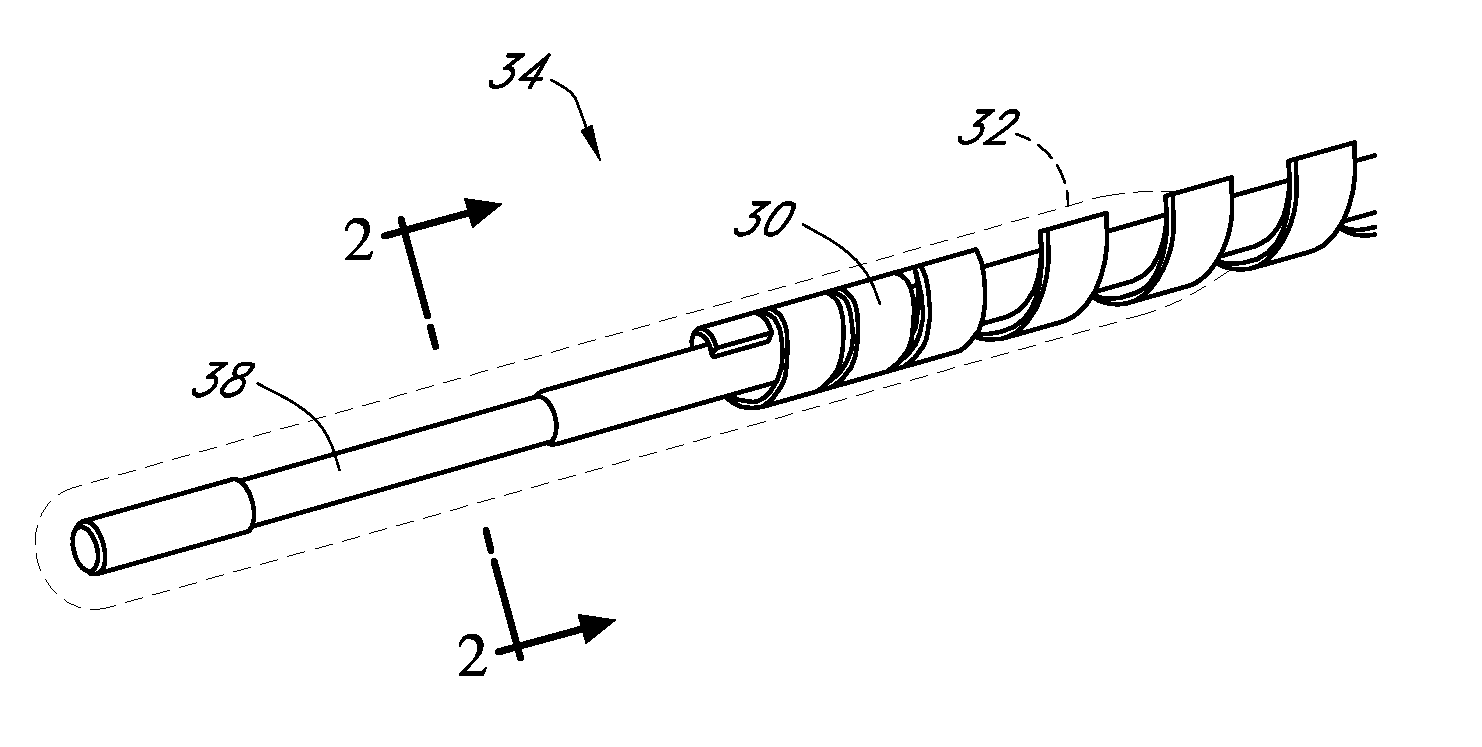
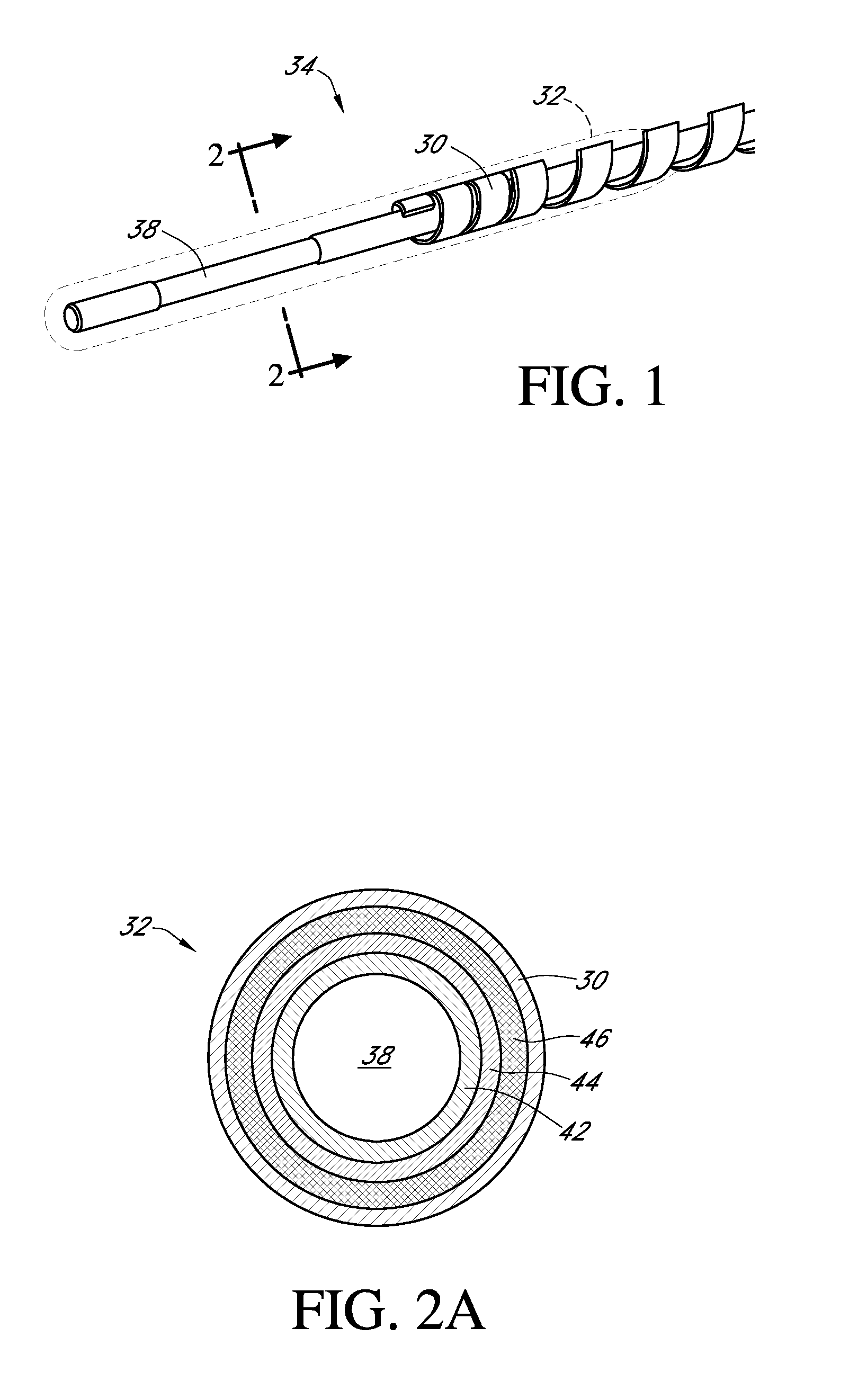
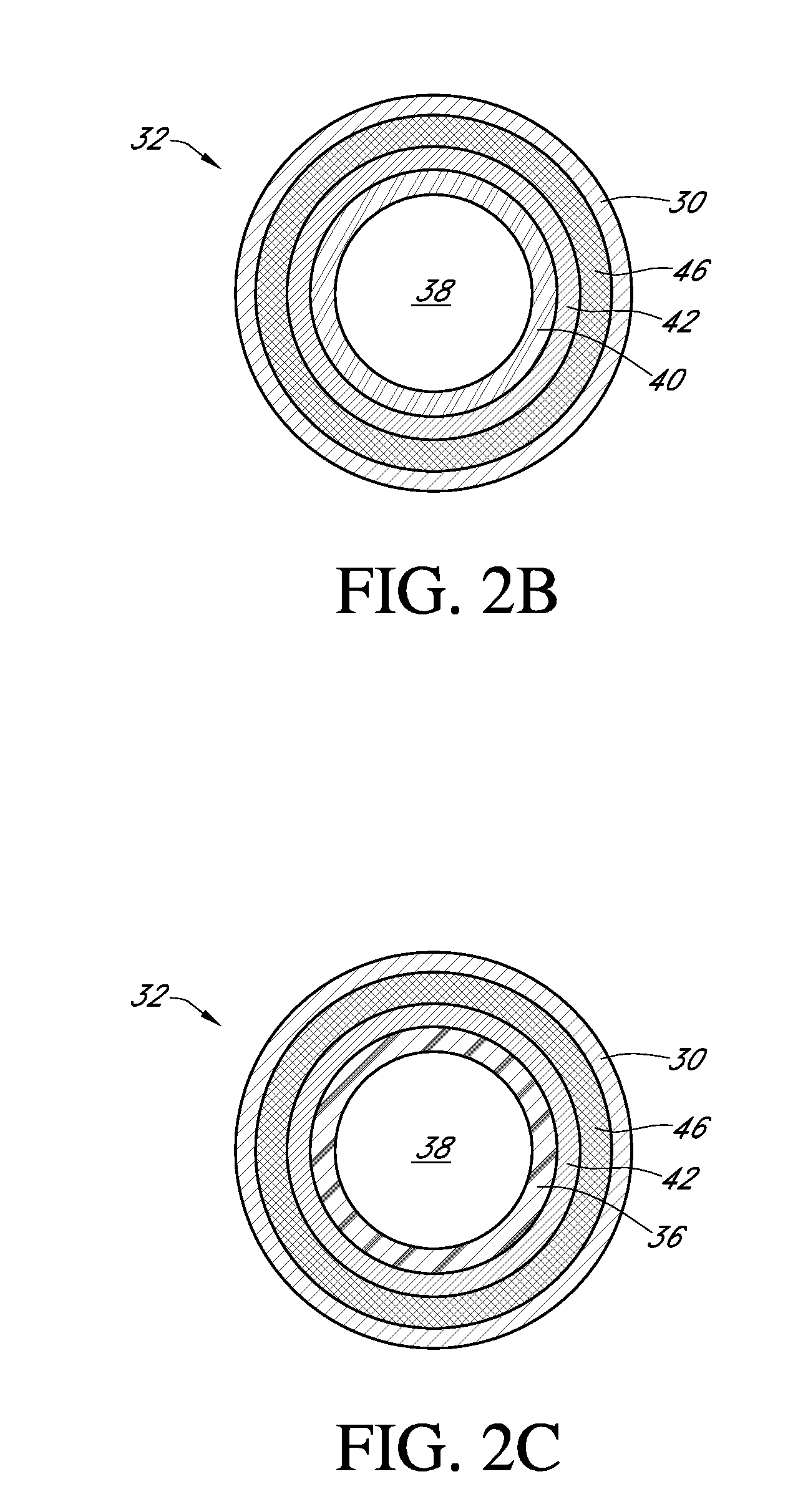
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
a technology of analyte sensor and polymer membrane, which is applied in the field of continuous measurement of analyte concentration, can solve the problems of many transcutaneous and intravascular sensors having problems in accurately sensing and reporting back glucose values continuously, and the complications of implantable glucose sensors within the body, so as to reduce the flux therethrough and reduce the effect of passage therethrough
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Preparation of Layered Interference Domains
[0249]Layered interference domains were prepared as follows. Nine poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) dip solutions were prepared by dissolving PAH having a molecular weight of approximately 100,000-200,000 g / mol in water to produce an aqueous solution with a concentration of approximately 50 mM of PAH. Each of the resulting nine solutions was then titrated with acetic acid or ammonium hydroxide to a pH of 10.0, 9.75, 9.5, 9.25, 9.0, 8.5, 8.0, 7.5, and 7.0, respectively.
