PVC/ABS alloy material and preparation method thereof
An alloy material, PVC resin technology, applied in high fluidity, high heat-resistant PVC/ABS alloy material and its preparation, high strength field, can solve the problem of difficulty in taking into account the use performance and processing performance, to improve the technical level, The effect of improving fluidity and excellent physical and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
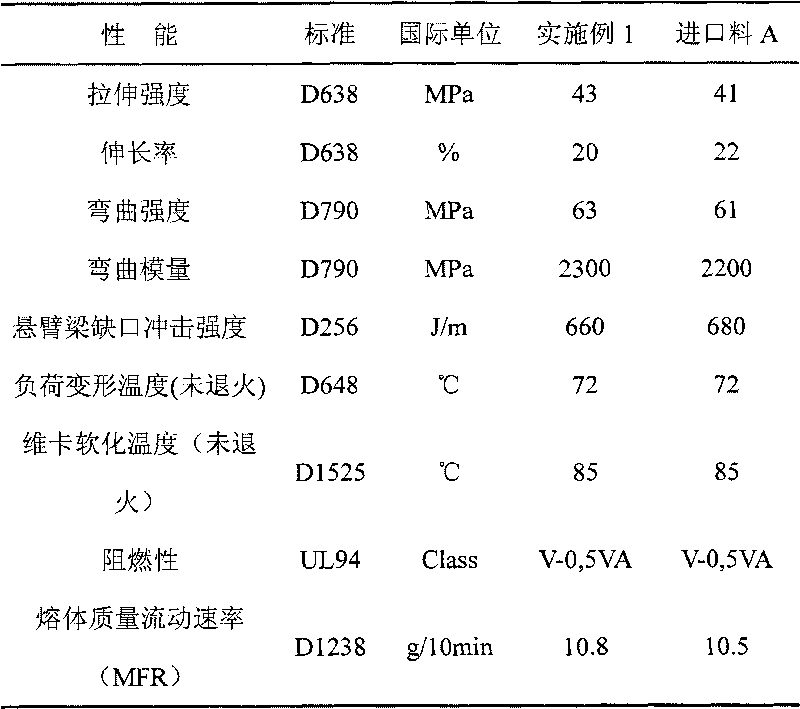
[0034] Take 65% of PVC powder, 10% of ABS resin, 5% of octyl tin mercaptide, 5% of methyl methacrylate and its copolymer, 8% of core-shell polymer of MBS type, α-methyl styrene type Copolymer 6%, antimony trioxide 1%. Mix the above-mentioned various raw materials in a high-speed mixer to 100°C to obtain a premix, knead the premix through a counter-rotating or parallel twin-screw extruder, and granulate through strand water cooling or die surface hot-cutting air After cooling and granulation, the properties of the obtained alloy material are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
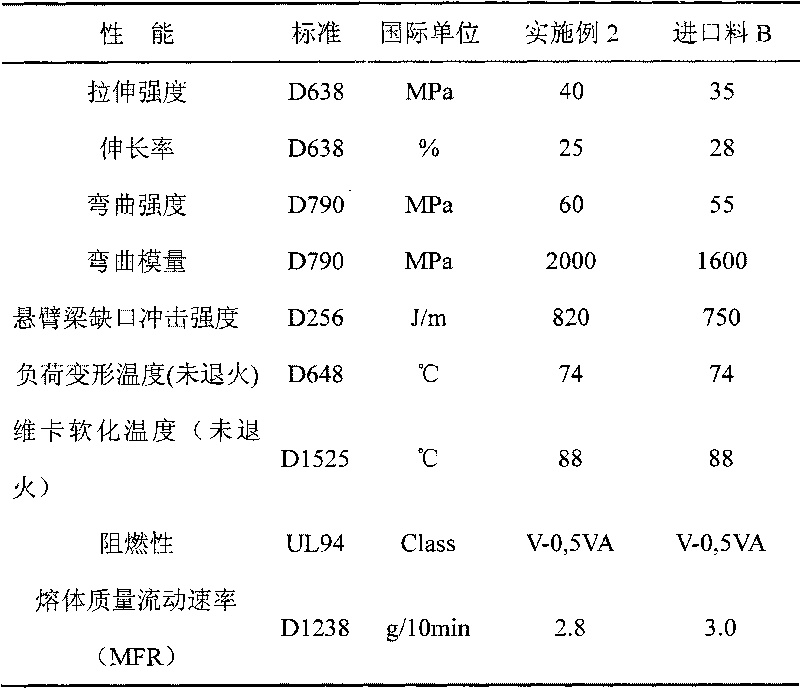
[0036] Take 40% of PVC powder, 33% of ABS resin, 4% of octyl tin mercaptide, 4% of methyl methacrylate and its copolymer, 13% of chlorinated polyolefin with chlorine weight content of 60%, α-methylstyrene Class copolymer 2%, magnesium hydroxide 2%, other additives 2%. Mix the above-mentioned various raw materials in a high-speed mixer to 130°C to obtain a premix, mix the premix through a counter-rotating or parallel twin-screw extruder, and granulate through the strand water cooling or the hot cutting air on the die surface After cooling and granulation, the properties of the obtained alloy material are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
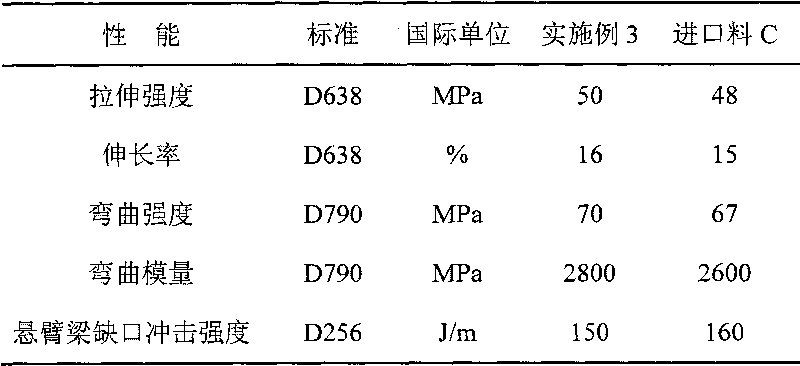
[0038] Take 20% of PVC powder, 48% of ABS resin, 3% of octyl tin mercaptide, 3% of methyl methacrylate and its copolymer, 3% of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and carbon monoxide copolymer, α-methyl styrene Copolymer 18%, chlorinated paraffin 2%, other additives 3%. Mix the above-mentioned various raw materials in a high-speed mixer to 120°C to obtain a premix, knead the premix through a counter-rotating or parallel twin-screw extruder, and granulate through the strand water cooling or the hot cutting air on the die surface After cooling and granulation, the properties of the obtained alloy material are shown in Table 3.
[0039] Table 1. Performance comparison between Example 1 and foreign imported alloy materials
[0040]
[0041] Table 2. Performance comparison between Example 2 and foreign imported alloy materials
[0042]
[0043] Table 3. Performance comparison between Example 3 and foreign imported alloy materials
[0044]
[0045]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vicat softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vicat softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com