Wafer grinding process
A grinding process and wafer technology, applied in the field of semiconductor wafer grinding process, can solve the problems of no adhesion, damage to bumps, easy to fall off, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0095] In order to have a further understanding of the purpose, structure, features, and functions of the present invention, the detailed description of the accompanying examples is as follows.
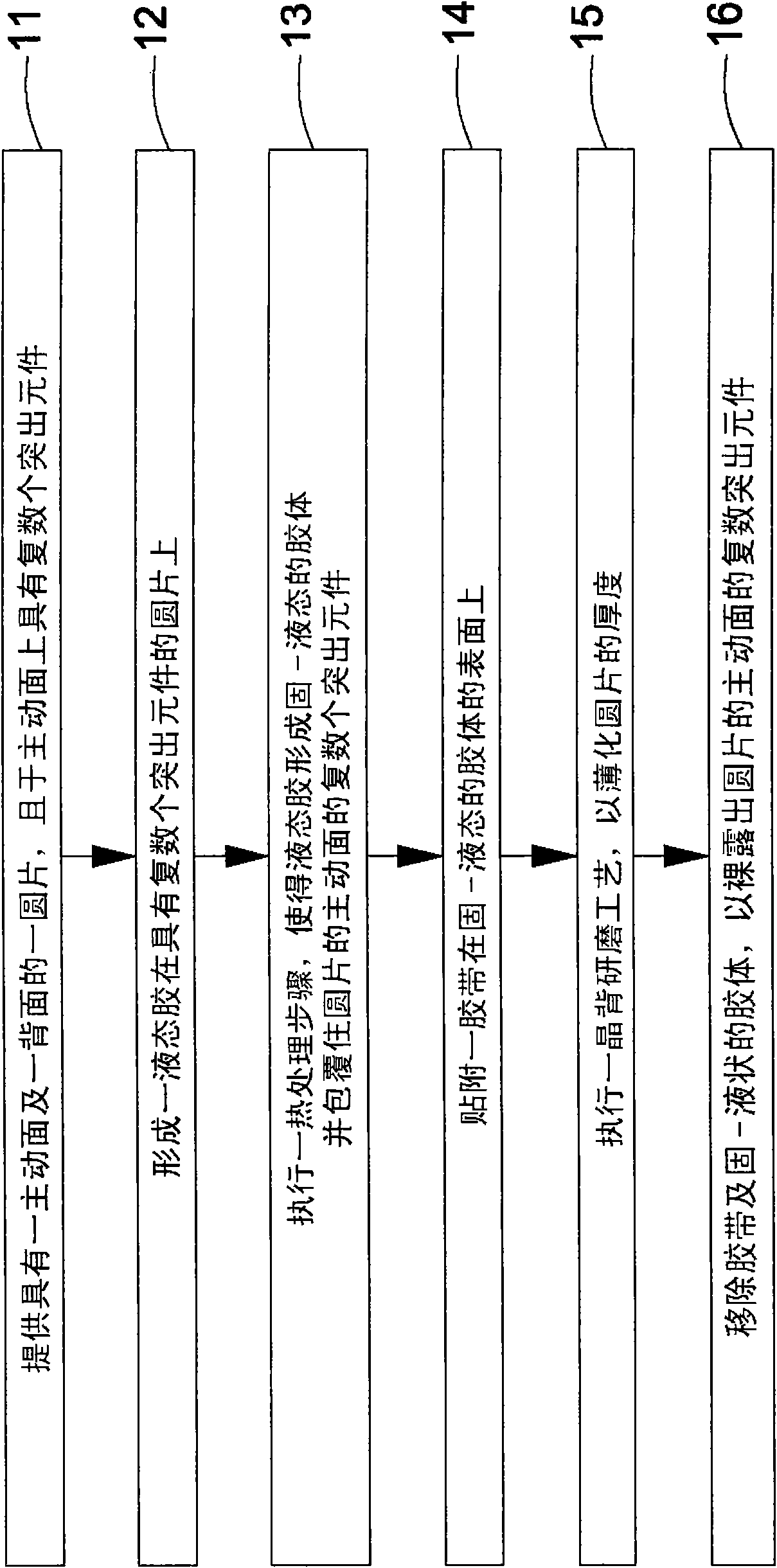
[0096] The direction discussed in the present invention is a crystal back grinding process of a semiconductor wafer. In order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention, detailed implementation steps will be set forth in the following description. Here, the detailed steps of well-known grinding methods and other back-end processes are not described in detail to avoid unnecessary limitations of the present invention. However, for the preferred embodiments of the present invention, it will be described in detail as follows. However, in addition to these detailed descriptions, the present invention can also be widely implemented in other embodiments, and the scope of the present invention is not limited. The scope of the patent shall prevail.
