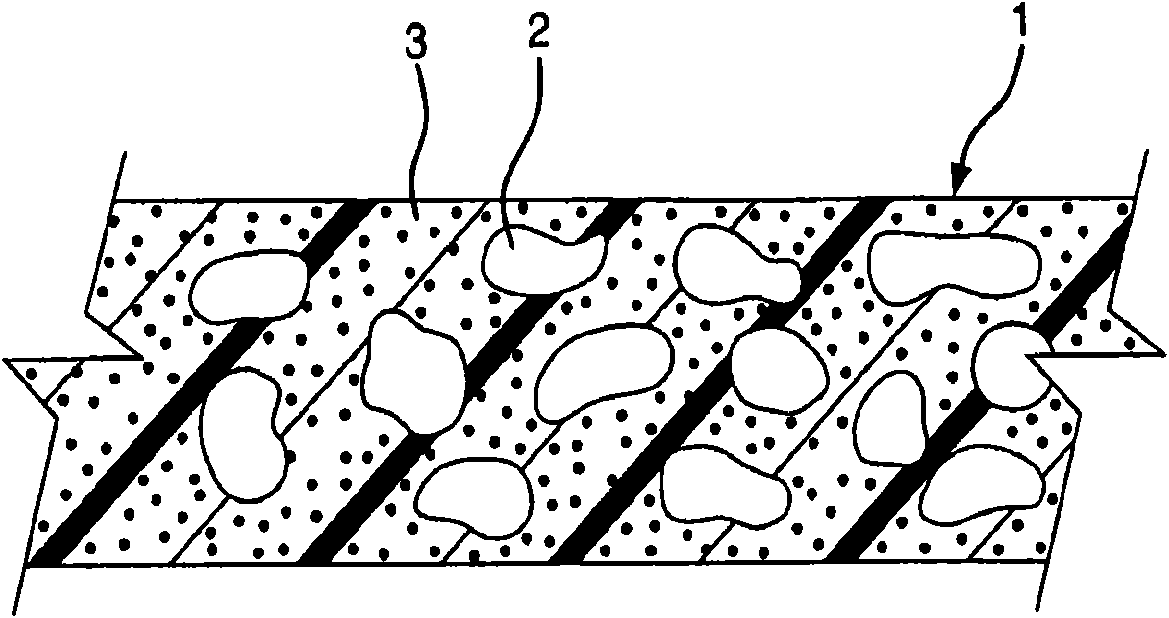
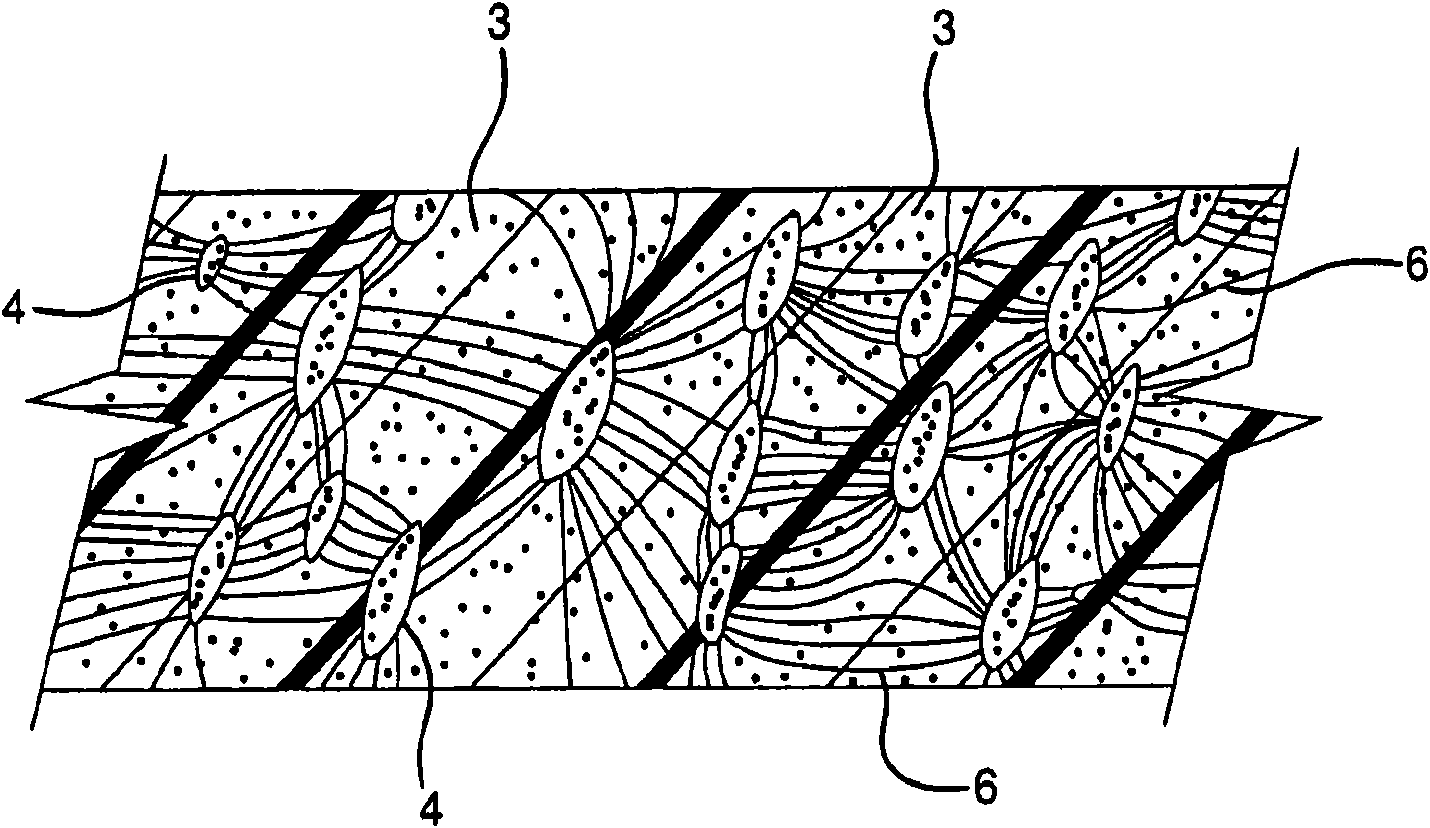
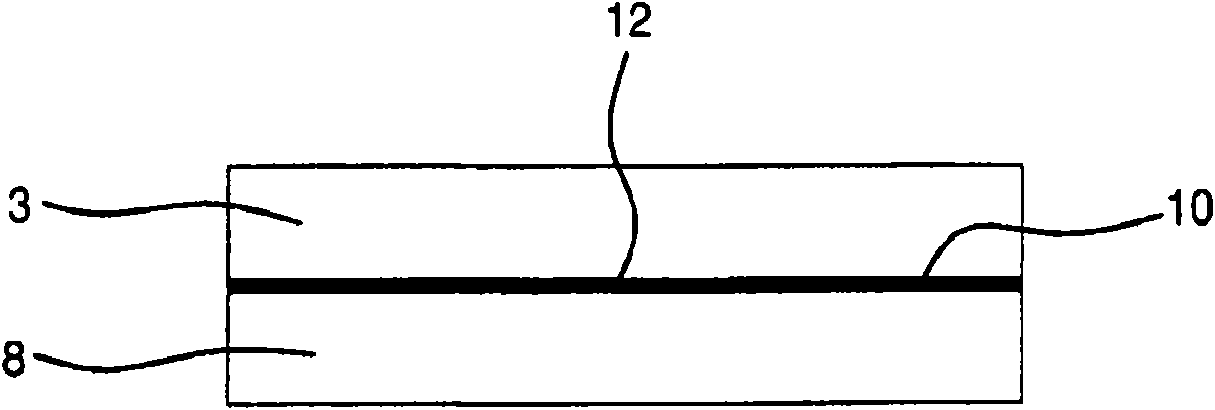
Polyester compositions, methods of manufacturing the compositions, and articles made therefrom
A composition and polymer technology, applied in the field of polyester and polymer composition, can solve the problems such as shape memory properties that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0196] Crosslinked polymeric reaction products of diacids, diols and triols were prepared according to a two-step process. In the first step, the following components were placed in a 500 ml glass reactor: the diacid component was 202.25 grams of sebacic acid (Aldrich, 99%), the diol was 43.46 grams of ethylene glycol (Aldrich, 99.8% anhydrous), the triol is 26.26 grams of glycerol (Aldrich, 99.5%+ spectrophotometric grade). The reactor was equipped with stirrer, heating device, steam condensing device, liquid volume measuring device, temperature regulating device, temperature measuring device and nitrogen purging device.
[0197] At room temperature, the reactants form a heterogeneous mixture of solid and liquid phases. As the temperature increased to about 170°C, the mixture formed a homogeneous liquid. Time and process parameters were recorded when all materials formed a single phase liquid. By-product water vapor formed from the reactor was condensed and collected in a ...
Embodiment 4
[0216] 67.3 grams of the intermediate prepared and described in Comparative Example 2 and 32.7 grams of the intermediate prepared and described in Comparative Example 3 were mixed in a 4 oz glass jar and placed in a vacuum oven at 125°C and atmospheric pressure. Place a 125 mm diameter Teflon TM The crystallization