[0250]Nine solutions for rinsing after PAH immersion were prepared by titrating water with ammonium hydroxide until a pH of 10.0, 9.75, 9.5, 9.25, 9.0, 8.5, 8.0, 7.5, and 7.0, respectively, was reached.
[0251]Five poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) dip solutions were prepared by dissolving PAA having a molecular weight of approximately 100,000 g / mol in water to produce an aqueous solution with a concentration of approximately 50 mM of PAA. Each of the resulting five solutions ...
example 2
Preparation of PAH / PVS Interference Domains
[0257]Layered interference domains were prepared using poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) and poly(vinyl sulfate) (PVS) as follows. Dipping solutions of PAH and corresponding rinse solutions were prepared according to Example 1.
[0258]Poly(vinyl sulfate) (PVS) dipping solutions and corresponding rinse solutions were prepared in a manner corresponding to the preparation of the PAA solutions described in Example 1.
[0259]Various interference domains were prepared by sequentially dipping a bare platinum wire into the PAH dip solution, followed by the corresponding rinse solution, followed by the PVS dip solution, and followed by the corresponding rinse solution. Interference domains were prepared with 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, and 14 layers by sequentially dipping the wire into PAH dip / rinse solutions followed by PVS dip / rinse solutions.
[0260]For example, a four-layered interference domain was prepared by: (1) dipping a bare wire...
example 3
Effect of Different Numbers of PAH / PVS Layers
[0262]The number of PAH and PVS layers in interference domains was varied to determine the effect of the number of layers on the permeability of the resulting interference domain to H2O2, acetaminophen, ascorbic acid, and uric acid. Sensors were prepared comprising platinum electrodes coated with interference domains prepared according to the procedure described in Example 2. Specifically, an interference domain containing a single layer of PAH was prepared. Also, interference domains containing 2, 3, and 4 layers of alternating PAH and PVS layers were prepared. An enzyme domain was added according to methods known in the art. The resulting sensors were sequentially placed into solutions that contained either H2O2, acetaminophen, ascorbic acid, or uric acid. The average current response (pA) for each solution was measured. The sensitivity of the current response versus the concentration of H2O2 was determined. The selectivity of the inter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com