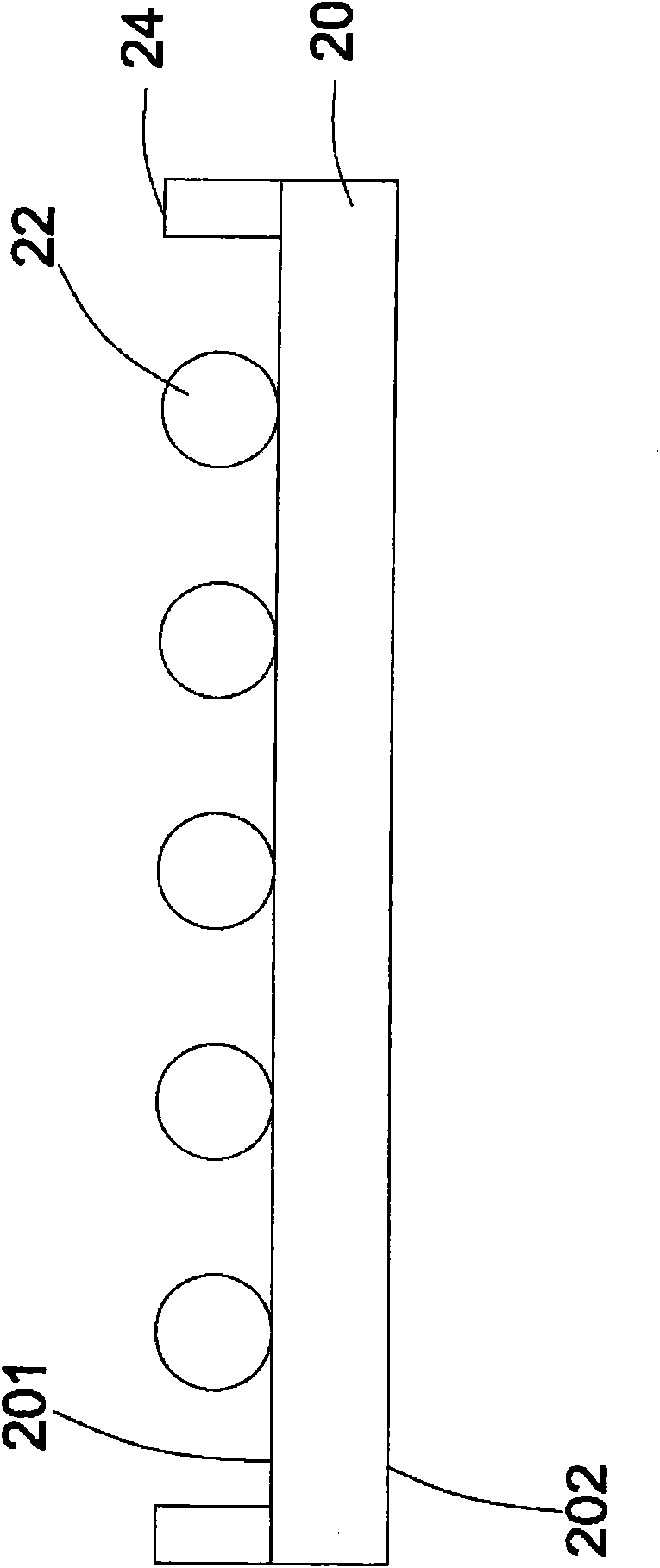
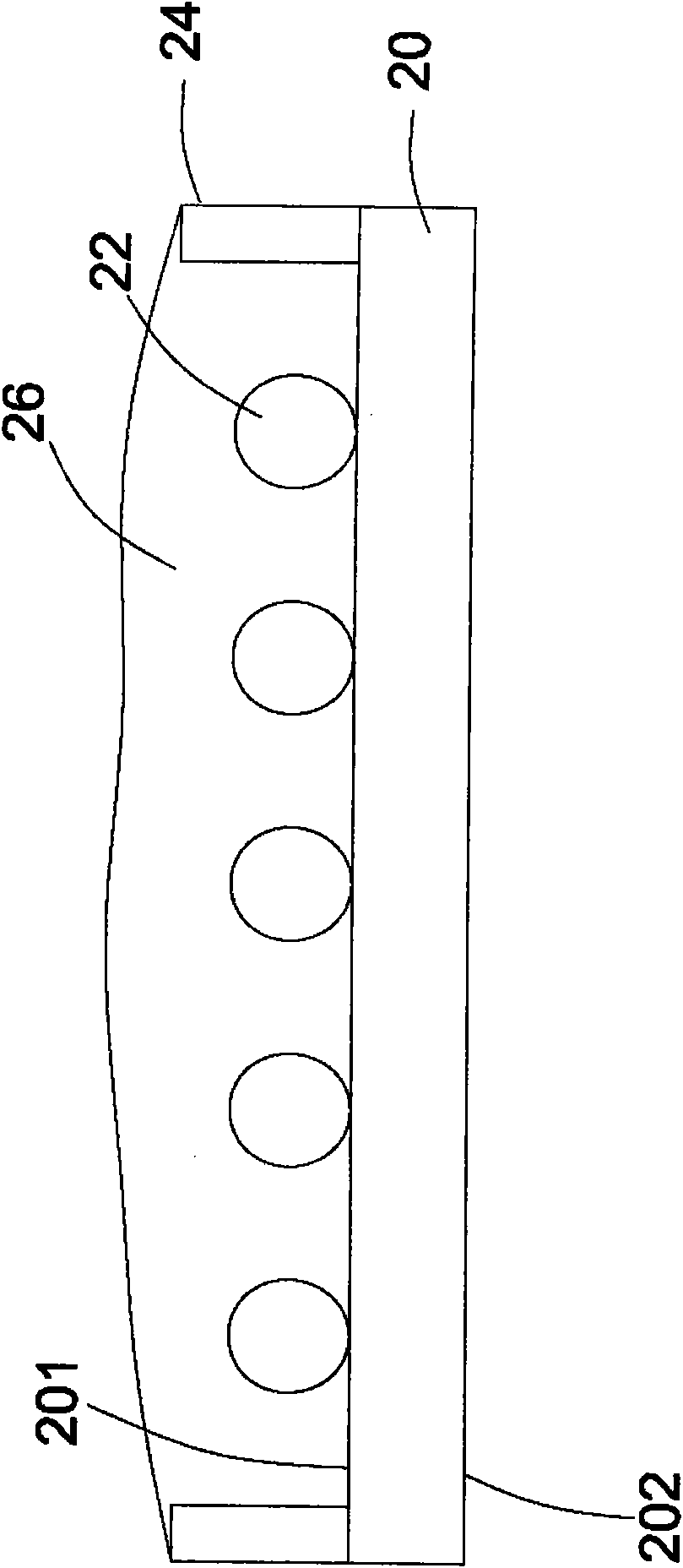
[0097] figure 1 It is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com