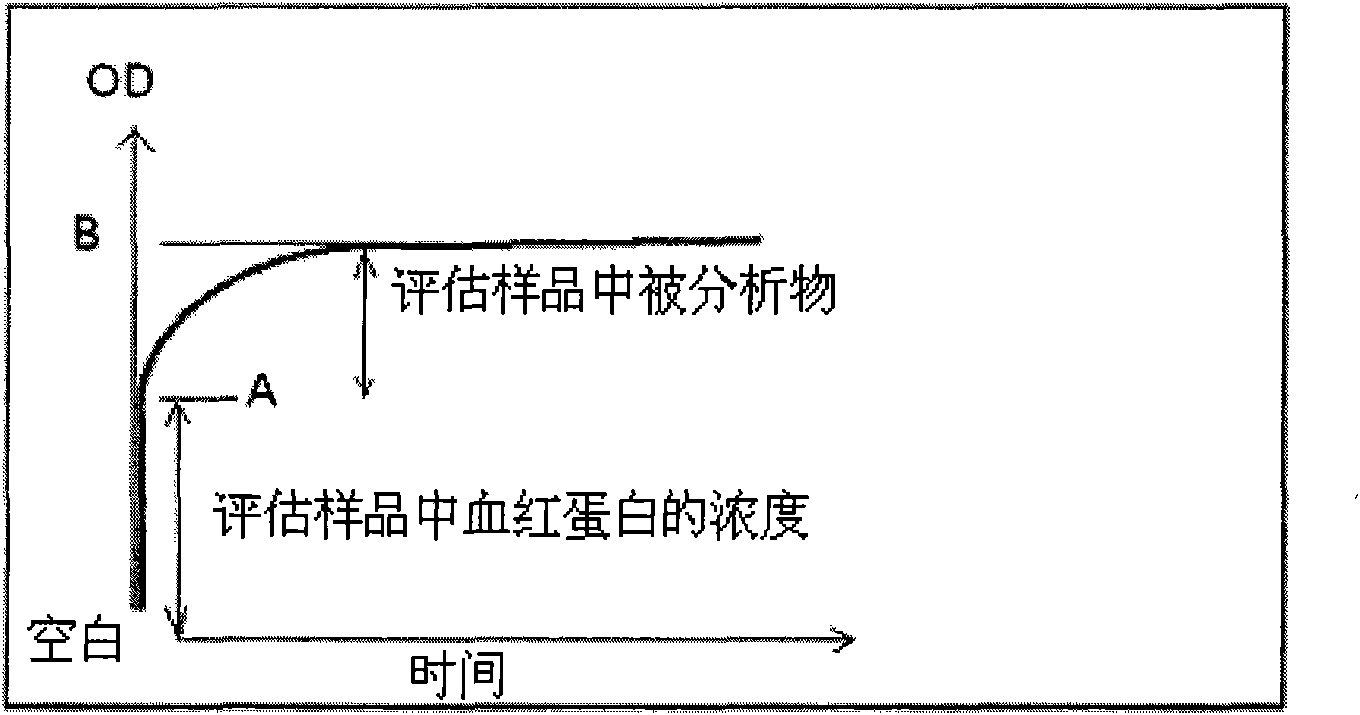
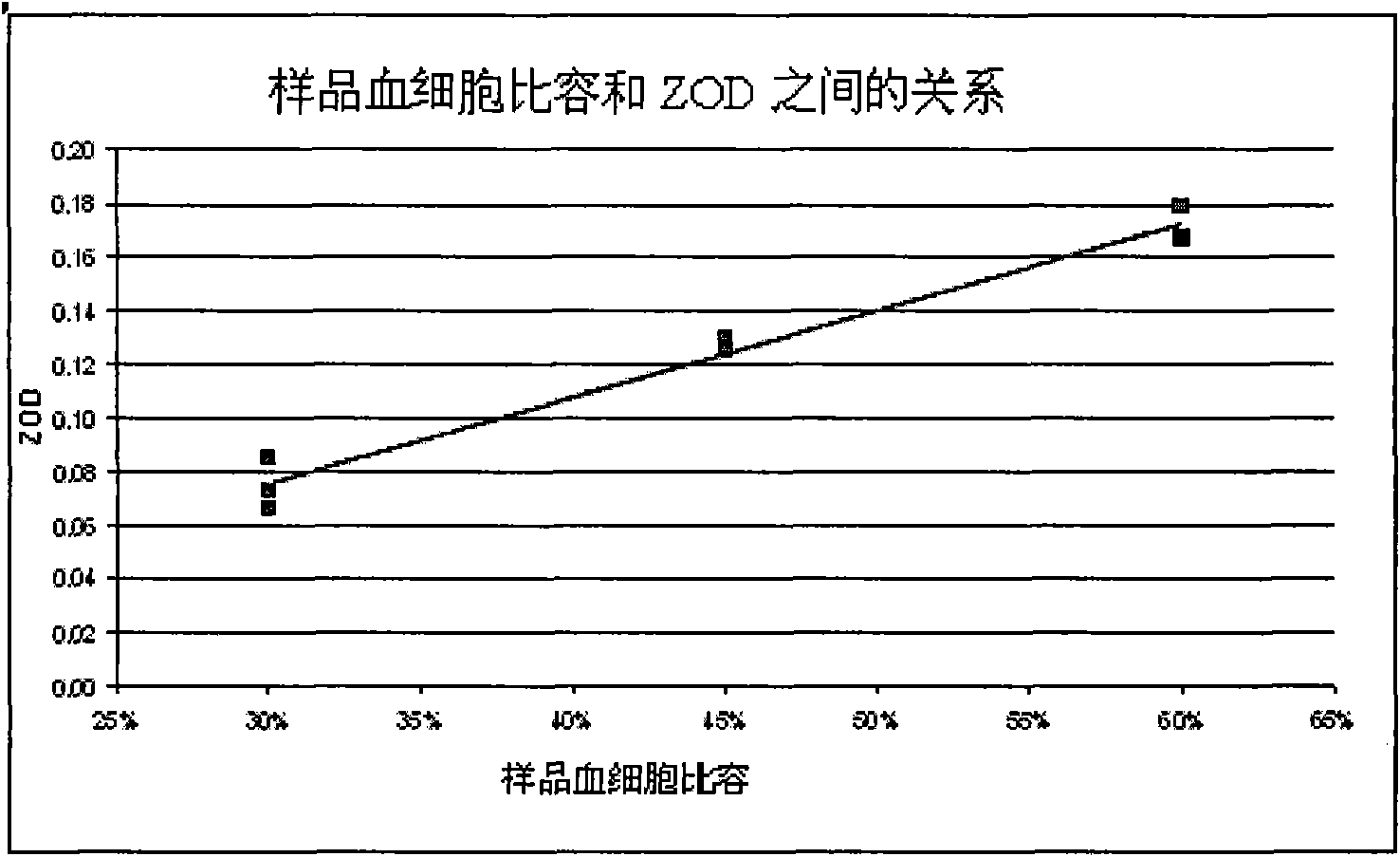
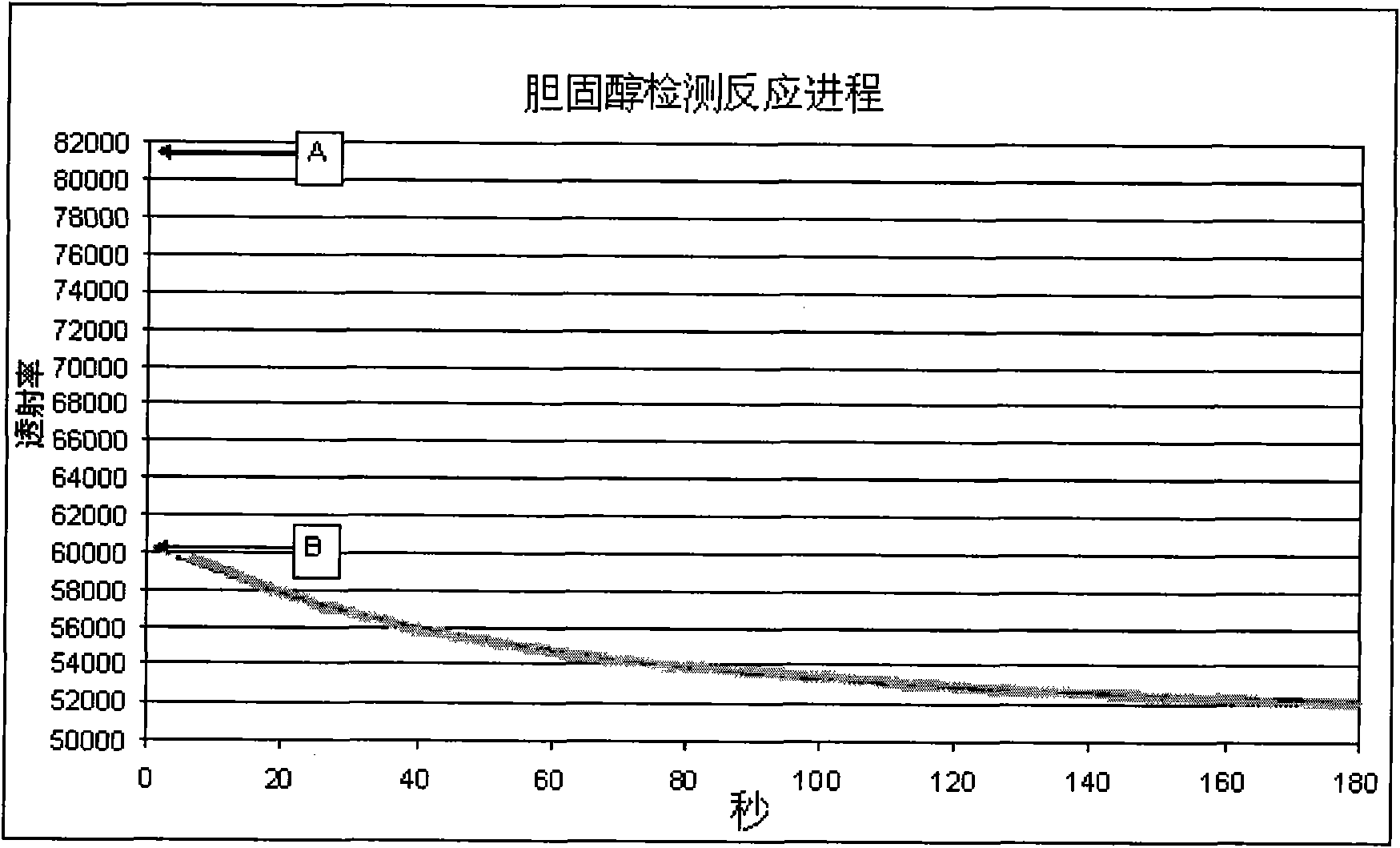
Whole blood assay
A technology for whole blood samples and measured values, applied in the field of whole blood detection, can solve the problems of increasing the complexity of system design and increasing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0053] A known volume (eg, 2.0 ml) of reagent containing buffer and a mixture of enzyme and reactants for the enzyme-linked reaction (shown below) is added to the reaction cuvette.
[0054]
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] The mixture was added to a photometer and excited at 510 nm. Blank transmittance readings were taken at <1 second intervals for approximately 5 seconds.
[0058] Then, at t 0 At time points, a fixed volume (5 μL) of blood, whose plasma cholesterol level is known, is added to the cuvette and mixed. The transmittance was measured at 510 nm when the mixing was complete and the reaction time was measured for 3 minutes. The time taken to create mixing and stop the vortex in the liquid means the transmittance recorded after the 10th second from the addition of the blood sample.
[0059] Table 1 below lists examples of blank and blood transmittance signals and reference readings.
[0060] Table 1
[0061] reading time
0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com