Power semiconductor module
一种功率半导体、层叠体的技术,应用在半导体器件、半导体/固态器件零部件、电固体器件等方向,能够解决没有公开影响等问题,达到抑制破裂、消除脆性、减少变形的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0136] The method for producing CuAlMn alloy particles is not particularly limited, and known methods for producing alloy particles can be appropriately used. An example of the production method is given below, but is not limited thereto.
[0137] First, Cu, Al, and Mn were melted in a high-frequency melting furnace under an Ar atmosphere to produce a CuAlMn alloy ingot as a precursor. The above-mentioned additional elements may be added to the ingot as needed. Next, the obtained ingot is pulverized by a powder production technique such as an atomization method to obtain CuAlMn alloy particles. The powdered CuAlMn alloy particles are plated with Ni and Au on the surface of the particles by a dropping method or the like. By adjusting the film thickness of the plating layer on the surface of the particles, the dispersibility of the CuAlMn particles in Bi—CuAlMn can be improved. The preferable film thickness of this plating layer is 0.01-3 micrometers.
[0138] When the insul...
Embodiment 1
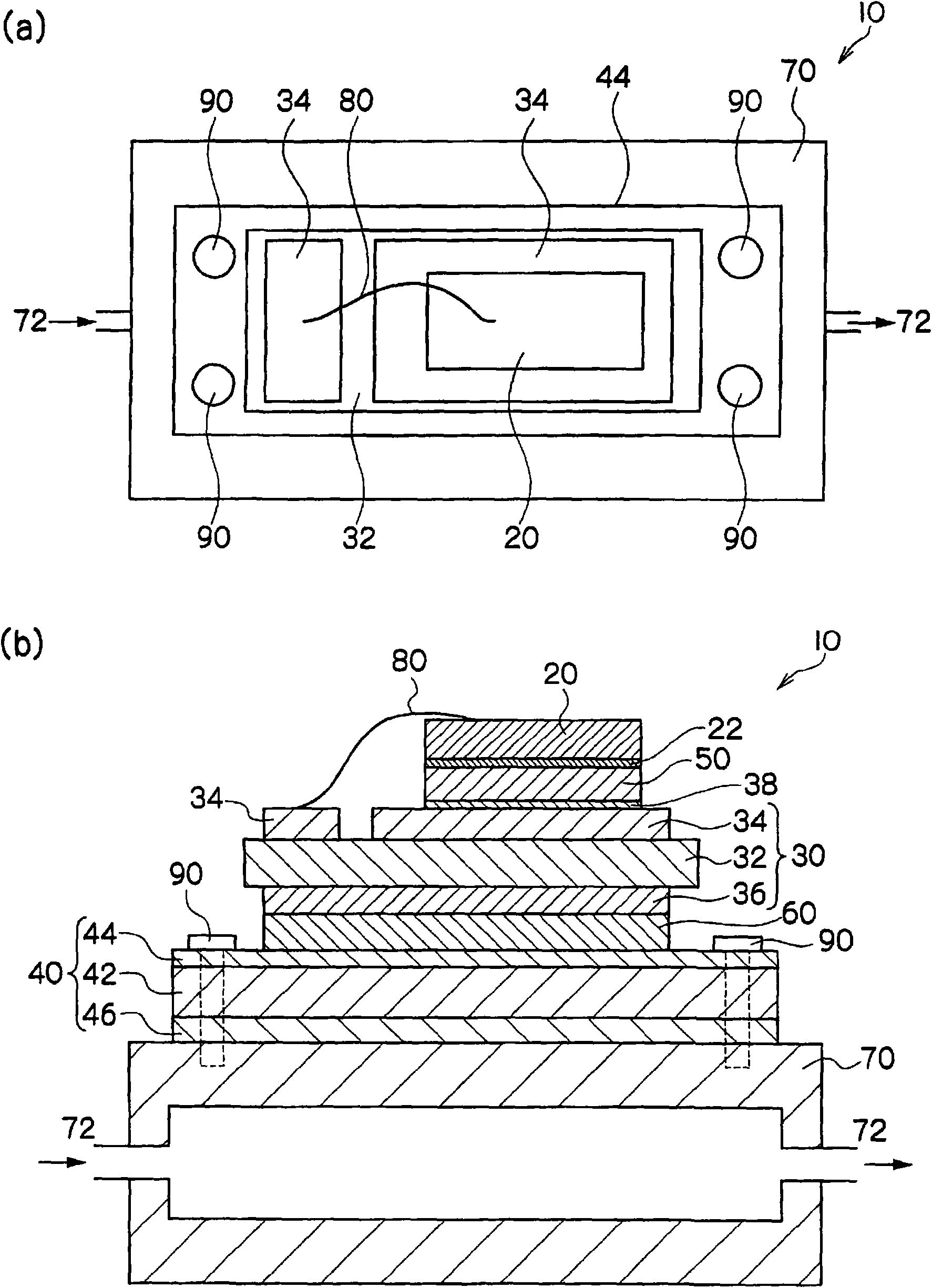
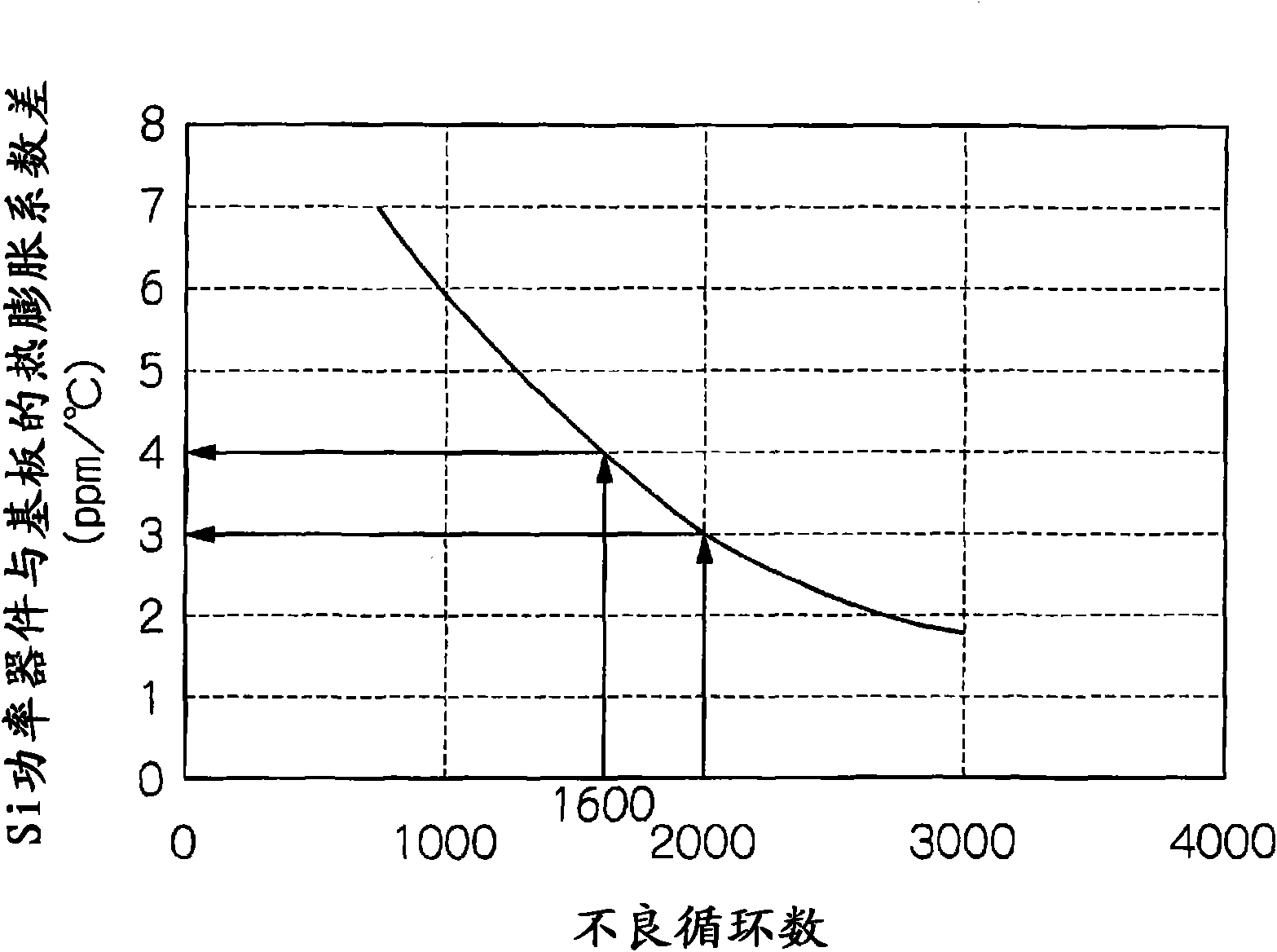
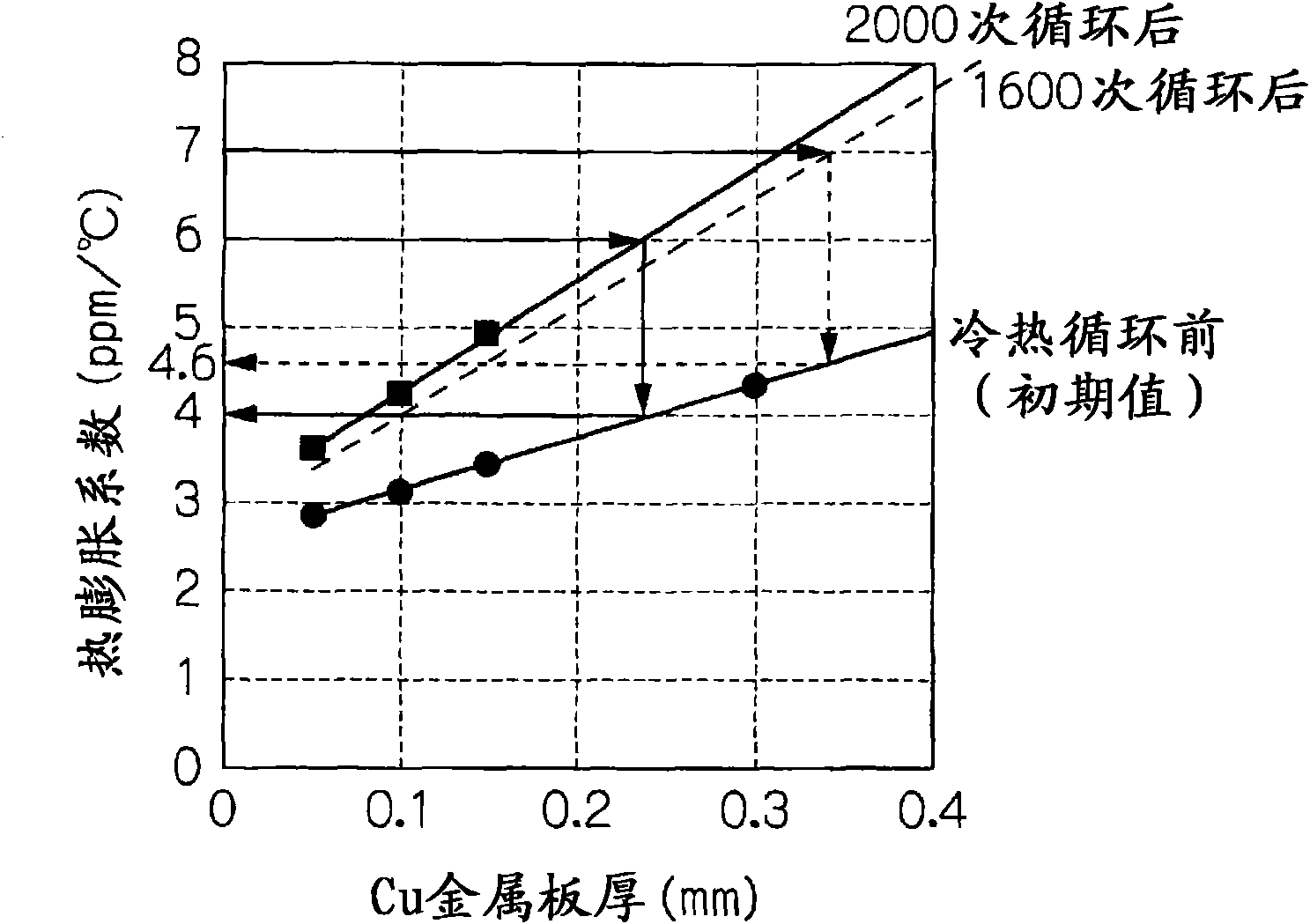
[0290] figure 1 The structure of the power semiconductor module of this embodiment is shown in .
[0291]
[0292] A 12 mm×9 mm power semiconductor element 20 using SiC (thermal expansion coefficient: 3 ppm / ° C.) was prepared, and a Ni layer 22 was formed on the outermost surface by sputtering. An Au layer (not shown) is formed on the surface of the Ni layer 22 by sputtering.
[0293]
[0294] As the insulating portion 30 , a laminate of Cu layer 34 / SiNx layer 32 / Cu layer 36 was fabricated.
[0295] First, SiNx with a thickness of 0.32 mm was prepared, and Cu layers 34 and 36 with a thickness of 0.05 mm were attached to both surfaces of the SiNx by brazing to produce a laminate-1.
[0296] In the same manner, but changing the thickness of the Cu layers 34 and 36 to 0.1 mm, 0.15 mm, and 0.3 mm, laminates-2, -3, and -4 were produced. In addition, the thickness of the Cu layer was made equal on both sides of SiNx.
[0297] In the laminated bodies-1 to 4, the Ni layer 38...
Embodiment 2
[0323] made as Figure 8 Shown is an evaluation test body-1 in which a power semiconductor element and an insulating part are joined with a Bi-based solder material.
[0324]
[0325] A 12 mm×9 mm power semiconductor element 20 using SiC (thermal expansion coefficient: 3 ppm / ° C.) was prepared, and a Cu layer 22 was formed on the outermost surface by sputtering.
[0326]
[0327] Insulator laminate-2 (thickness of Cu layer: 0.1 mm) of Example 1 was prepared.
[0328]
[0329] The Bi simple substance is cut into a thickness of 150 to 200 μm. The oxide film covering the surface of the excised Bi simple substance layer was removed by grinding and acid washing.
[0330] The Cu layer 22 of the power semiconductor element 20 prepared above and the Cu layer 34 of the insulating part 30 were arranged facing each other, and a Bi simple substance layer was interposed therebetween. 2 / N 2 The bonding was performed at a bonding temperature of 320° C. by a reflow method in a redu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com