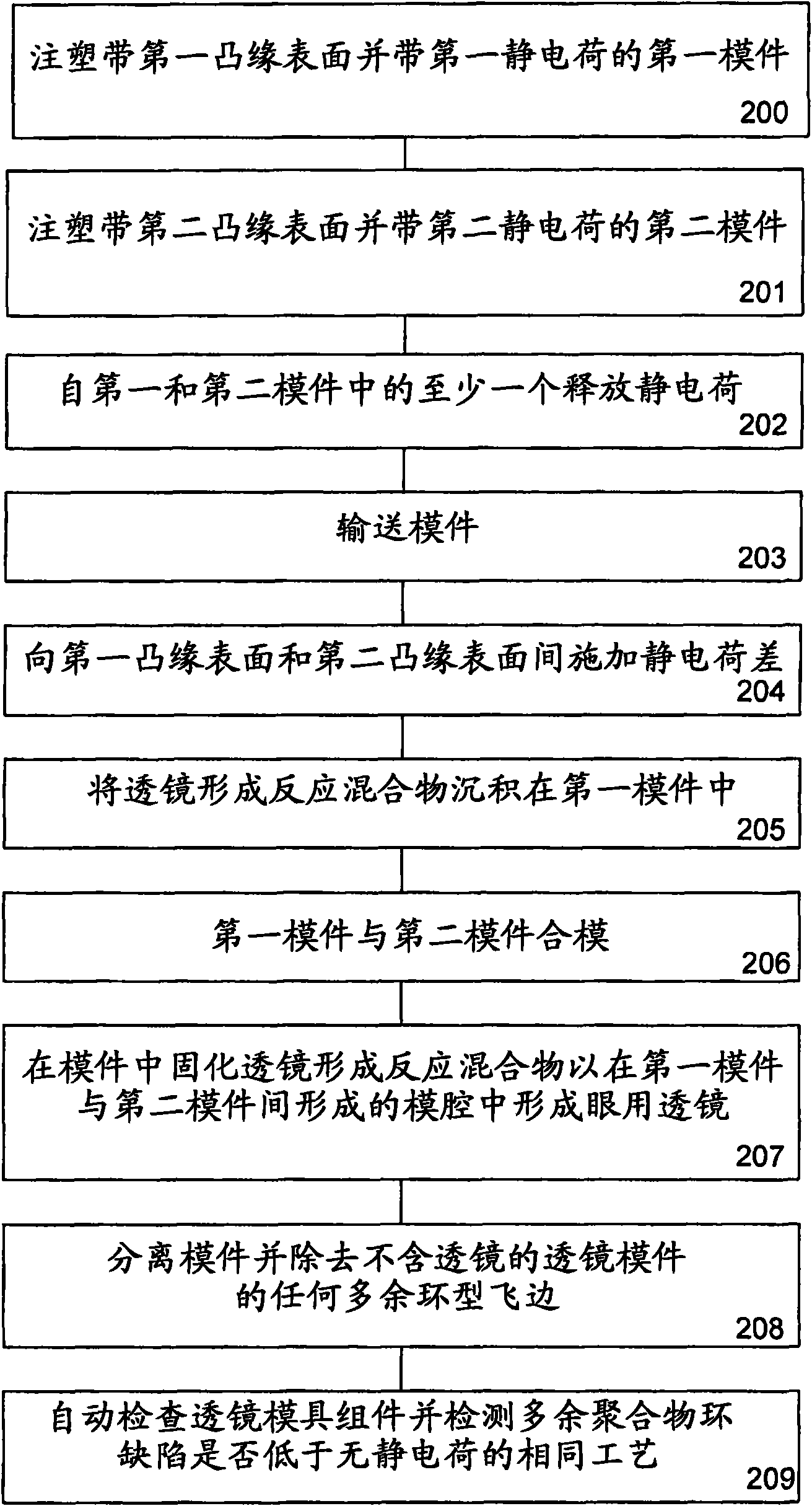
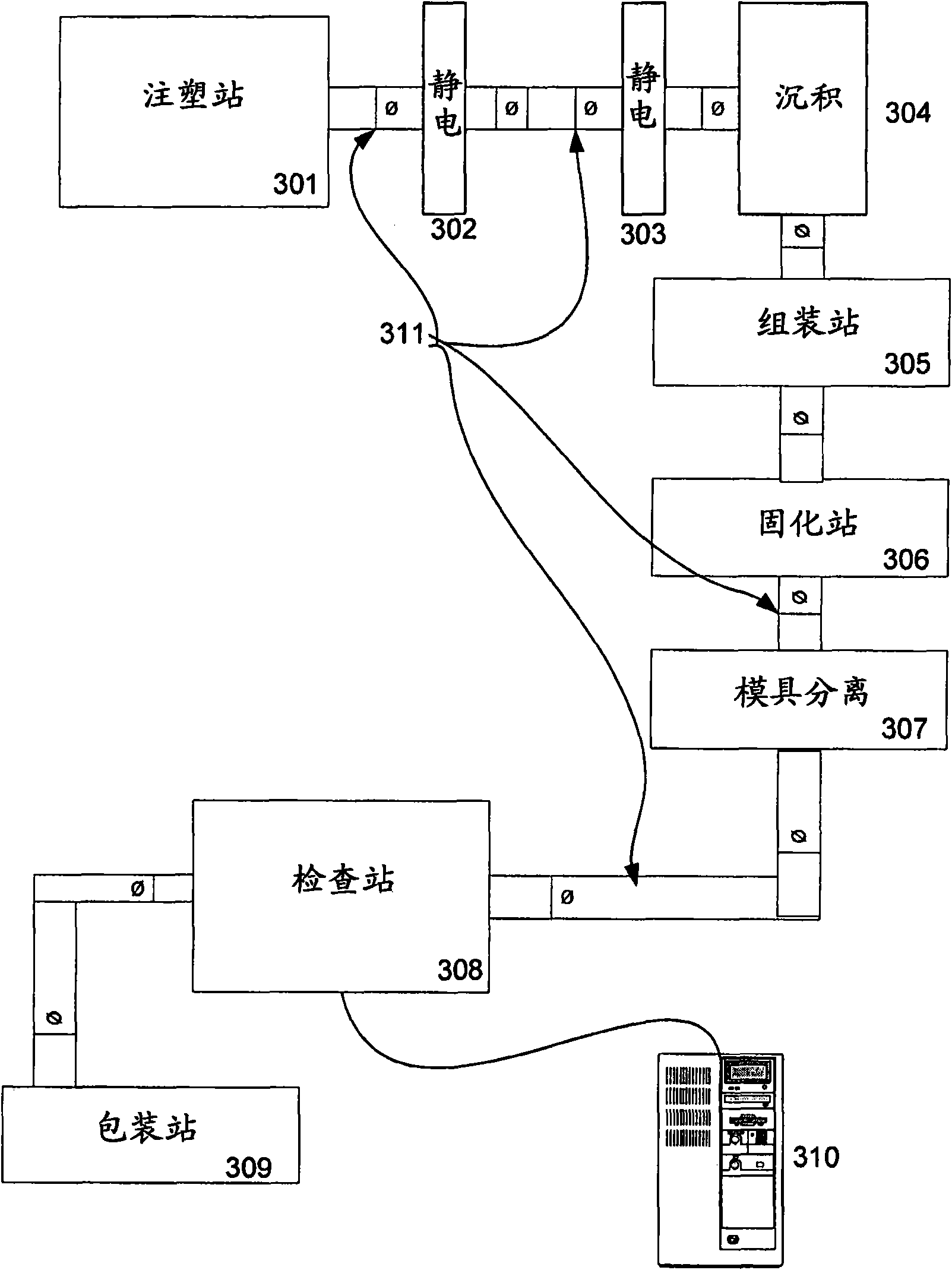
[0019] The use of electrostatic charge differences between dies used to form ophthalmic lenses to reduce the incidence of hole defects has been described separately. However, in accordance with the present invention, the use of a positive electrostatic charge on the front curve module may have the beneficial effect of reducing the incidence of hole defects, but may also disadvantageously increase excess polymer ring defects attached to the front curve module. Thus, according to the present invention, a relatively positive electrostatic charge (relative to the front curve) is applied to the back curve portion of the mold assembly, which provides the benefit of simultaneously minimizing hole defects and unwanted ring defects.
[0020] It is well known that the adhesion of polymerized monomeric material to the mold in which it is formed and polymerized is related to the surface energy of the mold material. Surface energy here refers to a material property similar to the surface t...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap