Release agent composition for polyurethane foam molding
A technology of polyurethane foam and mold release agent, which is applied in the field of mold release agent composition for polyurethane foam molding. It can solve the problems of poor surface properties, mold pollution, and regular mold cleaning, so as to prevent foam cracking, reduce friction sound, and eliminate VOC. The effect of countermeasures on the problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
[0042] Disperse the release component (A) in the lipophilic solvent (C) according to the prescribed ratio shown in Table 1, and mix and stir the oil-soluble oligomer (B) and the surfactant (D) in the dispersion to obtain Prepare the first mixed liquid, then mix the ether (E) and water according to the specified ratio shown in Table 1 to prepare the second mixed liquid, pour the second mixed liquid into the first mixed liquid while stirring and mix well , thereby becoming a water-based release agent composition of a W / O emulsion. Here, the "aqueous release agent composition" refers to a release agent composition containing at least 50% or more of water in the total amount. Table 1 shows the compounding ratio of each component when the total amount of the release agent composition of each Example and each comparative example is set to 100 each.
Embodiment 1
[0065] Object: Example 1, Comparative Example 1
[0066] Evaluation performance: bubble cracking, mold contamination
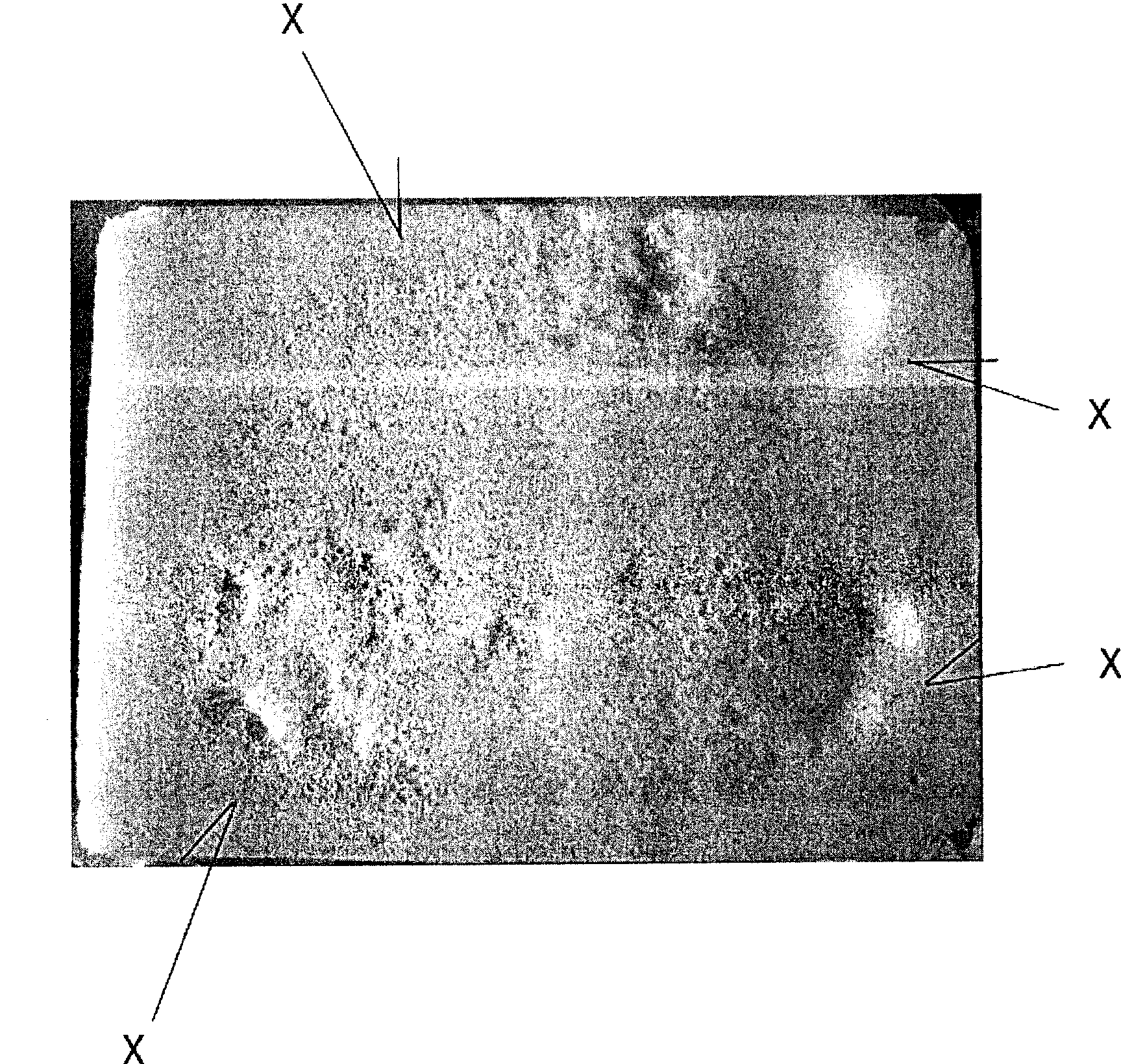
[0067] Contents: After spraying the release agent composition of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 above on an iron mold (170×115×21 mm) at 35° C., it was dried for 40 seconds. Next, using a commercially available raw material for cold-curing polyurethane foam, it was mixed at a predetermined compounding ratio, poured into a mold, and reacted at a temperature of 35° C. for 5 minutes. Then, the surface state (presence or absence of cracks) of the demolded polyurethane foam molded article was visually observed and evaluated. Regarding the evaluation in Table 1, "⊚" indicates a state without cell rupture, "◯" indicates a state where the cell diameter tends to be too large, and "×" indicates a state with cell rupture.
