Permanent magnet synchronous motor
A synchronous motor and permanent magnet technology, which is applied to synchronous machines, synchronous motors for single-phase current, synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of high asynchronous torque, enhanced strength and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0113] The first embodiment ( figure 1 with 2 )
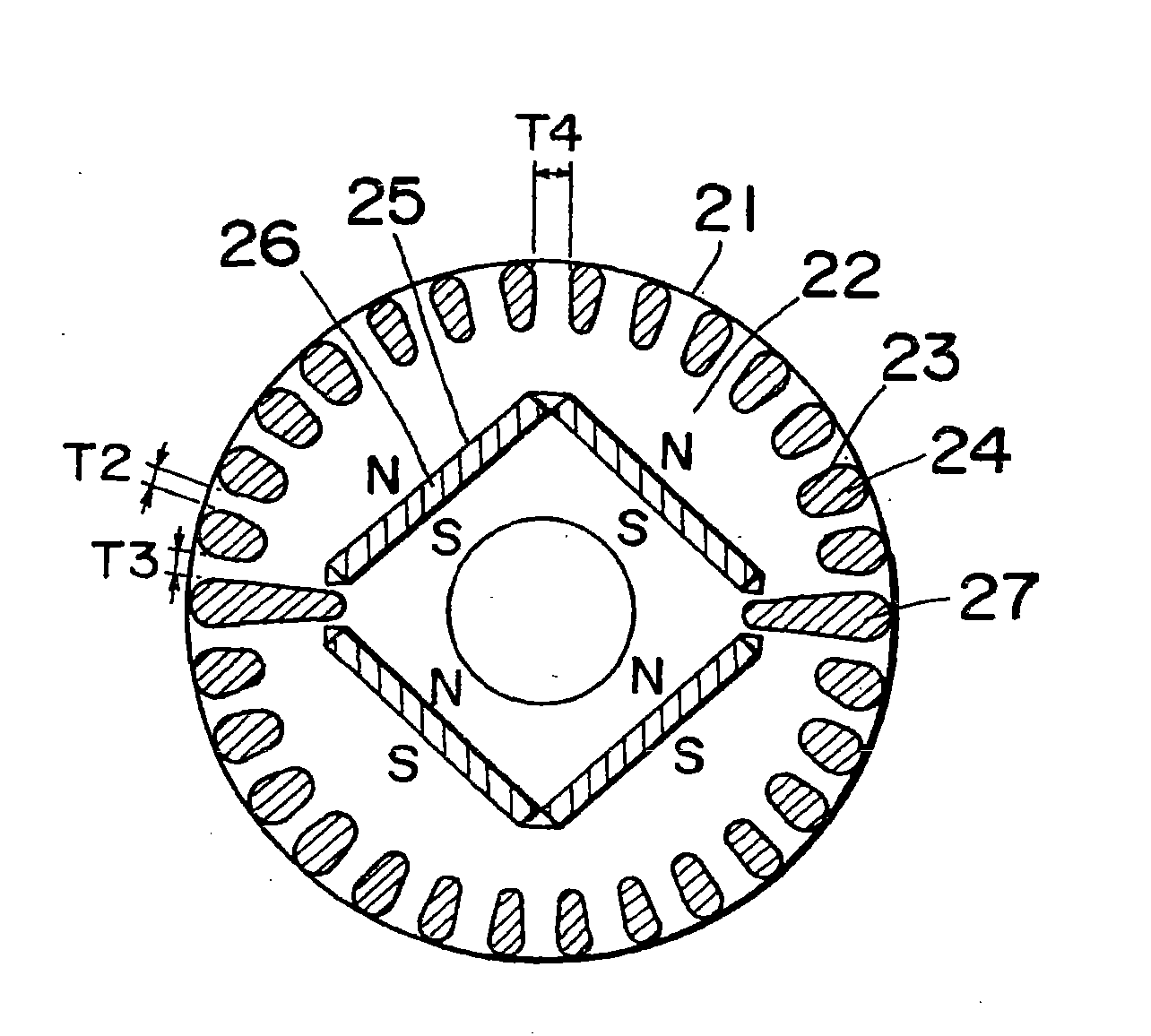
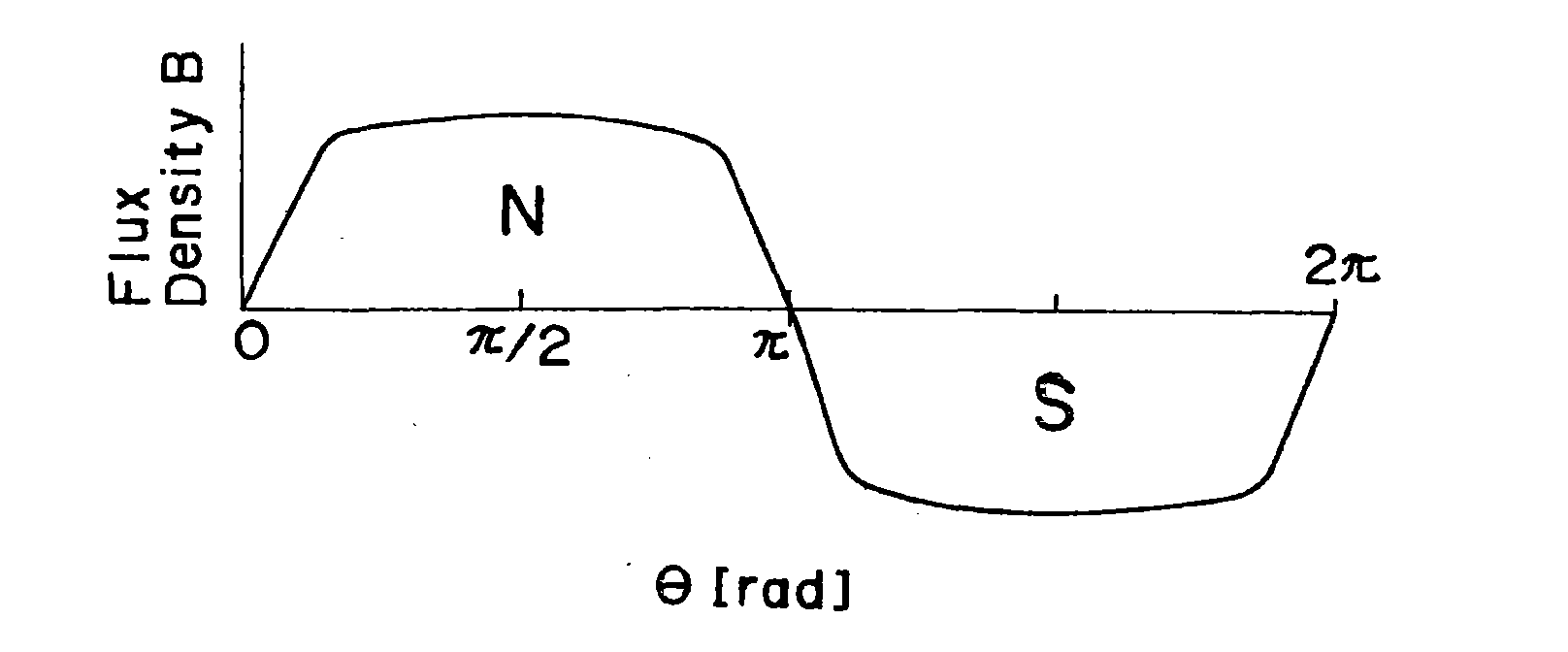
[0114] figure 1 is a cross-sectional view of a rotor for the self-starting synchronous motor using permanent magnets according to the first preferred embodiment of the present invention. In this figure, the rotor is indicated by reference numeral 21 and the rotor core is indicated by 22 . The rotor core 22 has a number of elongated holes 23 positioned on the outer circumference for accommodating a corresponding number of conducting rods 24 which are integrally cast together with a shorting ring (not shown) in any known die-casting aluminum technique. The axially spaced ends of the rotor core 22 thereby provide an actuating squirrel-cage conductor. The permanent magnets 26 are embedded in respective magnet holding holes, and the magnet holding holes are defined in the rotor core 22 and are located at one turn radially inside the conducting rod 24 .
[0115] exist figure 1 Within the range shown, two plate-shaped permane...