dish and laboratory mixing propeller assembly were also placed in the vacuum oven at this time. After 3 hours, the glass jar and its liquid intermediate contents were removed from the vacuum oven and immediately placed on an appropriately sized heating mandrel, a thermocouple was inserted into the molten mass, and the temperature was maintained at 125 ± 5°C for 5 minutes. The intermediate was then mixed at medium speed for 5 minutes until complete mixing appeared and a single phase liquid which could be considered homogeneous was formed. Transfer 25 g of liquid to preheated Teflon TM In the crystallization dish, put back in the vacuum oven of 125 ℃ and atmospheric...
Embodiment 5
[0219] 46.8 grams of the intermediate prepared and described in Comparative Example 2 and 53.2 grams of the intermediate prepared and described in Comparative Example 3 were mixed in a 4 oz glass jar.
[0220] Glass jars containing these intermediates were placed in a vacuum oven at 125°C and atmospheric pressure. Place a 125 mm diameter Teflon TM The crystallization dish and laboratory mixing propeller assembly were also placed in the vacuum oven at this time. After 3 hours, the glass jar and its liquid intermediate contents were removed from the vacuum oven and immediately placed on an appropriately sized heating mandrel, a thermocouple was inserted into the molten mass, and the temperature was maintained at 125 ± 5°C for 5 minutes. The intermediate was then mixed at a moderate speed for 5 minutes until the intermediate appeared to be completely mixed and formed a visibly homogeneous single-phase liquid. Transfer 25 g of liquid to preheated Teflon TM In the crystallizatio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com