[0068] In addition, the mold after molding was washed with mineral turpentine, and the amount of resinization reaction product remaining on th...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Target: Examples 2, 3, Comparative Examples 2-4
[0071] Evaluation performance: bubble cracking, mold contamination
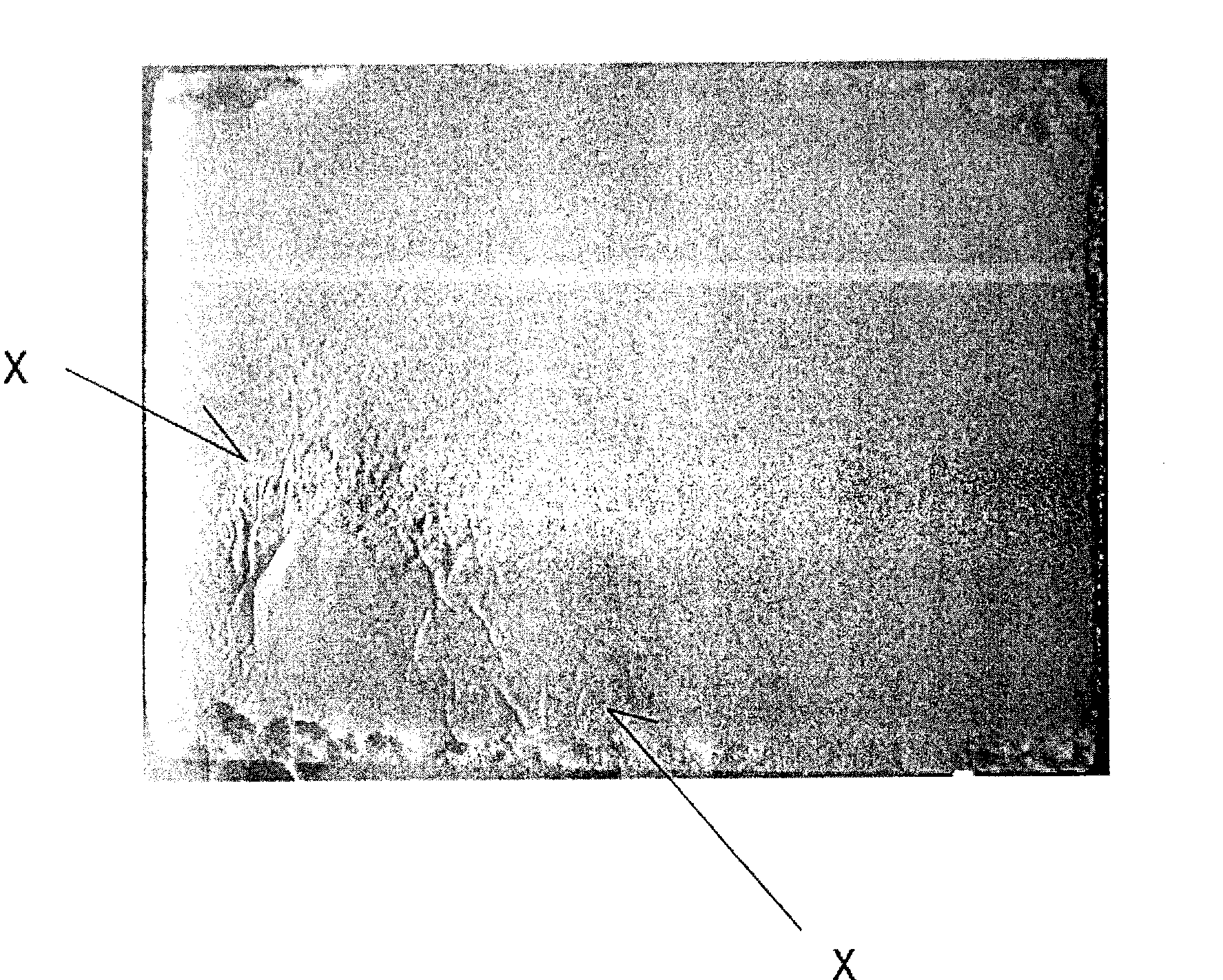
[0072] Contents: After spraying the release agent compositions of Examples 2 and 3 and Comparative Examples 2 to 4 above on an iron mold (170×115×21 mm) at 65° C., it was dried for 1 minute. Next, using a commercially available raw material for high elasticity (HR) polyurethane foam, it was mixed in a predetermined compounding ratio, poured into the mold, and reacted at a temperature of 65° C. for 7 minutes. Then, the surface state (presence or absence of cracks) of the demolded polyurethane foam molded article was visually observed and evaluated. The evaluation in Table 1 shows that it is the same as performance test 1.
[0073] In addition, the mold after molding was washed with mineral turpentine, and the amount of resinization reaction product remaining on the mold was visually observed to evaluate the degree of mold contamination. The evaluation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com