no. 2 example
[0146] The second embodiment ( image 3 )
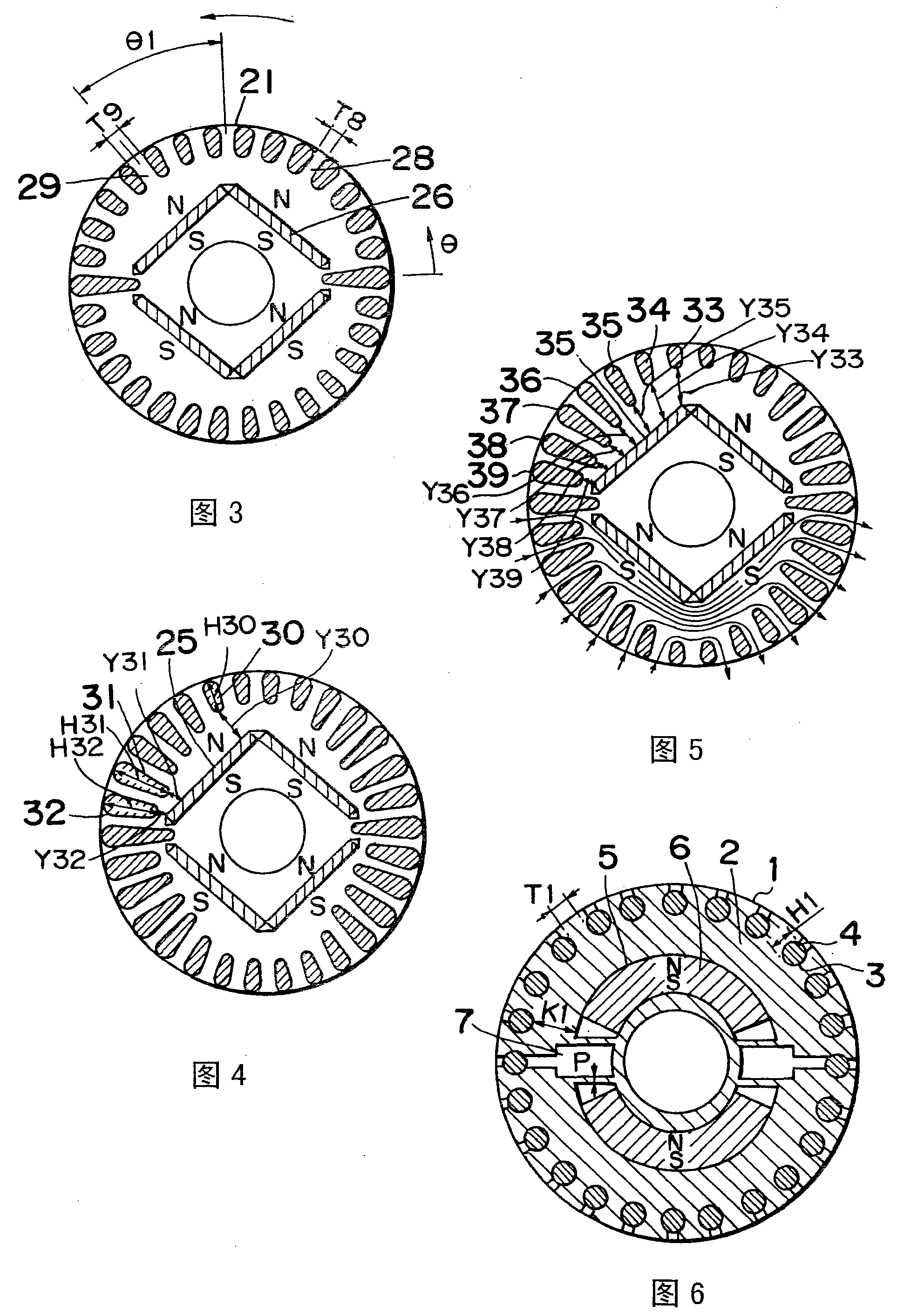
[0147] image 3 is a cross-sectional view of a rotor used in the self-starting permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the second preferred embodiment of the present invention. image 3 , the rotor 21 rotates in the direction indicated by the arrow. In operation under load, the combined magnetic flux of the magnetic flux emanating from the stator coil and the magnetic flux emanating from the permanent magnet 26 flows into the part 29 much more than the part 28. The part 29 is located along the rotor from the center of the rotor pole. Between adjacent long holes whose rotation direction is shifted forward by θ1. The portion 28 is located between two adjacent slots on the side offset from the center of the rotor pole to the rear. The size of the selected part 29, that is, the distance T8 between the two adjacent long holes on both sides of the part 29, is greater than the distance T9 between the adjacent long holes on the t...
no. 3 example
[0148] The third embodiment ( Figure 4 )
[0149] Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of a rotor for a synchronous motor according to a third preferred embodiment of the present invention. Figure 4 Among them, one of the long holes 30 is located near the center of the rotor pole, and the long holes 31 and 32 are located near one of the two ends of the rotor pole. These elongated holes 30, 31, 32 have different radial lengths H30, H31 and H32 respectively, and the distances Y31 and Y32 between the elongated hole 31 and the magnet holding hole 25 and between the elongated hole 32 and the magnet holding hole 25 are smaller than Y30, Y30 is the distance between the elongated hole 30 and the magnet holding hole 25, from which the magnetic flux diverging to the permanent magnets near the outer peripheral surface of the rotor magnetic pole is almost very small, otherwise, it is scattered to the outer peripheral surface near the center of the rotor magnetic pole. For this reason,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com